
Getty Images
Server administrator certifications: 5 nontech certs you need
Discover five nontechnical certifications that can advance your IT career by adding crucial business and leadership competencies to your skillset.
While technical certifications, like AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate, Azure Administrator Associate and Red Hat Certified Engineer, validate hands-on expertise with specific technologies, the current IT environment demands a more comprehensive skill set. Technical prowess alone rarely secures career advancement.
IT professionals must navigate complex business situations, communicate effectively with diverse stakeholders and provide meaningful leadership -- areas where traditional server administrator certifications fall short. This gap is precisely where nontechnical certifications prove invaluable.
This article examines five nontechnical certifications that can significantly enhance your IT career by complementing technical expertise and the essential business and leadership competencies increasingly sought by employers and clients alike.
Why pursue nontechnical certifications?
Before investing in nontechnical credentials, first clarify your professional goals. Consider the following reasons to expand beyond the usual server administrator certifications.
Strategic career advancement
If you aspire to climb the leadership ladder and influence organizational IT strategy, nontechnical certifications provide the business acumen and leadership skills necessary for senior roles. These certifications demonstrate your ability to think beyond technical implementations to strategic impact.
Business-technology alignment
Nontechnical certifications equip you to bridge the gap between technical teams and organizational leadership. Such cross-functional expertise enables you to develop partnerships and technology initiatives that support business outcomes.
Stronger team leadership
For current team leaders seeking to enhance team performance and service delivery, the proper certifications offer frameworks and methodologies to improve team dynamics.
Most IT professionals pursue nontechnical certifications with multiple goals in mind. Consider the certification options outlined below if you identify with these objectives.
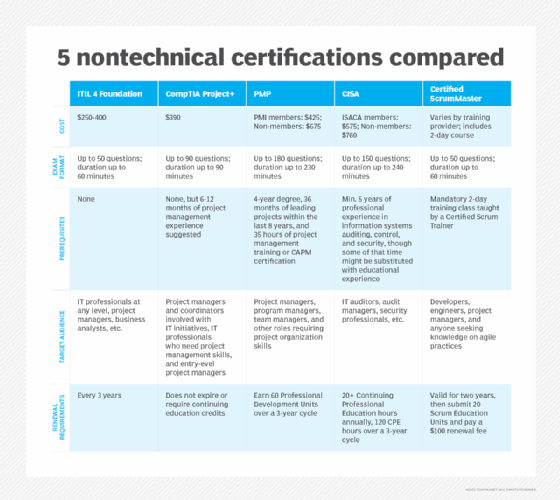
1. ITIL 4 Foundation
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) 4 Foundation certification provides a framework for IT service management best practices. The Foundation exam evaluates candidates' understanding of ITIL core concepts and terminology. It enables professionals to demonstrate mastery of service management principles, such as incident management, service delivery processes and continuous improvement methodologies within IT operations.
ITIL 4 Foundation certification costs between $250 and $400, depending on geographical region and whether additional training is included. The exam consists of up to 50 questions to be completed within 60 minutes. With no prerequisites, this certification remains accessible to industry newcomers while appealing to a diverse professional audience, including IT staff at all career stages, project managers, business managers and anyone involved in IT service delivery.
Certification renewal is required every three years.
2. CompTIA Project+
The CompTIA Project+ certification introduces IT professionals to project management concepts, including documentation, communication, scheduling and deployment management. This certification delivers the structured methodology to execute complex initiatives such as cloud migrations, server virtualization implementations, infrastructure as code (IaC) deployments and software rollouts.
The current certification, CompTIA Project+ PK0-005, costs $390 and features an exam of up to 90 questions with a 90-minute time limit. While no formal prerequisites exist, CompTIA recommends six to 12 months of project management experience before attempting the exam. The certification targets dedicated project managers coordinating IT initiatives, technical professionals seeking to enhance project management skills and entry-level project managers.
Unlike many professional certifications, CompTIA Project+ never expires and requires no continuing professional education (CPE) credits.
3. Project Management Professional (PMP)
The Project Management Professional certification is one of the most widely recognized nontechnical credentials for experienced project managers. It requires verified project management experience and formal Project Management Institute (PMI) endorsement. The PMP certification focuses on leadership skills, team management, stakeholder engagement and strategy implementation.
The certification costs $425 for PMI members and $675 for non-members. It consists of a rigorous 180-question examination that must be completed within 230 minutes. Qualification requirements include either a four-year degree with 36 months of project leadership experience within the past eight years and 35 hours of formal project management training or a Certified Associate in Project Management certification, or a two-year degree/high school diploma with 60 months of project leadership experience within the past eight years.
The PMP certification serves professionals in various leadership positions, including project managers, program managers and team leaders responsible for complex projects. For maximum benefit, maintaining PMI membership provides reduced certification costs and access to valuable professional development resources.
4. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
ISACA's Certified Information Systems Auditor certification validates expertise in information systems auditing, security protocols and control mechanisms. The credential covers five comprehensive domains: information systems auditing processes, governance and management, implementation, operations, and protection.
The certification costs $575 for ISACA members with a $45 annual maintenance fee, compared to $760 for non-members with an $85 yearly fee. ISACA membership requires a separate application process.
To qualify for CISA, IT professionals must have substantial professional experience -- a minimum of five years in information systems auditing, control and security. However, educational qualifications might substitute for a portion of this requirement. The certification primarily targets IT audit professionals, audit managers, security specialists and similar roles focused on governance and compliance.
Maintenance requirements include completing at least 20 CPE hours annually, accumulating 120 CPE hours over three years, and formal certification renewal every three years.
5. Certified ScrumMaster
The Certified ScrumMaster credential focuses on Agile project management and requires completion of a two-day training session delivered exclusively by a Certified Scrum Trainer. The intensive course prepares candidates for the certification exam, which evaluates proficiency of core Scrum concepts, including frameworks, roles, meetings, events and fundamental values.
The exam consists of 35 to 50 multiple-choice and true-false questions, with costs varying by training provider, as the mandatory two-day training course is included in the overall certification package. The credential appeals to software developers, engineers, project managers and individuals seeking to enhance their expertise in Agile methodologies.
Certification remains valid for two years, after which professionals must demonstrate continued learning by submitting 20 Scrum Education Units and paying a $100 renewal fee.
Exam preparation strategies
Nontechnical certifications require serious study, even though they differ from server administrator certifications in that they do not focus on hands-on approaches. The following tips will help you prepare.
Master the exam objectives
Download and analyze the official exam objectives document. This blueprint outlines all topics covered on the exam, allowing you to focus your study efforts precisely where they matter most.
Develop a structured study plan
Create a personalized study plan based on your strengths and weaknesses relative to the exam objectives. Establish a consistent study schedule and protect this time by eliminating potential distractions and interruptions.
Seek mentorship
Find an experienced mentor who has completed the certification process. Their guidance can prove invaluable, particularly for more complex certifications that require a nuanced understanding of concepts and methodologies.
Use formal training resources
Explore the range of formal training options available for your specific certification. These might include instructor-led classes (in-person or virtual), self-paced online courses, textbooks and specialized study guides.
Establishing a disciplined study routine and effective time management form the foundation of certification success. These organizational elements often prove more decisive than raw knowledge in determining your certification outcome.
Career development beyond technical skills
Advancing an IT career requires more than technical certifications and hands-on experience. Communicating effectively with stakeholders and aligning technical systems with business objectives makes you a more valuable professional while opening doors to new opportunities.
Start with these nontechnical certifications today and watch as your career possibilities expand.
Damon Garn owns Cogspinner Coaction and provides freelance IT writing and editing services. He has written multiple CompTIA study guides, including the Linux+, Cloud Essentials+ and Server+ guides, and contributes extensively to TechTarget Editorial and CompTIA Blogs.




