What is Agile software development?
Agile is a type of software development methodology that anticipates the need for flexibility and applies a level of pragmatism to the delivery of the finished product. Agile software development requires a cultural shift in many companies because it focuses on the clean delivery of individual pieces or parts of the software and not on the entire application.
Benefits of Agile include its ability to help teams in an evolving landscape while maintaining a focus on the efficient delivery of business value. The collaborative culture facilitated by Agile also improves efficiency throughout the organization, as teams work together and understand their specific roles in the process. Finally, companies using Agile software development can feel confident that they're releasing a high-quality product because testing is performed throughout development. This provides the opportunity to make changes as needed and alert teams to any potential issues.
Agile has largely replaced the Waterfall model as the most popular development methodology in most companies, but is itself at risk of being eclipsed or consumed by the growing popularity of DevOps.
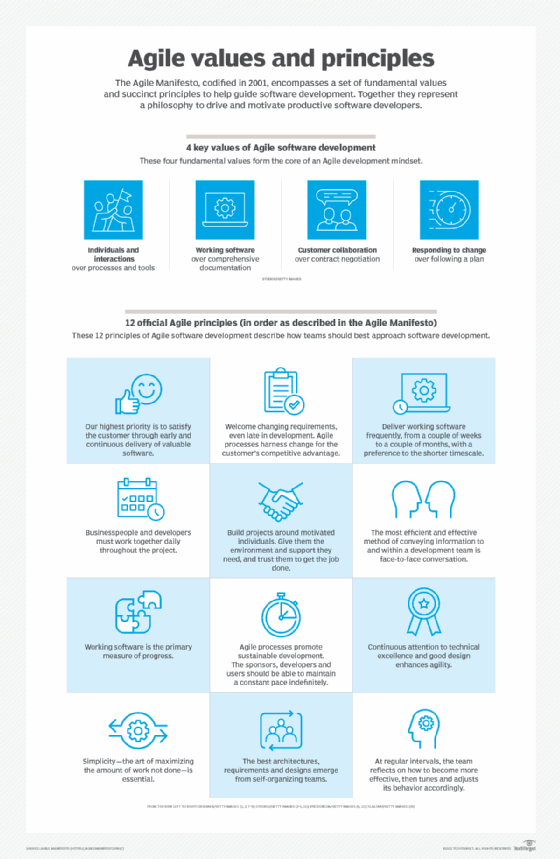
The 4 values of Agile
In 2001, 17 software development professionals gathered to discuss concepts around the idea of lightweight software development and ended up creating the Agile Manifesto. The Manifesto outlines the four core values of Agile, and although there has been debate about whether the Manifesto has outlived its usefulness, it remains at the core of the Agile movement.
The four core values outlined in the Agile Manifesto are as follows:
- Individual interactions are more important than processes and tools. People drive the development process and respond to business needs. They're the most important part of development and should be valued above processes and tools. If the processes or tools drive development, then the team will be less likely to respond and adapt to change and, therefore, less likely to meet customer needs.
- A focus on working software rather than thorough documentation. Before Agile, a large amount of time was spent documenting the product throughout development for delivery. The list of documented requirements was lengthy and would cause long delays in the development process. While Agile doesn't eliminate the use of documentation, it streamlines it in a way that provides the developer with only the information that's needed to do the work -- such as user stories. The Agile Manifesto continues to place value on the process of documentation, but it places higher value on working software.
- Collaboration instead of contract negotiations. Agile focuses on collaboration between the customer and project manager, rather than negotiations between the two, to work out the details of delivery. Collaborating with the customer means that they're included throughout the entire development process, not just at the beginning and end, thus making it easier for teams to meet the needs of their customers. For example, in Agile, the customer can be included at different intervals for demos of the product. However, the customer could also be present and interact with the teams daily, attend all meetings and ensure the product meets their desires.
- A focus on responding to change. Traditional software development used to avoid change because it was considered an undesired expense. Agile eliminates this idea. The short iterations in the Agile cycle allow changes to easily be made, helping the team modify the process to best fit its needs rather than the other way around. Overall, Agile software development believes change is always a way to improve the project and provide additional value.
The 12 principles of Agile
The Agile Manifesto also outlined the following 12 core principles for the development process:
- Satisfy customers through early and continuous delivery of valuable work.
- Break big work down into smaller tasks that can be completed quickly.
- Recognize that the best work emerges from self-organized teams.
- Provide motivated individuals with the environment and support they need and trust them to get the job done.
- Create processes that promote sustainable efforts.
- Maintain a constant pace for completed work.
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in a project.
- Assemble the project team and business owners daily throughout the project.
- Have the team reflect at regular intervals on how to become more effective, then tune and adjust behavior accordingly.
- Measure progress by the amount of completed work.
- Continually seek excellence.
- Harness change for a competitive advantage.
The Agile software development cycle
The Agile software development cycle can be broken down into the following six steps:
- Concept.
- Inception.
- Iteration and construction.
- Release.
- Production.
- Retirement.
Concept
The first step, concept, involves identifying business opportunities in each potential project as well as estimating the time and work that will be required to complete the project. This information can then be used to prioritize projects and discern which ones are worth pursuing based on technical and economic feasibility.
Inception
During the second step, inception, team members are identified, funding is established, and the initial requirements are discussed with the customer. A timeline should also be created that outlines the various responsibilities of teams and clearly defines when work is expected to be completed for each sprint. A sprint is a set period during which specific work must be completed and made ready for review.
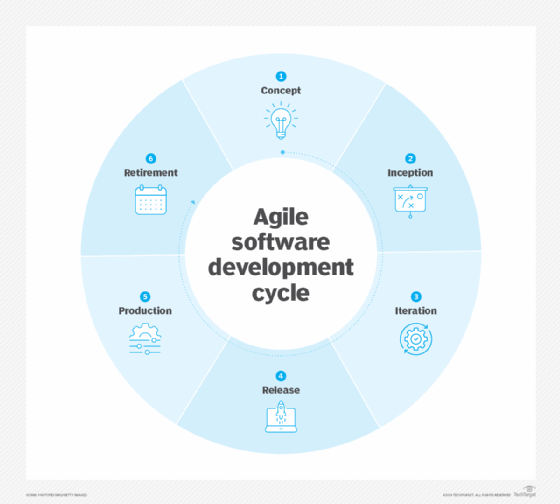
Iteration and construction
The third step, iteration and construction, is when teams start creating working software based on requirements and continuous feedback. The Agile software development cycle relies on iterations -- or single development cycles -- that build upon each other and lead into the next step of the overall development process until the project is completed. Each iteration typically lasts between two to four weeks, with a set completion date. The goal is to have a working product to launch at the end of each iteration.
Multiple iterations occur throughout the development cycle and they each possess their own workflow. A typical iteration flow consists of the following:
- Defining requirements based on the product backlog, sprint backlog and customer and stakeholder feedback.
- Developing software based on the set requirements.
- Conducting quality assurance testing, internal and external training and documentation.
- Delivering and integrating the working product into production.
- Gathering customer and stakeholder feedback on the iteration to define new requirements for the next sprint.
Release
The fourth step, release, involves final QA testing, resolution of any remaining defects, finalization of the system and user documentation and, at the end, release of the final iteration into production.
Production
After the release, the fifth step, production, focuses on the ongoing support necessary to maintain the software. The development teams must keep the software running smoothly while also teaching users exactly how to use it. The production phase continues until the support has ended or the product is planned for retirement.
Retirement
The final step, retirement, incorporates all end-of-life activities, such as notifying customers and final migration. The system release must be removed from production. This is usually done when a system needs to be replaced by a new release or if the system becomes outdated, unnecessary or starts to go against the business model.
Throughout the Agile cycle, different features can be added to the product backlog, but the entire process should consist of repeating each step over and over until every item in the backlog has been satisfied. This makes the Agile cycle more of a loop than a linear process. At any time, an enterprise can have multiple projects occurring simultaneously with iterations that are logged on different product lines and a variety of internal and external customers providing different business needs.
Types of Agile methodologies
The goal of every Agile methodology is to embrace and adapt to change while delivering working software as efficiently as possible. However, each method varies in the way it defines the steps of software development. The most widely used Agile methods include the following:
- Scrum.
- Lean software development.
- Extreme programming.
- Crystal.
- Kanban.
- Dynamic systems development method.
- Feature-driven development.
Scrum
Scrum is a lightweight Agile framework that project managers can use to control all types of iterative and incremental projects. In Scrum, the product owner creates a product backlog that enables them to work with their team to identify and prioritize system functionality. The product backlog is a list of everything that needs to be accomplished to deliver a successful, working software system -- this includes bug fixes, features and nonfunctional requirements. Once the product backlog is defined, no additional functionality can be added except by the corresponding team.
Once the team and the product owner have established the priorities, cross-functional teams step in and agree to deliver working increments of software during each sprint -- often within 30 days. After each sprint, the product backlog is reevaluated, analyzed and reprioritized to select a new set of deliverable functions for the next sprint. Scrum has gained popularity over the years, as it's simple, has proven to be productive and can incorporate the various overarching practices promoted by the other Agile methods. Its standout virtues -- often the reasons it's chosen above other options -- are its high level of transparency, and the involvement of the product owner at every step in the process.
Lean software development
This is another iterative method that focuses on using effective value stream mapping to ensure the team delivers value to the customer. It's flexible and evolving; it doesn't have rigid guidelines or rules. The Lean method uses the following primary principles:
- Increasing learning.
- Empowering the team.
- Fostering integrity.
- Removing waste.
- Understanding the whole.
- Making decisions as late as possible.
- Delivering the product as fast as possible.
The Lean method relies on fast and reliable feedback between the customers and programmers to provide fast and efficient development workflows. To accomplish this, it provides individuals and small teams with decision-making authority instead of relying on a hierarchical flow of control. To eliminate waste, the Lean method asks users to only select truly valuable features for their system, prioritize these chosen features and then deliver them in small batches. Lean software development also encourages automated unit tests to be written simultaneously with the code and concentrates on ensuring every member of the team is as productive as possible.
Extreme programming
The extreme programming (XP) method is a disciplined approach that focuses on speed and continuous delivery. It promotes increased customer involvement, fast feedback loops, continuous planning and testing and close teamwork. Software is delivered at frequent intervals -- usually every one to three weeks. The goal is to improve software quality and responsiveness when faced with changing customer requirements.
The XP method is based on the values of communication, feedback, simplicity and courage. Customers work closely with their development team to define and prioritize their requested user stories. However, it's up to the team to deliver the highest priority user stories in the form of working software that has been tested at each iteration. To maximize productivity, the XP method provides users with a supportive, lightweight framework that guides them and helps ensure the release of high-quality enterprise software.
Crystal
Crystal is the most lightweight and adaptable methodology. It focuses on people and the interactions that occur while working on an Agile project as well as business-criticality and priority of the system under development. The Crystal method works off the realization that every project possesses unique characteristics that require a slightly tailored set of policies, practices and processes. As a result, it's made up of a collection of Agile process models, such as Crystal Orange, Crystal Clear and Crystal Yellow. Each model has its own unique characteristics that are driven by different factors, including project priorities, team size and system criticality.
Like other Agile methodologies, Crystal emphasizes frequent delivery of working software with high customer involvement, adaptability and the elimination of bureaucracy and distractions. Its key principles include communication, teamwork and simplicity.
Kanban
Kanban uses a highly visual workflow management method that enables teams to actively manage product creation -- emphasizing continuous delivery -- without creating more stress in the software development lifecycle. It has become popular among teams also practicing Lean software development.
Kanban uses three basic principles: visualize the workflow; limit the amount of work in progress; and improve the flow of work. Like Scrum, the Kanban method is designed to help teams work more efficiently with each other. It encourages continuous collaboration and attempts to define the best possible workflow to promote an environment with active and ongoing learning and improvement. It's often favored over Scrum because of its greater flexibility, and team members tend to greatly appreciate the visual workflow. On the other hand, its flexibility can lead to ambiguity and difficulty in estimating completion times, compared to other methodologies.
Dynamic systems development method
The dynamic systems development method is a response to the need for a common industry framework for rapid software delivery. Originally a European innovation, DSDM offers benefits such as holding business cases at its core, facilitating on-time delivery and early incremental deliverables, and improved collaboration. It's based on the following eight key principles; failing to abide by any one of the principles introduces risk to successful completion of the project:
- Collaboration.
- On-time delivery.
- Demonstrated control.
- Continuous, clear communication.
- A constant focus on the business need.
- Iterative development.
- Creation in increments from firm foundations.
- Refusal to compromise quality.
In the DSDM, rework is built into the process and all changes must be reversible. System requirements are prioritized using the MoSCoW method, which ranks priority as follows:
- M: Must have.
- S: Should have.
- C: Could have, but not critical.
- W: Won't have now but could have later.
It's important in DSDM that not every requirement is considered critical. Each iteration should include less critical items that can be removed so higher priority requirements aren't affected.
Feature-driven development
Finally, feature-driven development blends software engineering best practices -- such as developing by feature, code ownership and domain object modeling -- to create a cohesive, model-driven, short-iteration process. FDD begins by defining an overall model shape, which in turn creates a feature list. The method then proceeds with iterations that last two weeks and focus on planning by feature, designing by feature and building by feature. If a feature takes more than two weeks to build, then it should be broken down into smaller features. The primary advantage of FDD is that it's scalable -- even to large teams -- since it uses the concept of "just enough design initially."
Advantages and disadvantages of Agile
The key differences have been compared over the years with Agile vs. Waterfall approaches.
In the Waterfall era of software development, coders worked alone, with little to no input before handing the software to testers and then on to production. Bugs, complications and feature changes either weren't handled well, or were dealt with so late in the process that projects were seriously delayed or even scrapped.
The idea behind the Agile model, in which everyone -- including the business side -- stayed involved and informed in the development process, represented a profound change in both company culture and the ability to get better software to market more quickly.
Collaboration and communication became as important as technology, and because the Agile Manifesto is open to interpretation, Agile has been adapted and modified to fit organizations of all sizes and types. The Agile cultural shift also paved the way for the latest software development evolution, DevOps.
And when communication and collaboration improve and transparency is enhanced, fewer mistakes are made and more mid-course corrections can occur -- bolstering quality, reducing risk and keeping schedules on track.
Benefits of Agile methodology include the following:
- Improved communication and collaboration.
- Adaptability.
- Transparency.
- Reduced risks.
- Improved delivery and customer satisfaction.
On the other hand, many would say the biggest disadvantage of Agile is the fact it has been modified -- some would say diluted -- by many organizations. This phenomenon is so widespread that the "Agile my way" practitioners are known as ScrumButs, as in, "We do Scrum in our organization, but …."
Although Agile opens the lines of communication between developers and the business side, it's been less successful bringing testing and operations into that mix -- an omission that might have helped the idea of DevOps gain traction.
Another potential concern about Agile is its lack of emphasis on technology, which can make it difficult to sell the concept to upper managers who don't understand the role that culture plays in software development. Furthermore, the necessity of completing sprints on time can create a stressful work environment for software developers. They might be forced to work extra hours and stay late to meet deadlines. Moreover, incremental delivery can result in fragmented output if team members working in different cycles get out of sync.
Finally, Agile methodologies might strain communication between developers and stakeholders through its emphasis on the active participation of the latter, as they speak different languages.
The disadvantages, then, include the following:
- Over-customized processes.
- Stressful time pressures.
- Potential for project derailment.
- Documentation often isn't thorough.
Take this quiz to gauge how well you know the basics of Agile and the Agile Manifesto.





