
Compare Amazon Lightsail vs. EC2 for your web app needs
Developers can use Amazon Lightsail to quickly build websites and applications, but EC2 affords teams more customization. Which service best benefits your organization's needs?
Amazon Lightsail is designed for speed and simplicity. The instances run on top of Amazon EC2 and are bundled with other AWS resources, though those services are abstracted so they're not visible to the user.
Simplicity comes with tradeoffs, however. Amazon EC2 enables far more ways to build, deploy and manage applications. It also remains the dominant AWS offering, alongside Amazon S3. But, for a subset of users, Lightsail is the better fit.
Let's take a closer look at the Lightsail vs. EC2 debate to see how IT teams could benefit from Lightsail and to evaluate pricing.
Benefits of Amazon Lightsail
Amazon Lightsail is a virtual private server (VPS) that bundles compute, storage, networking and DNS. It also has built-in capabilities that include a managed database, load balancer, support for containers and content delivery network (CDN).
Amazon Lightsail is for businesses that want to spin up a server without working through all the pricing, configuration and management details associated with a typical AWS deployment. Benefits organizations could see with Lightsail include the following:
- Standardized applications and configurations.
- Basic templates.
- Affordability.
- Developer-friendly features.
- Built-in security.
- Simplified UX.
Standardized applications and configurations
Developers can use Lightsail to build simple projects, such as a blog, website or basic e-commerce application, using standard applications and configurations. For example, to set up and configure a WordPress blog, just select a platform and a blueprint, such as a preconfigured WordPress instance. The following diagram illustrates how media content is delivered within Lightsail using its load balancer, database and S3 for WordPress.
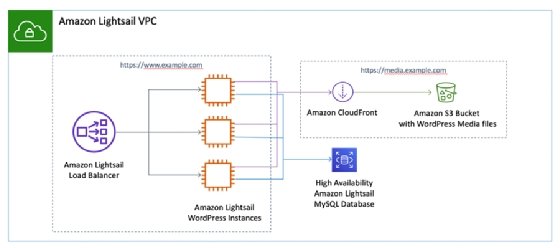
To do the same thing in EC2, users need to provision the instance, add Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) block storage or Amazon S3 object storage, provision the image, and then configure all the different resources and applications.
Basic templates
With Lightsail, users can create the same basic template in a few clicks. These templates also make Lightsail an attractive staging environment for testing new applications or features before deploying them on live instances.
Affordability
Lightsail presents a handful of options that are deployable at a predictable monthly price. However, the service is not ideal for applications that require a highly configurable environment or consistently high CPU performance, such as video encoding or analytics.
Developer-friendly features
Amazon Lightsail comes with a wide range of preconfigured software stacks for common use cases. It also supports a comprehensive API that developers can use to facilitate communication with other cloud services.
An SSH terminal interface enables developers to kick off more complex configurations and make changes using a standard shell interface. This also enables them to preconfigure scripts for particular scenarios. With a Secure FTP application, developers can copy application data from a backup or retrieve data from other systems as required using a standard FTP application.
Built-in security
Lightsail supports the same encryption and identity and access management as the rest of the AWS cloud. It's easy to add firewall rules to a Lightsail instance to control the traffic that connects with it. Lightsail templates are also preconfigured with security best practices. This reduces the risk of a developer accidentally leaving an S3 storage bucket open to hackers.
Amazon also automatically updates all applications and OS blueprints with new security patches. These can be applied automatically when running databases during a preconfigured maintenance window. However, these are not applied to running OSes, applications and container instances. As a result, the instance must be periodically stopped and restarted with the latest blueprint to take advantage of the latest updates.
Simplified UX
The AWS interface enables users to quickly set up a new instance from a checklist of OS and application templates. These templates have back-end, network interface and storage configurations for applications like WordPress, Drupal and Django. Choose the apps, location and name. Then, click Create, and the new service spins up in minutes. This can save considerable time for users unfamiliar with the nuances of cloud configuration and storage setup required with EC2.
Comparing Lightsail vs. EC2
The packaged nature of Lightsail makes it difficult to compare directly with EC2. IT teams need to connect AWS' flagship compute service with other AWS offerings -- each with its own pricing structure -- to create a viable environment to build and deploy applications.
For this comparison, some Lightsail features are shown and contrasted with what can be done natively in AWS when using EC2 as the linchpin. All pricing listed is based on the U.S. East Region.
Compute and block storage
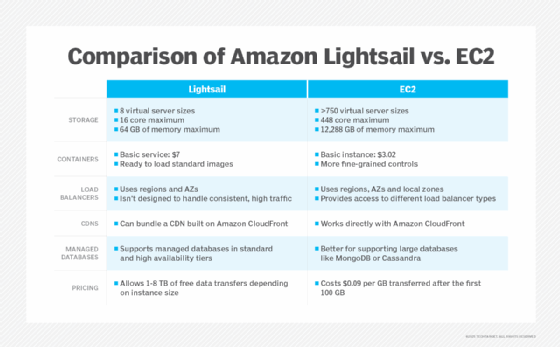
When it comes to compute options, there is no comparison. Lightsail has eight virtual server sizes; EC2 has more than 750. Lightsail tops out at 16 cores and 64 GB of memory; EC2 instances can reach 448 cores and 12,288 GB of memory.
Again, the point of Lightsail is not endless customization. For granularity and a massive range of configuration options, go with EC2 instead.
In terms of solid-state drive (SSD) storage, Lightsail's disk sizes range from 20 GB to 1,280 GB. EC2 has far more flexibility, but in most cases, users need to sort out the attached instance storage separately through EBS, which can cost an additional $0.08 per GB. With Lightsail, that is all preconfigured.
Teams that outgrow their VPS instance or need more control can take a snapshot and export it to a new instance in EC2.
Containers
Developers can use Lightsail containers to start loading standard Docker or other container images into the cloud. However, this service lacks the fine-grained controls of Amazon ECS or Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service.
Lightsail containers cost significantly more for the raw resources. The basic container service costs $7 per month for one-quarter of a virtual CPU (vCPU) with 512 MB of RAM and goes up to $160 per month for four vCPUs with 8 GB of RAM. An equivalent EC2 instance is $3.02 on the low end and $97 on the high end. The Lightsail packages also include data egress quotas, which are an additional cost with EC2.
All container services come with a flat 500 GB per month of transfer quotas, which otherwise adds $45 to the EC2 equivalent. Although this might tip the balance in favor of Lightsail containers, the main benefit lies in easy experimentation with basic container principles rather than cost savings.
Load balancer
Lightsail load balancers distribute traffic across instances in different availability zones (AZs). This addresses scaling issues and improves performance and redundancy. The load balancer also handles certificate management.
Lightsail's load balancers aren't designed to handle consistently high traffic volumes, however. AWS recommends developers use EC2 with Application Load Balancer instead for workloads that involve more than 5 GB of data per hour, 400,000 new connections per hour or 15,000 active connections running at the same time.
The Lightsail load-balancing service is priced at $18 per month. With EC2, developers can pick from Application, Network, Gateway and Classic Load Balancers. These services are charged on a consumption basis, so costs depend on the amount of traffic processed.
Content delivery network
Developers can bundle a Lightsail CDN built on top of the Amazon CloudFront network to improve the performance of applications accessed around the world. This is useful for websites, such as a blog, in which assets like CSS style sheets, JavaScript code, graphics and videos can be staged closer to users to reduce the response times. This can also reduce the load on the server, which can improve overall performance.
EC2 works directly with Amazon CloudFront or third-party CDN services, and it's better suited for complex configurations or workloads that require a lot of requests or video streaming.
The bottom tier of the Lightsail CDN provides 50 GB per month free for the first year and then $2.50 per month afterward. At the high end, 500 GB costs $35 per month. For Amazon CloudFront, traffic is charged based on data transfers out and HTTP requests. Data transfer pricing varies, with higher-volume tiers translating to lower per-gigabyte rates.
Managed databases
AWS supports managed databases in the standard and high availability Lightsail tiers. This simplifies the selection process for MySQL databases, as well as efforts to launch, secure, monitor and maintain those repositories.
The service automatically maintains a seven-day rolling database backup. Developers can configure longer-duration backups with snapshots, which are billed separately. These bundles are more expensive than Linux or Windows instances and have much more limited transfer allowances.
The high availability tier supports redundancy and failover to servers in different Amazon AZs. The standard managed databases start at $15 per month for 1 GB of RAM, 40 GB of storage and 100 GB of data transfers. These go up to $115 per month for 8 GB of RAM, 240 GB of storage and 200 GB of data transfers. The high availability tiers are priced at double these rates.
Lightsail managed databases don't provide the same level of performance or throughput that larger databases, such as MongoDB or Cassandra, might require. EC2 instances with provisioned IOPS SSD storage are a better option than Lightsail in these cases.
Lightsail can work with other AWS database offerings. It supports Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Relational Database Service and Amazon Aurora, but you might need to peer to a separate Amazon VPC to make it work.
The peering technique can connect to many, but not all, of the other AWS services. Peering is not required for smaller subsets of services, including Amazon S3 and Amazon CloudFront.
Data science research
Amazon Lightsail for Research helps data scientists and AI developers quickly spin up an environment to analyze large data sets without configuring or managing the cloud infrastructure components. This reduces the need for a powerful local computer. Both non-GPU and GPU-based versions are available, which perform better on larger analytics projects.
These environments come preconfigured with popular data analytics applications, such as JupyterLab, RStudio and Scilab. Additional packages and extensions for various data science workflows are available.
Upload data sets from a web browser to get started, and then delete the instance when they are done. The service also has budgeting controls to ensure that a particular analysis does not exceed a preconfigured cost limit.
There are no charges for uploading data, but there is a limit of 0.5 terabytes for standard tiers and 1 TB for GPU tiers for free data downloads per month, after which $0.09 per GB egress charges come into effect. This is the same for all Lightsail for Research instance sizes. In most analytics use cases, the resulting analysis or processed data tends to be smaller than the analyzed data.
Lightsail for Research is priced on an hourly basis, unlike the rest of the offerings mentioned previously, which are priced monthly. The top three tiers all come with GPUs. The most expensive tier, at $3.18 per hour, supports 16 vCPUs and 64 GB of RAM. All the tiers support 50 GB of SSD storage. At the bottom, pricing starts at $0.90 per hour for a server with four vCPUs and 8 GB of RAM.
At the end of an analytics cycle, Amazon stops the instance. However, it continues to charge $0.00685 per hour, which comes to $4.93 per month. This might be useful if a data scientist wants to save intermediate work for subsequent processing or make it easier to return to a particular set of configurations.
It's not clear what EC2 instance the standard tiers are comparable with. However, at the high end, GPU 4XL is comparable to g4dn.4xlarge, which costs $1.204 per hour and comes with 225 GB of storage. Lightsail for Research probably costs more per hour, but it could be a better option for data scientists to set up experiments without relying on IT or development teams.
Lightsail vs. EC2 pricing
Amazon Lightsail costs are lower for basic resource usage compared to the On-Demand Instances in EC2.
Linux/Unix, the smallest Lightsail instance, with 512 MB of RAM and 20 GB of SSD storage, is $3.50 per month to deploy. This is comparable to the EC2 equivalent, t3.nano, priced at $0.0052 per hour or about $3.38 monthly. However, this doesn't include SSD or data transfer costs. With a similar amount of SSD storage to the Lightsail package, t3.nano comes to $4.98 per month.
At the high end, the $380 per month Lightsail package includes 64 GB of RAM, 1,280 GB of SSD storage and 8 TB of data transfers. Compare this to its EC2 equivalent, m6g.4xlarge, which comes with 64 GB of RAM for $443.52 per month, or $5,545.92 per month with 640 GB of SSD storage.
Windows Lightsail servers are priced higher than the Linux variants due to licensing fees. The Windows plans start at $8 per month for 512 MB of RAM, 30 GB of SSD and 1 TB of data transfers. The high-end Windows plan costs $570 per month and includes 64 GB of RAM, 1,280 GB of SSD storage and 8 TB of data transfers.
Transfers and other fees
The Lightsail packages allow 1 TB to 8 TB of free data transfers, depending on instance size. EC2 instances cost $0.09 per GB transferred after the first 100 GB. This could add up to an additional $81 for 1 TB and $711 for 8 TB of outbound data transferred per month.
Data transfer savings represent one of the biggest cost differentiators between Lightsail and EC2. Note that the allowances are considerably smaller for other Lightsail services. However, it's challenging to dynamically scale Lightsail services up or down in response to load. This might result in higher costs to overprovision resources to prepare for spikes.
Remember to delete
In theory, a developer can start and stop a Lightsail instance and save money when it's not running. AWS still charges for Lightsail instances even when an instance is stopped. To suspend charges, a developer must back up the instance and delete it from Lightsail. The enterprise must also pay another fee to keep an IP address in use -- to help maintain web server continuity -- that is no longer associated with the Lightsail instance. This adds $.005 per hour or $3.60 per month.
Each account is limited to 20 Lightsail instances, five static IP addresses and three DNS zones. That might be fine for simple use cases, but an enterprise is unlikely to build a large-scale Lightsail deployment within these confines.
One major downside is that Lightsail does not dynamically scale as well as EC2. Any apparent cost savings might be spent on overprovisioning resources the team never consumes.
Competitive services
There are a variety of competitive VPS services, each with different competitive advantages. Consider DigitalOcean, which focuses on simplifying the developer experience for provisioning standard services as Droplets, thereby simplifying management. It also provides a developer-friendly UI to deploy a library of preconfigured instances. DigitalOcean is priced comparably to Lightsail.
Companies using other AWS applications should consider Lightsail since it can simplify integration and billing across multiple services. Other services make more sense for companies first exploring or testing various applications.
Editor's note: This article was updated to include additional information on the differences between Amazon Lightsail and EC2.
George Lawton is a journalist based in London. Over the last 30 years, he has written more than 3,000 stories about computers, communications, knowledge management, business, health and other areas that interest him.







