kanban
Kanban is a visual system used to manage and keep track of work as it moves through a process. The word kanban is Japanese and roughly translated means "card you can see."
Toyota introduced and refined the use of kanban in a relay system to standardize the flow of parts in their just-in-time (JIT) production lines in the 1950s. The approach, was inspired by Toyota studying supermarkets in the UK, gaining the idea of applying the techniques used in shelf-stocking to the factory floor. Toyota saw that store shelves were stocked with just enough product to meet consumer demand and inventory, and would only be restocked when there was a visual signal -- in this case, an empty space on the shelf. In 1953, Toyota began applying this approach to their main machine shop. Kanban later became a visual system in order to track work through production.
Kanban can come in the form of a traditional setup -- with physical signals in the form of a tag or labels -- or as eKanban, meaning electronic kanban.
How kanban works
In manufacturing, kanban starts with the customer's order and follows production downstream. At its simplest, kanban is a card with an inventory number that’s attached to a part. Right before the part is installed, the kanban card is detached and sent up the supply chain as a request for another part. In a lean production environment, a part is only manufactured (or ordered) if there is a kanban card for it. Because all requests for parts are pulled from the order, kanban is sometimes referred to as a "pull system."
There are six generally accepted rules for kanban:
- Downstream processes may only withdraw items in the precise amounts specified on the kanban.
- Upstream processes may only send items downstream in the precise amounts and sequences specified by the kanban.
- No items are made or moved without a kanban.
- A kanban must accompany each item at all times.
- Defects and incorrect amounts are never sent to the next downstream process.
- The number of kanban should be monitored carefully to reveal problems and opportunities for improvement.
The concept of providing visual clues to reduce unnecessary inventory has also been applied to agile software development. In this context, the inventory is development work-in-progress (WIP) and new work can only be added when there is an "empty space" on the team's task visualization board.
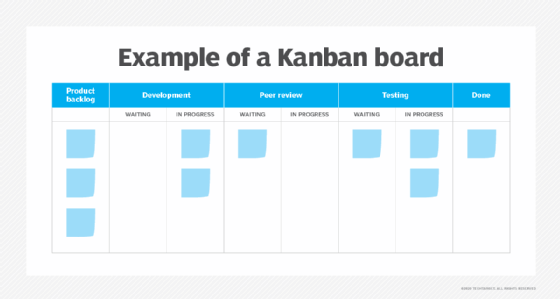
Kanban boards
A kanban board is a similar looking display to ta value stream map. Using a kanban board, a development team can track and create reports on the flow of work, including what adds value and what doesn’t.
For each step outlined in the top row of the board, the team must determine average cycle time -- the amount of time it takes to do the work of that stage -- and the non-value-add waiting periods between steps. When programmers complete a task in progress, they will move the card to the waiting stage, then the next task after that.