cutimage - Fotolia
How do RDMA storage systems improve latency reduction?
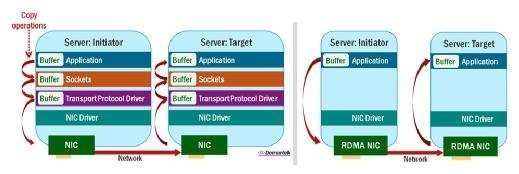
RDMA technology can help speed up I/O in storage environments by bypassing copy processes in the software stack when data is called up from a system's memory.
Remote Direct Memory Access technology enables more direct movement of data in and out of a server. The technology can be implemented for networking and storage applications. RDMA storage systems bypass normal system software network stack components such as a cache or operating system, as well as the multiple buffer copy operations they normally perform. This reduces overall CPU utilization and improves the latency of the host software stack, since fewer instructions are used to complete a data transfer. Some RDMA adapters may even have offload functions built into them.
RDMA storage networking protocols include iSCSI block protocols, and NFS or SMB (formerly known as CIFS) file protocols. RDMA can improve storage latency and reduce the CPU utilization of the host server performing I/O requests. This allows a higher rate of I/O requests to be sustained or a smaller server to perform the same rate of I/O requests. This can make RDMA storage networking valuable in environments that can tolerate very little latency such as supercomputing environments and some database workloads.
InfiniBand uses RDMA natively. RDMA can be added to Ethernet by using special adapters. With the addition of faster gigabit Ethernet speeds in 2016, RDMA over Ethernet may be useful to further reduce overhead.
Technologies that use RDMA include:
- ISCSI Extensions for RDMA (Ethernet only).
- Internet Wide-Area RDMA Protocol. This runs on top of standard TCP/IP (Ethernet only).
- NFS over RDMA: Linux RDMA transport for NFS (Ethernet or InfiniBand).
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet: Requires a data center bridging switch that provides a lossless fabric (Ethernet only).
- SMB Direct: Windows Server feature for file servers that takes advantage of RDMA-capable network adapters (Ethernet or InfiniBand)
- SCSI RDMA Protocol (InfiniBand only).
In the future, RDMA storage technology may be enabled for scale-out file systems, scale-out distributed SANs or other applications.








