organic search results
What is organic search?
Organic search results are the unpaid listings that appear on a search engine results page (SERP). These results are based on factors such as relevance to the user's search query, incoming links, valid search engine optimization (SEO) efforts and domain authority. Organic search results don't contain ads and differ from paid search results, which are also known as pay-per-click advertising. Advertisers can't buy organic search results.
Instead, strategies to follow SEO best practices -- sometimes called ethical SEO or organic SEO -- are designed to boost a website's SERP position without the website owner paying or resorting to unscrupulous practices. These discouraged practices can include techniques such as keyword stuffing, which is also referred to as unethical SEO.
The position of a link on a search results page is important. Depending on the search term, organic search results often make up only a small portion of the page. Since search ads are at the top of the results page, on a device with a relatively small display -- such as a notebook, tablet or smartphone -- the visible organic search results may consist of only one or two items.
Why is organic search important?
Although paid advertising provides instant results, organic search strategies can provide long-term results. Organic search traffic is the first source of visits for most sites and can be a crucial component of a buyer funnel, leading to higher conversions and return on investment (ROI).
The following attributes highlight the importance of organic search:
- Offers a competitive advantage. An organic search strategy promotes a business's visibility for targeted keywords. If pursued aggressively, organic search traffic can help outrank competitors on search engines without having to invest in paid or digital marketing strategies. For example, a company that improves its organic search traffic ranks higher in search engines, which ultimately pushes competitors down the list.
- Cost-effective and scalable. Organic search provides companies with a cost advantage. While pay-per-click ads are guaranteed to put a company's website in front of potential visitors, over time, these ads can be cost-prohibitive. Organic traffic costs nothing, especially if a company invests in effective SEO principles. An organic strategy is also more scalable since it doesn't require an upfront investment or a high maintenance budget. Businesses can keep growing without having to continually expand their marketing expenses.
- Provides long-term results. Organic search strategies optimize a company's presence on search engines over a longer period of time, as they aren't dependent on cost-per-click or monthly expenditures.
- Highly targeted. If a company invests in effective SEO strategies, its website will likely appear when consumers are actively searching for keywords that are closely related to the company's industry. Websites that rank for relevant keywords gain regular targeted traffic, which helps build new leads and long-term customers.
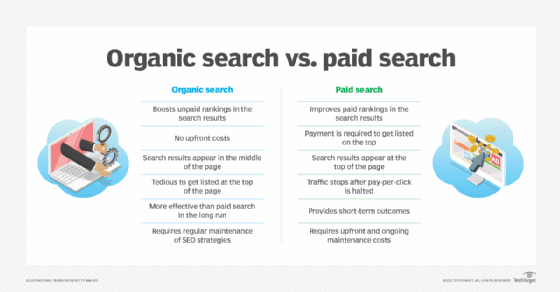
Organic vs. paid search
The main difference between organic and paid search is the cost, but there are a few other distinguishing factors as well.
Organic search can be characterized by the following:
- focuses on boosting unpaid rankings in the search results;
- places search results in the middle of the page;
- can require tedious efforts to get a site listed at the top of the page;
- is more effective than paid search in the long run;
- costs nothing to invest in; and
- requires regular maintenance of SEO strategies.
Paid search, on the other hand, involves the following factors:
- focuses on improving paid rankings in search engines;
- places search results at the top of the page;
- allows for a site to rank in the top position quickly with payment;
- halts traffic after payment for the advertising campaign stops;
- requires upfront and ongoing maintenance costs; and
- provides short-term outcomes.
Besides organic and paid traffic, there are other traffic sources on search engines:
- Direct. The source of this traffic is unknown.
- Email. Traffic is generated from email marketing.
- Social. Traffic comes from a social media network.
Organic search results page features and examples
When a user queries Google or another search engine, they're presented with the SERP. While a SERP mainly consists of paid and organic search results, it can also include various features, such as shopping ads, featured snippets, video results, knowledge graphs and top stories. SERP results vary by user, even when using the same search query or search engine, as they're customized based on the individual user, their searcher intent, interests and a myriad of ranking factors. Google calls these search result features or search features and continually tests and improves them to provide a user-friendly experience to website visitors.
Below are some of the most common SERP features that one may encounter on Google.
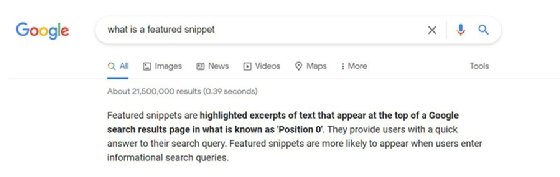
Featured snippets. These are displayed above the regular organic traffic results. A highlighted portion of text or video from a top-ranking website is pulled to provide users with a direct and brief answer to their query.
Video carousel. A video carousel displays feature videos related to the user's search query. It may link to a video hosting platform, such as YouTube, Vimeo or a page with embedded video. The entire video carousel takes up one organic position.
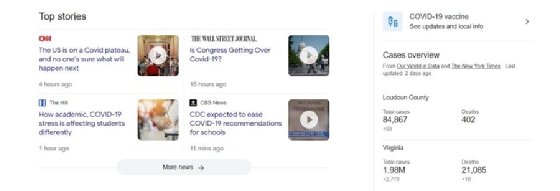
Top stories. This is a carousel of recently published stories or breaking news that users are currently interested in. It generally shows up in the organic search results for buzzworthy topics. Google also highlights when the top story or feature was published and by whom.
People also ask (PAA). These are questions automatically generated by Google that people commonly search for and may be related to a user's query. The PAA boxes are tied to answers with a short excerpt that users can click on and expand to read. This helps give users an answer to their initial query without them having to click on other results.
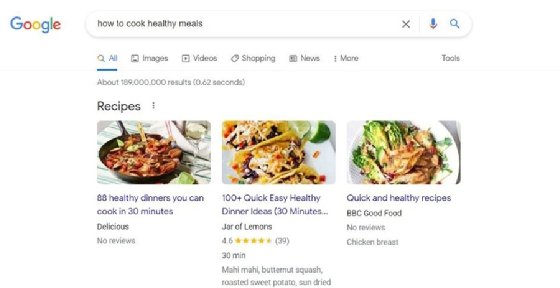
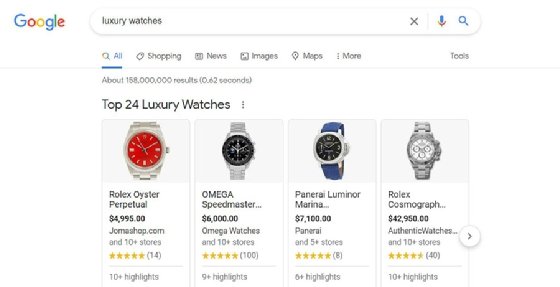
Image carousel. Also known as image packs, these appear when Google believes that visual content or images offer a more comprehensive results page. An image carousel presents images in a row or block of related images; once clicked, they take users to the Images search tab, from where they can get to the actual website hosting the image.
Organic search ranking factors
Every business wants its content to appear in the top three ranking pages of Google and other search engines. Various ranking factors -- from optimized keywords to meeting Google algorithms to the quality of the content -- can get a website a premium spot on the SERP.
The following are some factors that Google considers when evaluating pages for ranking:
- Internal and external link structure. Content can't be ranked in a search engine until it has been linked to various internal and external sources. Internal links or hyperlinks direct a user to an internal page of a website. These pages give Google an idea of a website's structure and hierarchy and improve its search visibility. External links, on the other hand, direct readers to a page on a different website. This may seem counterintuitive, as no business wants its potential customers to be directed away from its site. However, linking to trustworthy and reputable sources can boost an organization's ranking, as it can help Google determine the content type of a business from an SEO perspective.
- Backlink structure. Also known as an inbound link, a backlink is a link from any third-party website to another company's website. Backlinks help search engines understand the relevance of a website in reference to the search queries. For example, if a company publishes a blog post with informative content, another website might link back to that post as a source for its blog. A good backlink structure can improve the organic search ranking for a website, generate targeted referral traffic and help search engines index the website more quickly.
- Technical factors. The time it takes for a page to load is known as page speed. It's one of the leading SEO ranking factors, as the faster a website loads, the higher on the page Google ranks it. The speed of a page also dictates the user experience (UX) and is of great significance to Google. In 2018, Google announced a search engine algorithm update that focused on mobile page speed, which penalized slow-loading sites on mobile devices by ranking them lower on the SERP. Google also provides a free online mobile testing tool to see how well a site is performing in terms of speed. Besides the page speed, the length of a URL can also play a role in search engine ranking. Shorter URLs generally rank better in search results and they're also easier to type and remember, which ultimately improves the UX.
- Quality and structure of content. These are important factors in SEO ranking. Original content that's well written and provides valuable information relevant to the searcher's intent seems to rank higher. For example, a high-quality blog post appeals to search engines and also attracts consumers, increasing user engagement and lowering the bounce rates for a website.
- Media enhancements. Media options, including videos and images, provide SEO benefits that can help organic content rank higher in the SERP. Images and videos add context to written content, which keeps users engaged for longer and increases the chance of potential conversions and greater pageviews per visit. Images and media also break up the monotony, making it easier for readers to digest the information. For example, most users accessing a financial report on a company's website would prefer to see the financial data presented in a graph or a pie diagram as opposed to just numbers.
- Mobile optimization. Websites that are optimized for smaller screens and mobile devices fare better in search engine rankings because a greater percentage of searches are conducted through mobile devices. According to StatCounter, as of July 2022, mobile purchases account for 62.06% of the market share as opposed to 37.94% for desktops. Since responsive pages provide a better UX, unoptimized websites that aren't easy to navigate on mobile devices are at a disadvantage when it comes to search engine rankings.
- Encryption. Attitudes regarding encrypted internet communications have changed drastically, and most mainstream browsers now support HTTPS, which loads pages through secure connections only. However, many websites still use the old-fashioned HTTP and don't invest in a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate. This can be a big factor in search engine rankings because an insecure website displays the "Not Secure" warning next to the domain name in the browser bar, which can avert site visitors. Google also values encrypted sites, and therefore having an SSL certificate can provide a website with a boost in search engine rankings.
Organic search reporting metrics
Without detailed website tracking in place, it can be challenging for a business to discover opportunities to increase organic search traffic and revenue. By incorporating website metrics, a business can get a better understanding of its site performance and boost search engine rankings and ROI.
The following are important organic search reporting metrics that a business should track regularly:
- Keyword ranking. This refers to a website's organic ranking position in the search results for specific keywords. Businesses need to track how their keywords are ranking to determine if their organic SEO strategy is working. To rank at the top of search engine results, the website and content should be optimized for both specific and long-tail keywords. Businesses should also decide which keywords are the most important for their product or business offerings and then focus their efforts on ranking well for those Google Analytics and various SERP trackers can help track the metrics for specific keywords.
- Number of visitors. This metric tracks the total number of visitors to a site and can gauge the amount of interest in a site and its content. A low number of visitors indicates that the site isn't performing well. This provides an opportunity for the business to create engaging content that will rank higher on the search engines and deliver more traffic to its website.
- Average page views. This metric gives a broader perspective on the average page views per session along with the total number of pages a visitor is accessing on a certain website. It's an easy way to assess the performance of a website. For example, if most visitors are only viewing one or two pages of a website before exiting, it could indicate that the site is either difficult to navigate or the content might be irrelevant.
- Bounce rate. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors that leave a site without viewing additional pages. This can happen for many reasons, including a slow-to-load page or a page that lacks the information, products or services that the visitor is looking for. Generally, the quicker a site visitor leaves a website, the higher its bounce rate. A high bounce rate can negatively affect the search engine ranking of a website. Therefore, businesses must investigate which pages are showing high bounce rates so they can enhance the content on those pages.
- Average time on page. The average time a visitor spends on each page can be a key indicator of the type of content being offered and the amount of interest visitors have in that topic. If visitors are spending a lot of time on certain pages, it's a sign that they're finding the content on those pages to be valuable. But visitors spending less time on certain pages indicates that the content isn't engaging or might be irrelevant to their needs. Tracking this metric can provide deeper insights into the most liked pages and help improve the overall content of a website.
Tools for organic search reporting
Organic search reporting tools enable companies to understand which strategies are working for them and where they should be spending their marketing budget.
Below are a few popular organic search reporting tools.
Google Search Console. This is Google's free and comprehensive web analytics platform that anyone can use to track and monitor how their website ranks in Google's eyes. Website owners can view keyword rankings and referring domains, as well as their mobile website's performance. Google Search Console also provides insight into a website's highest traffic pages and related queries and offers alerts on page experience issues.
Google Analytics. GA is a web analytics tool that provides insights into a website's traffic by collecting data and creating reports. It offers a hybrid model with both free and premium versions and separates the data by its source, such as organic, paid search, referral, direct or social for precise monitoring. Besides tracking the number of website visitors, this tool also provides key insights into how a site is performing and what can be done to reach the desired goals. GA also enables users to monitor social media activities, identify trends, track mobile app traffic and integrate other sources of data to help make business decisions.
SE Ranking. This is a comprehensive cloud-based SEO and digital marketing platform geared toward business owners and large-scale enterprises. SE Ranking started as a ranking tool but over the years has grown into a complete platform that includes keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink monitoring, site audits, keyword ranking and automated white label reporting. The white label reports are customizable, and users can choose the modules they want to include, such as rankings, competitors, traffic, website audit and finance reports. Users can also schedule the reports to be generated and delivered at specific time intervals and can compare and display certain ranking periods for SEO progress and analysis.
SEMrush. This SEO tool is designed for in-depth keyword searches, which can be helpful when a business wants to perform a thorough analysis of its competition. SEMrush provides a full overview of each keyword that the competition ranks for, the amount of traffic it drives to their site and a link to check out the ranking page.
A great SEO strategy has multiple components. Learn the four tips for creating an efficient SEO strategy for content marketing.
