What is an application?
An application, also referred to as an application program or application software, is a computer software package that performs a specific function directly for an end user or, in some cases, for another application. An application can be self-contained or a group of programs. The program is a set of operations that runs the application for the user.
Application examples
Some types of applications include the following:
- Word processors.
- Database programs.
- Web browsers.
- Deployment tools.
- Image editors.
- Communication platforms.
Applications use the computer's operating system (OS) and other supporting programs, typically system software, to function. An application requests services from and communicates with other technologies via an application programming interface (API).
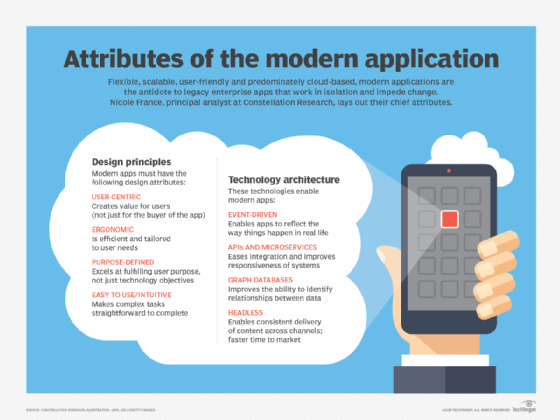
Applications vs. system software
Unlike application software, system software programs operate in the background and do not directly interface with the computer user. System software manages the operation of a computer or instance and typically includes the OS, hypervisor and drivers. These are generally low-level or basic programs as compared to end-user facing applications.
Applications use system software for access to basic hardware resources, such as memory, storage and other utilities. For example, an application relies on system software for access to the file system to manage and store files.
Types of applications
Applications can vary in many ways, including how they're built, what platform they run on, whether they are open source or proprietary, or for which market they are used.
For example, a mobile application developer can write their code as a native, web or hybrid application -- these terms can also describe desktop applications. The developer codes a native application to run on specific hardware, such as a camera or GPS, and in the same programming language as the underlying OS. For example, the Photos application on Mac OS X is written in Objective-C, which is the same language that Mac OS X uses.
An end user typically accesses a web application via a web browser, such as Google Chrome. A developer can write web applications in several languages, including JavaScript, CSS and HTML, but they cannot directly access the hardware on which the application is installed.
Hybrid applications have APIs that can access device resources, similar to a native application, but are typically written in languages such as HTML and CSS. Additionally, developers often code mobile applications to work on a specific device platform.
Application licensing
Applications can also be grouped into categories by licensing style. Proprietary software programs, such as Adobe Photoshop, are applications that are owned under copyright. End users can buy or license proprietary applications through the vendor providing the software. They cannot modify these applications; they can only add functionality to them via third-party add-ons.
Open source applications, such as WordPress, provide the source code for end users and developers to use and modify. Software companies and individual developers typically make open source applications freely available under a generic or public license, such as GNU.
A developer or team of developers can create an application for a specific vertical market. A vertical application typically serves a specific industry or departmental need, such as a medical billing system. By contrast, a horizontal application, such as a word processor or web browser, applies to a wide range of industries.