
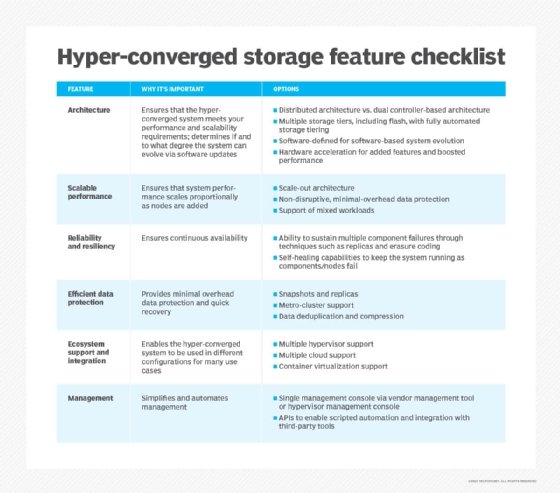
What is hyperconverged storage?
Hyperconverged storage is a software-defined approach to storage management that combines storage, compute, virtualization and networking technologies in one physical unit that's managed as a single virtualized system. This modern approach is one aspect of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI).
In HCI, various resources, including storage, are untethered from individual hardware, consolidated through virtualization and managed using software-defined networking (SDN). This makes hyperconverged storage more flexible, scalable, cost-effective and easy to manage compared to traditional storage solutions.
Why hyperconverged storage?
Hyperconverged storage is a type of software-defined storage (SDS) because each node has a software layer running virtualization software identical to all other nodes in the cluster. That software layer virtualizes the resources in the individual node and shares them with the other nodes in the cluster. This enables administrators to use resources as a single storage or compute pool.
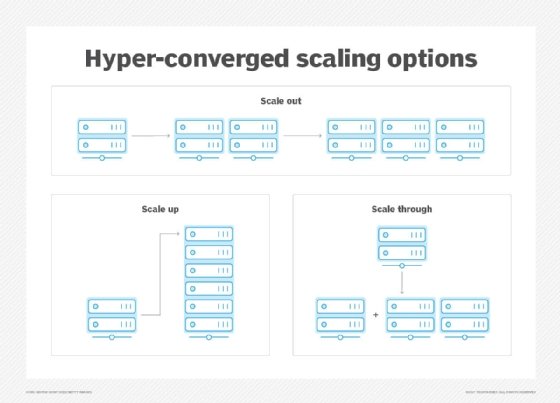
Hyperconverged storage provides greater control over storage provisioning in a virtual server environment. Besides providing administrators with single-pane-of-glass management capabilities, hyperconverged storage nodes can be connected and scaled out horizontally. This lets administrators create a distributed storage infrastructure in which direct-attached storage components from each physical server are combined to form logical DAS components that accommodate a logical, scalable, flexible pool of disk capacity.
Hyperconverged storage vs. converged storage
In an HCI system, each physical box or appliance is a node in the larger cluster of shared resources, including storage. The storage attached to the node is shared with the other nodes in the cluster, providing a larger, flexible storage pool. Instead of using dedicated hardware, node resources are virtualized using SDN. This provides greater flexibility and control over the storage resources than converged storage.
The SDS controller is at the core of hyperconverged storage. The SDS function, built into individual nodes, abstracts and pools storage resources to facilitate dynamic resource allocation and easy management.
As with hyperconverged storage, converged storage systems also combine network and storage resources in a physical server or appliance. However, in converged storage, the storage resources are not virtualized or pooled together. The storage is directly attached and only available to that physical box. These prebuilt resources are independent of each other and, therefore, can be separated and used for other applications.
Advantages of hyperconverged storage
A primary advantage of hyperconverged storage -- and HCI in general -- is that specialized hardware is rarely required to add capacity. More nodes can be added easily to a storage cluster for easy, cost-effective scale-out storage.
The virtualization aspect accommodates the use of commercial off-the-shelf hardware and inexpensive, industry-standard x86 processors to add or remove nodes as workloads change and business needs evolve. This means HCI storage devices are a cost-effective choice for many kinds of workloads.
Simplified management is another benefit. With a software-defined approach, storage is combined with compute and networking in one virtualized system. All the resources in a node are virtualized and shared across all the nodes in a cluster. This large storage pool is easy to manage and lowers the storage total cost of ownership. A single, unified dashboard enables full system control and facilitates data center management.
Hyperconvergence eliminates the need for storage provisioning and streamlines many common storage tasks. This helps IT teams focus on more strategic tasks, increases IT agility and reduces operational expenses.
Hyperconverged storage is well suited to workloads requiring high performance. By using high-speed storage devices, like solid-state drives and highly automated processes, hyperconverged storage solutions advance fast, responsive resource allocation and sharing for use cases like disaster recovery (DR), data analytics and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI).
Other key advantages of hyperconverged storage include the following:
- Appliances can be built from commodity hardware to enhance performance without substantially increasing costs.
- Hardware vendors offer turnkey appliances for specific use cases and demanding workloads.
- Scaling up as workloads evolve can occur easily by installing extra nodes.
Read more about the advantages of using HCI.
Disadvantages of hyperconverged storage
It's also important to acknowledge some limitations of hyperconverged storage.
Because base HCI nodes include both storage and compute, a user must add compute even if they only need more capacity, or vice versa. This can increase the system's cost. Many HCI platforms now include storage- or compute-centric nodes to alleviate this problem.
Vendor lock-in is another concern. While extra resources can be bolted on to the system to increase its capacity, some solutions require that these resources come from the same vendor. Some hyperconverged storage systems are unable to effectively share resources from different manufacturers in a fully elastic manner. These limitations can hinder efforts to optimize storage performance.
Some base-level hyperconverged storage systems don't include built-in multi-redundant facilities. As a result, the failure of even a single component can create a single point of failure that affects the availability and performance of the entire system.
Hyperconverged storage can improve the performance of heavily resource-dependent workloads, like data analytics. However, it may not be optimal for complex workloads, like high-performance computing and AI. Some vendors offer tailored solutions for these workloads -- albeit at higher costs.
Many vendors, including Dell EMC, HPE and Cisco, are also developing hyperconverged storage solutions that adapt to AI workloads to deliver the necessary application performance and can also easily integrate into an organization's existing IT framework. Other disadvantages of hyperconverged storage include the following:
- Conventional hyperconverged appliances consist of tightly integrated hardware, making it difficult to upgrade compute or storage independently of one another.
- Some vendors only support scaling up storage capacity by adding nodes and not component upgrades. Some hyperconverged systems don't allow connectivity to external storage arrays or a storage area network (SAN).
- Moving away from hyperconverged storage to a different architecture may introduce operational disruptions that affect business continuity and increase costs.
Use cases for hyperconverged storage
Hyperconverged storage can be used as a general-purpose data storage environment, but certain use cases are ideal for it. Some of the more popular use cases are the following:
- Public cloud, private cloud or hybrid cloud infrastructure.
- Data protection through backup and DR.
- VDI and desktop as a service.
- Branch office deployments, where server resources are needed on-site rather than in the data center.
- Server virtualization.
- Server consolidation.
- Edge computing.
- Development and testing.
- Data analytics.
Explore the many use cases for HCI.
Hyperconverged storage vendors and products
Hyperconverged storage systems can be delivered as appliances, providing both the hardware and the software, or as software-only products. Early players and products in the hyperconverged storage market included Nutanix Virtual Computing Platform and SimpliVity OmniCube.
In 2025, the following are the key players in the hyperconverged storage space:
- Dell EMC.
- Cisco.
- HPE.
The Dell EMC VxRail hyperconverged platform is powered by 4th Generation Intel Xeon scalable processors and supports VMware vSAN Express Storage Architecture. According to Dell, VxRail can boost even the most demanding workloads across core, edge and cloud. Next-gen VxRail automates full-stack lifecycle management and provides a consistent operational model across the infrastructure landscape for easy storage management.
HPE acquired hyperconverged pioneer SimpliVity in January 2017. The SimpliVity platform delivers self-managing, self-optimizing and self-healing HCI and includes advanced features, like machine learning, predictive analytics, built-in data protection and policy-based automation.
Cisco Compute Hyperconverged with Nutanix provides advanced cloud operating models and enhanced support and resiliency capabilities to simplify infrastructure delivery at any scale. This hyperconverged platform automates HCI deployments and helps organizations scale compute and storage resources easily. The product is available in multiple configurations through two families: C-Series (rack servers) and X-Series (modular systems).
Other hyperconverged storage vendors and products include Nutanix, NetApp, DataCore and Nimboxx.
Read more about the innovative companies developing HCI products for a wide range of applications and use cases.







