
Getty Images/iStockphoto
Key differences in software RAID vs. hardware RAID
Hardware RAID generally costs more than software RAID but may offer better performance. Consider factors like cost, performance needs and OSes to find the best fit.
In recent years, organizations have continued to add software-based components to their storage infrastructure. This includes RAID to maximize storage capacity and reduce risks of data loss. Some organizations are moving from hardware RAID to software RAID.
The key difference between software RAID and hardware RAID is that software in the OS manages the former, while controllers independent from the OS manage the latter. They are also different in cost, performance and access speeds.
RAID is a virtual storage resource using multiple storage devices -- the array -- managed by a controller that links one or more computing devices to the array. RAID presents the disks to users as logical storage resources. Many different options for RAID storage are available, and the costs can vary as widely as the available selection of devices and controllers.
As with any storage initiative, determine the specific storage requirements when establishing selection criteria. Factor in anticipated storage growth, physical space the drives may require, and additional power and HVAC requirements.
Hardware RAID
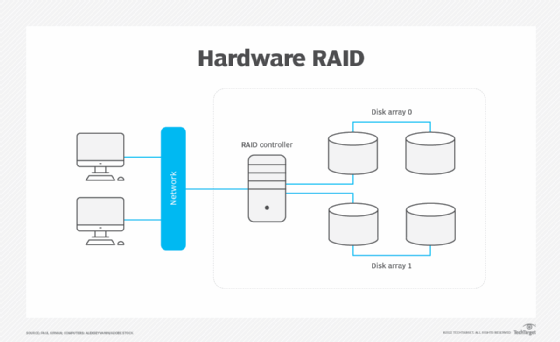
When RAID first appeared on the market, it used a hardware configuration. RAID offerings included the storage devices and the controller, which connects to one or more computers and multiple storage devices in the array. Figure 1 depicts a hardware RAID array.
Configure all RAID-related components for specific user requirements and the RAID level. Organizations can make changes to a disk array and controller independently of the computing devices.
Advantages of hardware RAID include the following:
- Hardware RAID data access is usually faster.
- The controller manages disks independently of the associated computer and does not need to use processing power.
- It is easy to replace a downed disk by removing and replacing the device.
Disadvantages of hardware RAID include the following:
- Although hardware RAID is often more reliable since it does not take processing power away from the disks, it can be more expensive than software RAID.
- It may not be compatible with the associated OS.
- Performance issues may occur when using different technologies such as SSDs.
Software RAID
By contrast, software RAID embeds disk controller software in the computer system and must be compatible with the OS. Figure 2 depicts a software RAID array.
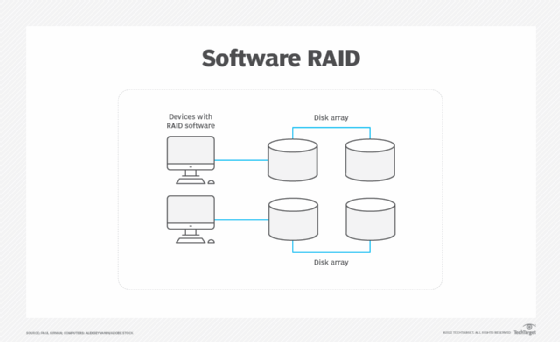
As with hardware systems, configure software RAID-related components for specific user requirements. Changes to the disk array and the controller require more user interaction with the OS because the RAID controller is part of the OS.
Advantages of software RAID include the following:
- It is typically less expensive than hardware RAID since no RAID controller is needed.
- The controller manages disks as part of the associated computer.
- Software RAID can be implemented in one OS and used by multiple devices.
Disadvantages of software RAID include the following:
- Data access can be slower compared to hardware RAID.
- Attached devices must be compatible with the associated OS.
- Replacing a disk is more complex because the OS must tell the RAID controller to shut down.
Comparing software RAID vs. hardware RAID systems
To decide between hardware RAID and software RAID, consider the following categories and features.
Performance and flexibility
- Use hardware RAID when high performance and flexibility are required or when a high-level RAID implementation is needed.
- Software RAID's performance is comparable to hardware RAID but may be limited since it shares OS processing overhead.
Cost
- Hardware RAID may be more expensive than other options.
- Software RAID doesn't require a separate controller, which keeps costs down.
RAID controller
- Hardware RAID requires a RAID controller. Replace RAID controllers with a similar unit if a controller is lost.
- Software RAID does not use an external controller.
Access speeds
- Hardware RAID speeds depend on the controller, network and number or types of drives.
- Software RAID access speeds can be as fast or faster than hardware RAID based on the controller software and the drives.
OSes
- Hardware RAID operates independently of the OS. Multiple OSes can share hardware RAID.
- Software RAID uses a driver in the OS and uses the associated OS.
Reasons to use RAID storage
Hardware and software RAID support most storage requirements if they are configured to the user's specifications. Add more drives to the array to increase storage capacity.
RAID also provides primary storage and secondary support for applications, as well as files and databases. They are important components of an organization's data protection and DR strategies. While they provide additional support for data protection and DR, implementing RAID should not be the primary data backup and DR strategy.
Types of RAID systems
Several different types of RAID storage are available, depending on storage requirements and the need for device reliability and resilience. The following is a brief summary of the most widely used RAID options:
- RAID 0. High-performance storage using disk striping but no parity, which means no fault tolerance.
- RAID 1. Storage mirroring using at least two drives; each data write goes to both disks, which provides high availability and backups if needed.
- RAID 5. Disk striping for performance combined with parity for availability; typically used for resilient arrays but with slightly less performance than RAID 0; loss of one drive does not affect the entire array.
- RAID 6. Higher reliability than RAID 5 through striping and double parity stripes that can absorb disk failures on two drives in an array before any loss of data.
- RAID 10 (1+0). High performance that combines disk mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0) for fault tolerance; a minimum of four disks is needed.
- RAID 50 (5+0). Using a six-disk minimum, high-reliability option that combines striping with parity distributed across each disk; this helps to survive disk outages that are on different arrays.
Another option: Hybrid RAID
Hybrid RAID uses capabilities of both hardware and software RAID systems. For example, organizations can implement a hardware configuration that connects its controller to the OS to augment software-based RAID. This provides flexibility to support different OSes.
While hybrid RAID may be a viable approach, check the storage configuration and performance capabilities before investing.
Editor's note: This article was updated in August 2025 to include information on RAID levels and improve the reader experience.
Paul Kirvan, FBCI, CISA, is an independent consultant and technical writer with more than 35 years of experience in business continuity, disaster recovery, resilience, cybersecurity, GRC, telecom and technical writing.








