What is acceptance testing?
Acceptance testing is a quality assurance (QA) process that determines to what degree an application meets end users' approval. Depending on the organization, acceptance testing might take the form of beta testing, application testing, field testing or end-user testing.
A QA team conducts acceptance tests to ensure the software or app matches business requirements and end-user needs. An acceptance test returns either a pass or fail result. A fail suggests that there is a flaw present and the software should not go into production.
Acceptance testing enables an organization to engage end users in the testing process and gather their feedback to relay to developers. This feedback helps QA identify flaws that it might have missed during the development stage tests, such as unit and functional testing. Additionally, acceptance testing helps developers understand business needs for each function in the tested software. Acceptance testing can also help ensure the software or application meets compliance guidelines.
Acceptance testing process
Acceptance testing occurs after system tests but before deployment. A QA team writes acceptance tests and sets them up to examine how the software acts in a simulated production environment. Acceptance testing confirms the software's stability and checks for flaws.
Acceptance testing includes the following phases: plan, test, record, compare and result.
Once the test is written according to the plan, end users interact with the software to gauge its usability. The software should meet expectations as defined by the business in the requirements. When the tests return results, IT should report and fix any flaws that show up. If the results match the acceptance criteria for each test case, the test will pass. If test cases exceed an unacceptable threshold, they will fail.
Types of acceptance testing
Acceptance testing encompasses various types, including user acceptance and operational acceptance.
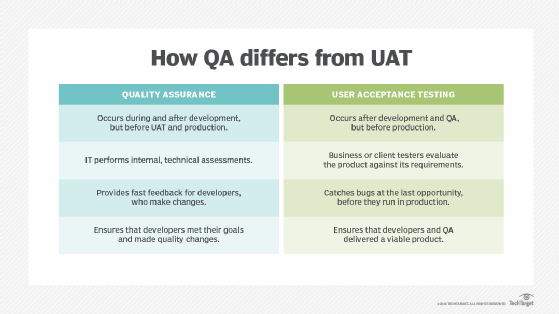
User acceptance testing (UAT), also called end-user testing, assesses if the software operates as expected by the target base of users. Users could mean internal employees or customers of a business or another group, depending on the project.
Operational acceptance testing reviews how a software product works. This type of testing ensures processes operate as expected and that staff can sufficiently use and maintain the system. Operational acceptance testing examines backups and disaster recovery, as well as maintainability, failover and security.








