
Getty Images
How to deploy Data Duplication on Windows Server
Data deduplication is necessary to stay ahead of storage demands and maintain available space. Windows Server Data Deduplication is one tool that can help.
Storage capacity is essential for managing data costs and performance. File server and backup administrators must use every advantage to stay ahead of user storage demands and budgetary requirements.
Data deduplication replaces redundant data in file blocks, vastly reducing storage space consumption. It works best on devices with redundant data, such as servers storing backup jobs or virtualization images. Hash comparisons identify duplicate information, replacing it with pointers to a single source.
Microsoft introduced the Windows-specific Data Deduplication feature with Windows Server 2012. Today, it's still an integral part of Windows Server. Microsoft indicates that Data Deduplication users can save significant storage space, including up to 50% savings for user documents and 95% for virtualization libraries.
Integrating data deduplication into storage infrastructure can reduce storage costs, increase storage capacity and maintain file servers' overall efficiency and capability. This article shows how to install and configure Windows Server Data Deduplication, as well as provides best practices and troubleshooting tips.
Deduplication use cases
Any Windows Server that hosts significant amounts of data is a potential candidate for the Data Deduplication utility, including file servers, backup storage servers and virtualization hosts. Most enterprises include at least one -- but likely all three -- of these server types.
When isolating storage environments to their own volumes, then consider the following deployments:
- Software development shares.
- Multimedia storage shares. Deduplication does not always help these file types.
- Large data volumes.
Install Data Deduplication
Ensure the device's current Windows Server version supports data deduplication. This shouldn't be a problem, since this feature exists on Windows Server 2012 onward. Data Deduplication requires the NTFS file system.
Data Deduplication isn't installed by default. Use the following steps to install it.
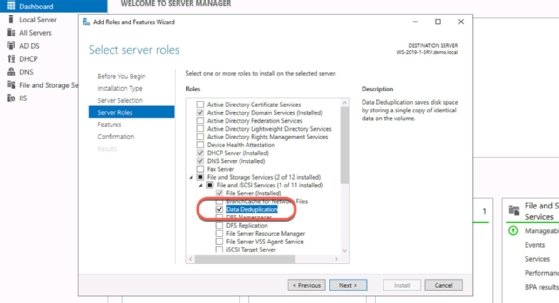
- Open Server Manager.
- Select Manage and Add Roles and Features.
- Select Next through the three pages that follow.
- Expand File and Storage Services and expand File and iSCSI Services.
- Select Data Deduplication.
- Select Add Features when prompted.
- Click Next through the remaining pages.
- Click Install on the Confirmation page.
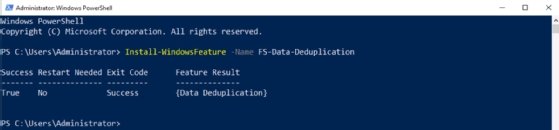
Most Windows administrators use the GUI to manage servers. However, the following PowerShell cmdlet can also install Data Deduplication:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name FS-Data-Deduplication
Configure and enable Data Deduplication
Manage Data Deduplication using the File and Storage Services node in Server Manager. The File and Storage Services interface provides a wealth of information and configuration options for storage management. Explore these options carefully. Tools such as FSRM enable many reporting and data control features to optimize storage. Efficient data management techniques improve the quality and efficiency of backup jobs.
Use the following steps to access the configuration interface:
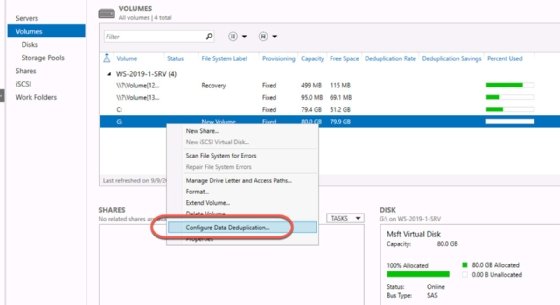
- Expand File and Storage Services.
- Expand the Volumes node.
- Right-click the volume you want to manage with data deduplication and select Configure Data Deduplication.
- Modify the Data Deduplication setting from Disabled to General-purpose server.
- Specify a file age for deduplication. The default is three days.
- Exclude file types as needed.
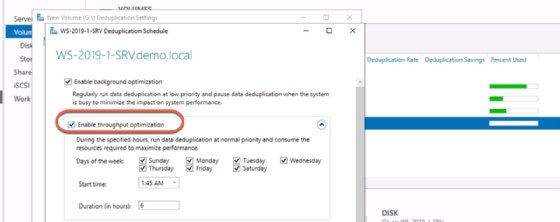
- Select Set Deduplication Schedule.
- Check the boxes for Enable background optimization and Enable throughput optimization.
- Configure the schedule to run at night, when the server is least active. Be careful of other processes that might also run at night, such as backups.
- Click OK and Apply to enable deduplication with your specified options.
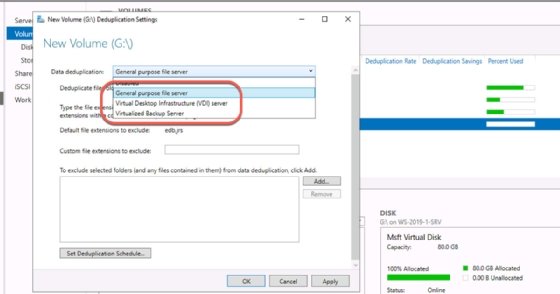
The different deduplication types optimize the process for particular types of data. The General-purpose server will meet the needs of most administrators, but users have the following options:
- General-purpose: Best for standard file servers.
- Hyper-V: Optimized for Hyper-V workloads or VDI devices.
- Backup: Prioritizes deduplication of backup sets.
Defining a file age helps to avoid applying deduplication resources to frequently changing files. By selecting file ages, deduplication can focus only on inactive files, such as those older than three days.
Finally, optimize deduplication by excluding file types that will not benefit from it. These can include database files, some multimedia, highly compressed files and files smaller than 32KB.
Monitor, optimize, and assess volumes for deduplication
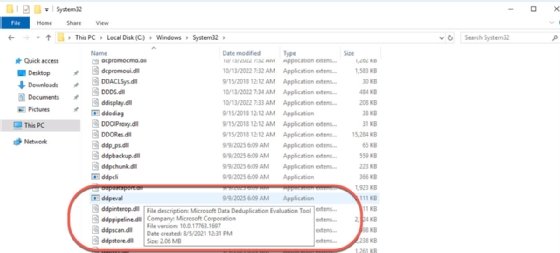
There's no reason to install and manage deduplication on volumes unless it improves storage efficiency. It stresses the server's CPU, memory and storage subsystems, so justifying its use is crucial. The Data Deduplication Saves Evaluation Tool -- ddpeval.exe -- estimates how much storage space deduplication can recover on a volume.
Find the following command-line tool in the Windows\System32 directory after you install Data Deduplication. It doesn't run on system or boot volumes, and will fail on volumes where deduplication is already configured.
Use the following steps to evaluate drive G: on the local system as an example.
- Type ddpeval.exe G:
- Evaluate a specific directory, such as SalesData, by typing ddpeval.exe "G:\SalesData".
The tool also works across the network using a UNC path. To follow this path, type ddpeval.exe "\\fileserver01\g$\SalesData".
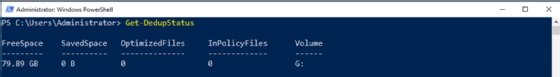
PowerShell also reports deduplication information. Use the Get-DedupStatus cmdlet to display the current deduplication status.
Alternative products
Windows Server Data Deduplication is free, tightly integrated with Windows, offers solid configuration and monitoring capabilities and is independent of backup and recovery tools, avoiding vendor lock-in. However, there are other data deduplication products on the market that might be better suited to some organizations.
Organizations should investigate other tools if they use a cloud or hybrid infrastructure, or require deduplication across Windows and Linux file servers. Dedicated utilities can also offer performance and automation advantages. Most of these examples integrate deduplication into more extensive backup and imaging services rather than as standalone utilities.
Some alternative tools include the following:
- Veeam Backup and Replication supports backup and recovery for hybrid and cloud environments with integrated deduplication.
- Arcserve UDP has extensive backup and recovery capabilities with integrated deduplication.
- Acronis Cyber Protect is an image-based backup product with integrated deduplication.
Best practices and troubleshooting
Data Deduplication isn't an experimental technology. Administrators worldwide use it to manage storage costs and increase data backup efficiency. However, administrators should be aware of troubleshooting tips and best practices.
Troubleshooting
Use the following tips to troubleshoot and optimize deduplication jobs.
- Verify that sufficient memory is available for deduplication processes. The recommended quantity is 1 GB of RAM per 1 TB of data.
- Verify sufficient processor capability by checking for conflicting jobs.
- Consider storage system I/O performance.
- Use the ddpeval.exe utility to confirm whether deduplication will be effective or helpful.
- Check Event Viewer logs, specifically the Microsoft-Windows-Deduplication/Operational log.
PowerShell can also view and monitor deduplication performance. Use the Get-DedupJob, Get-DedupStatus and Update-DedupStatus cmdlets to display more information.
Best practices
Keep the following best practices in mind for the next deduplication deployment
- Use current versions of Windows Server for the most advanced features.
- Don't enable Data Deduplication on system volumes. Use it only on volumes containing data.
- Ensure volumes have enough free space for deduplication processes.
- Avoid scheduling conflicts with backup software and data replication software.
- Run deduplication during off-peak hours.
- Test data deduplication to gauge its effect on performance and storage.
- Compress data after deduplicating it.
Damon Garn owns Cogspinner Coaction and provides freelance IT writing and editing services. He has written multiple CompTIA study guides, including the Linux+, Cloud Essentials+ and Server+ guides, and contributes extensively to Informa TechTarget, The New Stack and CompTIA Blogs.







