What is field service management (FSM)?
Field service management (FSM) is a system of managing off-site workers and the resources they require to do their jobs efficiently. Originally, this was a manual process that involved phone calls and paperwork exchanged among field service technicians, customers and office personnel. Today, FSM software handles much of the information exchange and manages the field service process.
FSM software lets field workers view and make changes to schedules, work orders, customer account records, inventory, invoices, and other databases and records. The tools also give customers a way to schedule service, track service requests and technicians' progress, engage field personnel and have input in the field service process. FSM software is accessible through mobile devices.
Field service management software is popular in industries like telecommunications, where field technicians need information about service requests, scheduling and other details. It is also used in industries such as healthcare, letting homecare workers track and update patient information. Specialized industries, like mining, use FSM software to give workers information about the location of a needed service and what's needed to minimize downtime.
As mobile workforce capabilities have improved, FSM software has become more integral to the work and workflow of field service workers. It schedules and dispatches technicians for service calls. It also provides information through work orders, account information, product inventory and availability, and product knowledge bases. Advanced FSM software provides capabilities such as voice to text and integration with internet of things (IoT)-connected devices.
What are the main elements of effective field service management systems?
Field service management consists of several components:
- Contract management involves managing service-level agreements and ensuring that providers meet their SLA commitments. SLAs specify the type of service provided and the standards that the provider will meet.
- Customer self-service components enable customers to pay for, schedule and track a job, as well as communicate with staff.
- Dispatch management designates which field technician is sent where and when they are sent out.
- Employee training provides field service teams with the skills they need to do their jobs and stay up to date on product and service changes.
- Inventory management tracks parts and supplies as they are ordered, stored, used and sold. It helps workers know what to order, when to order and reorder, and how much to order.
- Job scheduling establishes work order completion timelines, employee schedules and service appointments.
- Work order management assigns work orders to employees and tracks them to completion with job status updates.
Why is field service management important?
Field service management enables off-site workers to do their jobs efficiently. Field service software tools provide them with the resources they need and establish a communication channel among office workers, field workers and customers. Each party is connected to the field service process through the software. FSM software helps structure and automate repetitive tasks, thus reducing errors.
These tools also help off-site workers adapt to changing circumstances in real time. If a job doesn't go according to plan, technicians can quickly access knowledge bases and technical support groups for expert advice and answers.
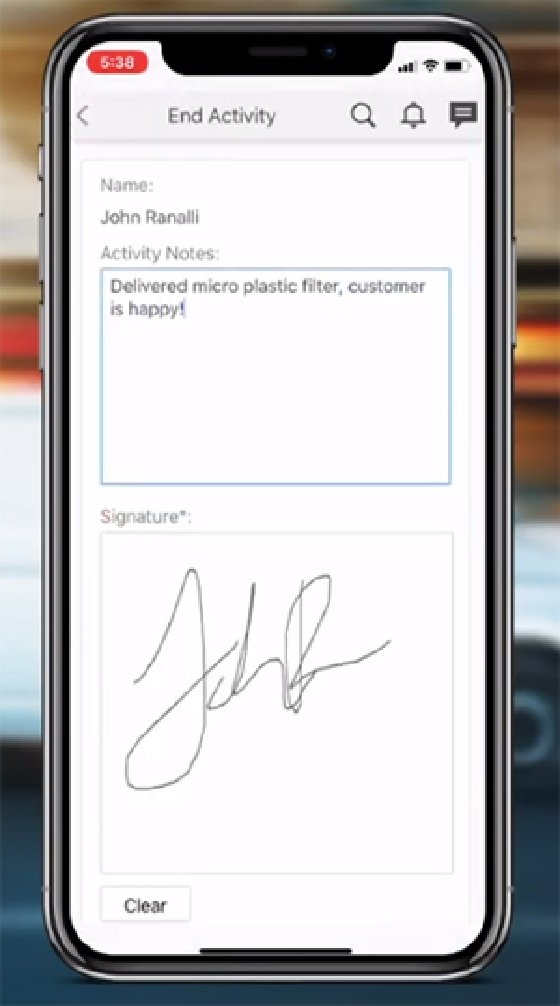
For example, if a technician runs into an issue servicing a machine, they could snap a picture of it and write a description of the problem on the mobile FSM app. The technician can receive instant feedback without having to leave the job site.
FSM applications are also important for improving customer satisfaction. They provide customer experience (CX) that delivers information on order scheduling, service requests, work progress and payment. Field work goes more smoothly when customers are informed and engaged in the process. It also increases customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Why use FSM software?
Field service management software generally is a software-as-a-service platform that lets technicians work from mobile devices. Field service is mobile by nature. Today's software enables technicians to do more work on-site, rather than transferring equipment back to the service organization's offices to be fixed.
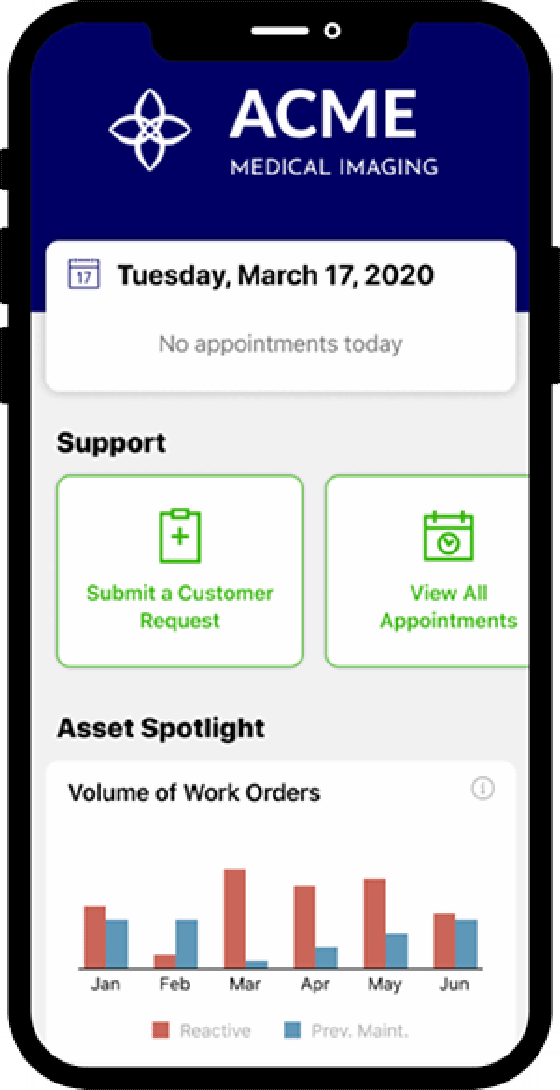
FSM apps have dashboards that show technicians details about upcoming jobs and work orders, including the following:
- Customer contact information.
- Location of the service event.
- Directions to the job site.
- Purpose of the visit.
- Account associated with the work order.
- Background on the machine to be serviced.
- Priority work involved.
Some core features of field service management software are the following:
- Mobile access for all field technicians.
- Support for the field service lifecycle.
- Customer portals and notifications.
- Job scheduling and status updates.
- Knowledge and asset repositories.
- Inventory and parts management.
- Interface to a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
- Payment processing and integrated invoicing features.
- Regulatory and warranty compliance measures.
- Route optimization and Global Positioning System navigation.
- Time tracking and driver logs.
- Analytics and reporting.
Modern field service platforms use augmented reality (AR) to perform tasks like information overlay, knowledge capture and training. Technicians can use AR to superimpose a digital twin of a machine they are repairing onto the physical machine. This approach can provide a technician with directions for the repair or maintenance work they are doing.
AR can also virtually connect technicians to an expert who can watch over the technician's shoulder as they work. Some tools have chatbots that automate repetitive tasks, such as customer notifications or scheduling job follow-up appointments.

FSM software can also use AI to analyze and draw insights from data repositories. For example, FSM software could analyze maintenance data and recommend preventative maintenance for a machine or product.
Some field service management providers combine field service management with other applications in a single offering. FSM can be paired with enterprise resource planning, enterprise asset management and CRM applications. Managing key performance indicators relating to service and support is also addressed.
Field service management system vendors
When evaluating FSM software options, be sure to check for AI capabilities, as these can dramatically enhance the overall capabilities of an FSM tool. FSM may also be a module within a larger CRM or similar system or can be available via cloud services.
The following is a brief list of some FSM vendors:
- BuildOps.
- Contractor Plus.
- FieldEdge.
- FieldEx.
- IFS Field Service Management.
- Jobber.
- Kickserv.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Field Service.
- Oracle NetSuite Field Service Management.
- Praxedo.
- Salesforce Field Service.
- SAP Field Service Management.
- Service Fusion.
- ServiceMax Core.
- ServiceNow Field Service Management.
- ServiceTitan.
- Zuper.
What are the benefits of field service management?
FSM software can be an asset to businesses in several ways, including the following:
- CX. FSM tools promote better CX by giving customers real-time insight into the work being done. It also lets them communicate directly with technicians and back-office personnel in real time, all of which helps the service company meet and exceed customer expectations.
- Efficiency. Companies can improve field service operations by letting technicians optimize work order routing and scheduling. FSM software also lets companies spend less time documenting details and increases the task completion rate and the timely resolution of issues.
- Flexibility. FSM software makes customer service activities more nimble. Management has more insight into the work process and CX using FSM tools, and they can coordinate jobs in ways that satisfy everyone.
- Increased productivity. Improved data insights and access to better back-office support through real-time communication enables field technicians to cut down on errors. These capabilities also improve technicians' first-time-fix rates and increase the quality and quantity of field operations work.
- Improved safety and compliance. Field service management tools enable technicians to attach digital proof of work to their work orders and preserve a compliance audit trail. This approach helps organizations comply with safety and other regulations.
- Reduced operational costs. Field service management tools digitize paper-based tasks, such as invoicing and data entry, lowering administrative costs.
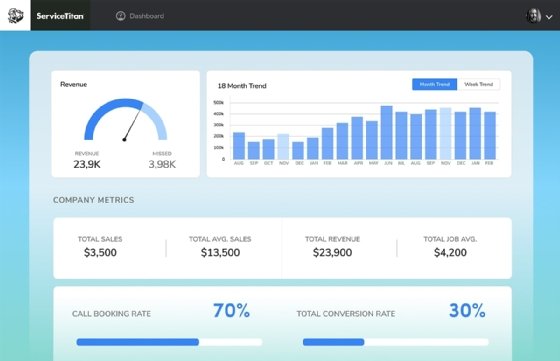
- Reporting and monitoring. FSM software provides technicians and back-office staff with easy-to-understand information about their jobs, improving service delivery and decision-making. Job completion rate and average revenue per job are examples of the types of metrics provided.
What are the challenges of field service management?
There are several challenges to field service management, including the following:
- Data availability. Technicians sometimes work in environments that have limited or no internet connectivity. In such cases, they must proactively store job-related data locally on a device so it can be accessed without an internet connection. A technician leaving a job to access data or having to make repeat visits can negatively affect customer satisfaction and quality of service.
- Difficulty adapting. Technicians may struggle with new FSM tools as they are introduced.
- Monitoring technicians. Field technicians working remotely, sometimes without internet connections, can be difficult to track and monitor.
- Tool integration. Organizations may have implemented multiple tools over time for different tasks as the services they provide developed. Those tools may not always be compatible with one another.
- Underutilized customer feedback. FSM apps collect customer data and feedback. However, this data can go to waste if staff cannot respond appropriately or don't collect the right kinds of CX metrics.
Industry use cases of field service management
Some examples of industries that use field service management are the following:
- Education. Field service applications can help with university facilities maintenance. Campus managers and technicians can use these tools to perform preventative maintenance and fix active problems. They can also help find new uses for unused campus space or other campus resources.
- Healthcare. Homecare employees use FSM software to track patient data. Field technicians may use it to repair and perform maintenance on remote medical devices.
- Hospitality. A field service application might be used to coordinate hotel maintenance jobs in ways that don't disturb guests, while still having visibility into all the building's assets.
- Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Technicians use field service management applications to schedule appointments and perform HVAC evaluations, maintenance and repairs with easy access to support.
- Industrial and manufacturing. Technicians are dispatched for preventive repair and maintenance on a wide variety of machines that FSM applications can help them diagnose and fix. They can also provide locations of service jobs and integrate with industrial IoT devices to provide predictive maintenance
- Postal and food delivery. FSM software is used to track deliveries and delivery drivers as they proceed along their routes. It may also be used to gather an inventory of deliveries.
- Telecommunications. Technicians installing cable and phone lines use FSM software to track work orders and service locations. Customers use it to schedule routine maintenance or installations.
Standards for field service management
Because of the increased importance of field service management, several standards have been developed. They provide important guidance in all aspects of the field service lifecycle -- for example:
- Contractor Plus Best Practices. Specifies 17 best practices optimized for contractors that are based on the company's FSM software.
- FieldEx Best Practices. Specifies 15 best practices to ensure optimal field service management that are based on the company's FSM software.
- Field Service Management Best Practices. Includes lists of best practices developed by individual vendors to provide best-in-class field service management.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001. Povides an international quality standard framework for performance that can be applied to FSM activities.
- ISO 20000-1. Describes the international standard for service management systems -- companion standards provide additional details on all aspects of planning, delivering and managing a service management system.
- ITIL Service Operation. Provides a set of 34 IT service and support standards from the Information Technology Infrastructure Library that includes field service operations and management.
- Service Capability & Performance Standards. Specifies 13 key attributes needed to manage a field service operation.
AI and field service management
Field service management capabilities can be greatly enhanced with AI. Among the ways AI can help are data analytics to provide greater service delivery insights, enhanced technician scheduling and tracking, and automation of repetitive tasks.
Learn how AI, machine learning and deep learning are being used to build next-generation field service IoT technology that understands and evaluates service situations in real time.







