WORM (write once, read many)
What is WORM (write once, read many)?
In computer media, write once, read many, or WORM, is a data storage technology that allows data to be written to a storage medium a single time and prevents the data from being erased or modified. Data stored on a WORM-compliant device is considered immutable; authorized users can read the data as often as needed, but they cannot change it. Immutable storage plays a pivotal role in meeting data security and compliance requirements and protecting against ransomware and other threats.
Storage media that support WORM storage are purposely non-rewritable to prevent anyone from intentionally or accidently erasing or modifying the data after it is initially stored. Because of this feature, government agencies and enterprises have long used WORM devices for archival purposes. Organizations subject to compliance rules find the technology useful. For example, the Securities and Exchange Commission requires brokers and dealers to retain their digital records on storage media that preserves the records in a non-rewritable, non-erasable format.
How do optical WORM storage devices work?
WORM media was developed in the late 1970s using optical disks. Over the years, these disks have varied from 5.25 to 14 inches in diameter. They have offered capacities from 140 MB to 500 GB on a double-sided medium. Low-powered lasers are used to write data to a WORM device. This type of laser makes permanent marks on the surface of the disk.
In the past with WORM disks, typically the drive on which data was written was the only one that could read it. In some cases, this is still is the way it's done today. Although this feature has hampered the technology's marketplace acceptance to some degree, vendors continue to offer optical WORM storage devices.
For example, Sony launched the third generation of its Optical Disc Archive products in June 2020. It scales from 165 TB to 2.9 PB of immutable storage in a standard 42U rack. The Sony platform uses specialized disk cartridges to provide WORM storage. The cartridges contain archive media -- the physical disks -- that are designed for WORM data access. The latest generation of cartridges contain 11 disks and can store up to 5.5 TB of data. They can be written to only once but promise to be readable for 100 years.
Other types of optical media -- such as certain types of CDs, DVDs and Blu-ray disks -- also support write once, read many operations and are sometimes considered WORM devices. However, experts continue to debate whether media that can be written in more than a single session, such as multisession CDs, are really WORM devices.
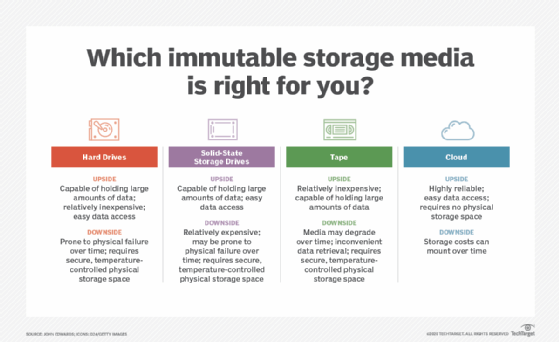
Other types of WORM storage
WORM technology has also been adapted to other media, such as:
In addition, the technology can be implemented through the hardware and software. There are no specific requirements for how it is delivered, except for the following three rules:
- The data can be written only one time.
- It must be immutable.
- Authorized users must be able to read the data a number of times.
IBM's approach with its Ultrium 3 tape drive systems is similar to that of its Optical Disc Archive. The Ultrium 3 supports the IBM LTO WORM Data Cartridge, which contains write-once, read-many tape media that prevent data from being altered or deleted. The Hewlett Packard Enterprise StoreEver LTO-8 Ultrium tape drive offers a similar type of cartridge to support WORM data storage on the StoreEver systems.
Some vendors are also building WORM capabilities into their storage software. For instance, NetApp ONTAP 9 includes SnapLock, a built-in feature that provides WORM protection and data retention controls for stored data. SnapLock enables customers to create volumes that cannot be modified or erased, preventing files from be altered or deleted until a specified date. Huawei offers a similar software feature, called HyperLock, with its OceanStor storage systems. HyperLock sets files to a read-only state as soon as they're written. After that, the files cannot be modified, renamed or deleted.
WORM protections have also moved to the cloud. Amazon's object storage service, Amazon S3. The service includes the Object Lock feature, which enables customers to store objects based on the WORM model. Customers can specify a retention period that determines how long the objects remains locked. Amazon S3 lets customers store data on either HDDs or SSDs.
What is WORM technology used for?
There are a variety of reasons organization use WORM technology, include the following:
- Regulatory requirements. Some industries, such as financial securities and healthcare, are required to use immutable data storage for security and privacy
- Safeguard active files. WORM technology is used to ensure unauthorized people cannot alter business and other documents. It also prevents accidental changes from being made.
- Archive integrity. Organizations use WORM technology to store important historical documents to ensure they aren't altered while stored.
- Data security layer. WORM technology also is part of an overall data security strategy to protect intellectual property, trade secrets and other important data.
The future of WORM technology
WORM capabilities are an important part of future storage technologies in development. For instance, Microsoft's Project Silica is investigating the use of silica glass to store cold data in the cloud for extended periods of time.
Project Silica focuses primarily on WORM archival storage, providing a write-once medium that is readable for thousands of years. As a proof of concept, the project team embedded a digitized version of the 1978 Superman movie into a piece of quartz glass that's 2 millimeters thick and 75 millimeters square in area.
Find out why immutable backups are a must in today's data center and the various approaches and factors to consider.







