What is enterprise risk management (ERM)?
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is the process of planning, organizing, directing and controlling the activities of an organization to minimize the harmful effects of risk on its capital and earnings. Enterprise risk management can include financial, strategic and operational risks, as well as risks associated with accidental losses and other issues.
ERM is an organizationwide strategy to identify and prepare for potential hazards. Risk management requires understanding and analyzing the possible risks an organization might face. As a result, the ERM process must be proportionate to the size or complexity of the organization. ERM is designed to manage and identify risks across an organization and its extended networks.
ERM is a holistic approach to managing risk, requiring a broad management-based approach. Rather than leaving risk management to individual business units, it promotes a unified strategy that supports long-term sustainability by aligning risk practices with broader organizational goals.
ERM implementation standards have been formalized through frameworks such as one developed by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, an industry group known as COSO that also maintains and updates an internal control framework. In some industries, industry and government regulatory bodies oversee organizations' ERM policies and procedures. In an increasing number of industries, boards of directors are required to review and report on the adequacy of risk management processes in their organizations.
Why is enterprise risk management important?
An ERM program can help increase awareness of business risks across an entire organization and instill confidence in strategic objectives. It can also improve compliance with regulatory and internal mandates and enhance operational efficiency through more consistent applications of processes and controls.
Enterprises benefit when they shift corporate culture from focusing on meeting IT compliance obligations to targeting overall risk reduction. This is because risk reduction relies heavily on visibility into the overall security of the organization.
Building a strategic ERM program forces businesses to put well-established practices in place, such as the following:
- A governance model that includes senior management -- as well as organizational elements, such as security, risk assessment and management, compliance, IT operations and legal -- among other business stakeholder areas.
- A strategy that incorporates internal policies and standards for all security and risk concerns, as well as operational focal areas, such as system configuration.
- Procedures that include internal and external risk threat and vulnerability management to monitor adversaries and risk exposure factors that can potentially influence the risks to the enterprise and its assets.
ERM is a continuous work in progress that needs to grow and evolve. Organizations must regularly revisit, revise and update all elements of the program.
What are the 5 key components of enterprise risk management?
Based on the COSO ERM framework, the five key components of ERM are the following:
- Governance and culture. This ERM component emphasizes the importance of leadership commitment and a supportive culture. It includes the organization's risk management philosophy, risk appetite, ethical values, integrity and personnel competence. This fundamental element dictates how risk is viewed and addressed throughout the organization.
- Strategy and objective-setting. This component integrates risk management into strategic planning processes. It ensures potential threats and opportunities are evaluated as part of decision-making. By establishing clear risk appetite definitions, organizations create boundaries that guide acceptable risk-taking activities across different business units and functions.
- Performance. This component highlights the importance of identifying, assessing, responding and reporting on risks that are linked to the achievement of strategy and business objectives. It ensures that the organization can achieve its objectives, while managing risks within its risk appetite.
- Review and revision. This ERM component emphasizes its continuous nature, requiring regular monitoring of the risk environment and performance to identify relevant changes. These changes might necessitate adjustments to the risk management approach, ensuring ongoing alignment with the organization's objectives and risk appetite.
- Information, communication and reporting. Effective communication is key to ERM, and this component focuses on ensuring that relevant information is identified, captured and communicated in a way that enables individuals to act. It also establishes effective information flow across the organization to support both decision-making and risk management efforts.
ERM implementation best practices
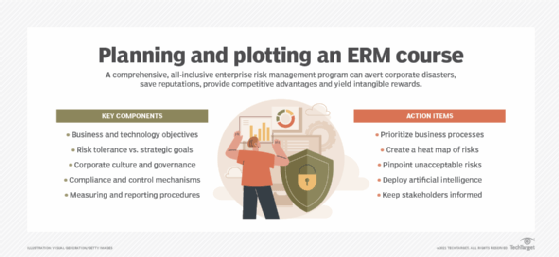
Best practices to follow when implementing ERM include the following:
- Define the program's scope. Identify and prioritize business processes and their related risks. This involves determining the parts of the organization and the types of risks that should be included. A well-defined scope helps to manage expectations and ensures a focused and manageable ERM process.
- Secure leadership buy-in. Strong support from the board of directors and senior management is crucial for providing resources and setting the tone for a risk-aware culture. Their engagement ensures buy-in and effective risk management across the organization, fostering a culture of shared risk responsibility.
- Establish a clear ERM framework. Develop a formal framework outlining the ERM approach, including roles, responsibilities, processes and methodologies. Many organizations adopt established frameworks, such as the COSO ERM framework or ISO 31000 from the International Organization for Standardization, which goes by the acronym ISO worldwide.
- Develop a blueprint. Use risk heat maps to determine which threats could jeopardize business objectives and critical strategies. That information should be shared and controls set to offset the risks.
- Devise an action plan. Create a risk treatment plan to pinpoint unacceptable risks and resolve risk gaps. This plan should outline specific tasks, assign responsibilities, set timelines and allocate necessary resources for implementing the chosen risk treatments. A well-defined action plan ensures that risk management strategies are translated into concrete steps.
- Digitally transform. Use AI and other advanced technologies to automate inefficient and ineffective manual processes, analyze large data sets, identify patterns and provide predictive insights into potential risks. For example, AI can be used in ERM initiatives to monitor real-time data for early warning signs of supply chain disruptions, cybersecurity threats and financial anomalies.
- Set up strong risk reporting. Develop a comprehensive risk reporting framework that provides clear and actionable information to decision-makers. This lets them make well-informed, risk-aware choices and ensures transparency in how risks are managed and mitigated.
- Monitor and measure. Establish risk profiles and key risk indicators to identify control deficiencies and evaluate how the ERM program is progressing, how it deviates from corporate policies and how many risk incidents occur.
How is ERM different from traditional risk management?
With traditional risk management processes, individual division heads typically make risk-based decisions. Each functional leader oversees risk management within their own silo. For example, the chief technology officer handles IT-related risks, the treasurer oversees financial risks and the chief operating officer manages risks related to production and distribution. This siloed approach focuses on minimizing risk at the lowest possible level, frequently resulting in a risk-averse culture that can limit innovation and growth opportunities.
Enterprise risk management requires a more holistic desiloed approach and elevates risk management to the board and executive levels to ensure leadership is actively engaged. Instead of managing risk in a siloed way, organizations adopt a companywide approach and create a portfolio of the most significant risks to an organization or objective. This process generates a top-down enterprise view of all significant risks that can impact an organization.
ERM also recognizes that some level of risk is inherent in pursuing strategic objectives. It emphasizes the importance of clearly defining the organization's risk appetite and cultivating a risk-aware culture that balances informed risk-taking with sound mitigation strategies.
In larger or more complex organizations, a traditional risk management approach can lead to several issues, including the following:
- Risks falling between silos. Some risks may be overlooked because no single leader is responsible for them.
- Risks affecting silos in different ways. A risk's significance might be underestimated if its effect varies across departments.
- Risks spreading across silos. A risk response in one area might inadvertently create risks in another.
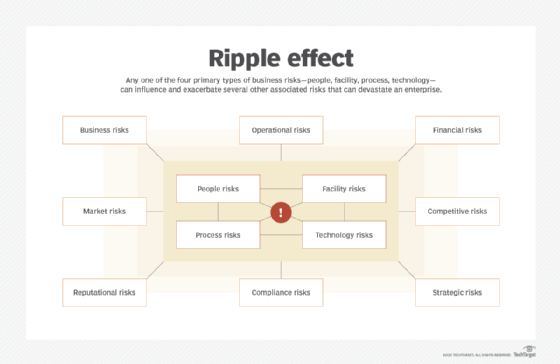
Risks addressed by ERM
Enterprise risk management addresses a broad spectrum of risks that affect an organization's ability to achieve its objectives. These risks are typically categorized into the following types:
- Strategic risks. These risks affect an organization's long-term goals and strategies, such as changes in the market, competitor actions and poor strategic decisions. For example, entering a new market without adequate research can expose a company to strategic risks.
- Operational risks. Operational risks arise from day-to-day activities, including process failures, technology issues, supply chain disruptions and human error. Effective internal controls and real-time incident tracking are essential for mitigating these risks.
- Financial risks. These relate to an organization's financial health, such as market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk and interest rate risk. Organizations must assess and manage these risks to maintain financial stability and profitability.
- Compliance risks. Failing to adhere to laws, regulations and internal policies increases an organization's risk exposure. For example, not managing compliance risk effectively can lead to legal penalties, financial losses and reputational damage.
- Reputational risks. These stem from potential damage to an organization's image or brand. For example, negative publicity, ethical breaches and product failures can negatively affect an organization's reputation.
- Technology risks. These involve threats to IT systems, data security and technological infrastructure. Organizations must conduct regular risk assessments and develop incident response frameworks to protect against these threats.
- Health and safety risks. These risks pertain to the health and safety of employees and other stakeholders. For example, workplace accidents, exposure to hazardous materials and public health emergencies can disrupt operations and harm individuals.
- External risks. These are risks outside the organization's control, such as natural disasters, economic downturns and geopolitical events.
What are the benefits of enterprise risk management?
ERM provides organizations with a host of potential benefits, including the following:
- Improved risk awareness. By creating a healthy risk culture, organizations can integrate risk evaluation into business and IT practices, improving risk management across the organization. For example, when risk awareness is embedded in the organizational culture, employees at all levels become more attuned to potential threats and opportunities. This approach leads to proactive consideration of risks during decision-making in both business operations and IT processes.
- Enhanced decision-making. ERM's standardized risk reporting supports long-term metrics, and measurement encourages better decision-making practices. These reports detail key risk indicators, mitigation strategies and emerging risks, so directors and executives can focus on critical risk areas. This leads to improved mitigation decisions and a deeper understanding of risk appetite, thresholds and tolerances.
- Better allocation of resources. ERM encourages a broader and more structured approach to identifying and assessing risks beyond traditional silos. By considering risks across categories, such as strategic, operational, financial, compliance and technological areas, organizations gain a more holistic understanding of their vulnerabilities and potential opportunities. This wider perspective provides better allocation of resources and the development of more comprehensive risk management processes. For example, companies might apply limited endpoint security licenses to the most exposed and critical systems.
- Enhanced compliance. ERM helps organizations coordinate and manage compliance with laws, regulations and internal policies, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage. This helps organizations operating under strict regulatory frameworks. In those cases, ERM provides a central framework to manage and coordinate compliance efforts across diverse business functions and objectives.
- Increased stakeholder confidence. A strong ERM framework demonstrates proactive risk management to stakeholders, including investors, regulators and customers. This transparency fosters trust and can enhance the organization's reputation.
What are the challenges of enterprise risk management?
There are also potential downsides to ERM, including the following:
- Increased initial expenditures. Capital and operational expenditures often increase initially because ERM programs can require expensive, specialized software and services and the engagement of external consultants or service providers to assist with the initial setup and training. These expenditures, while crucial for establishing an effective ERM system, can present a financial hurdle, particularly in the early stages of adoption.
- Siloed risk management practices. Many organizations maintain separate risk management functions for different areas, such as operational, financial and compliance risks. A siloed approach can lead to duplication of efforts, inefficiencies and a fragmented view of risks, making it difficult to understand interdependencies and respond effectively.
- Complex regulatory requirements. ERM initiatives increase emphasis on governance and complex regulatory environments, requiring business units to invest a significant amount of time in risk management. Maintaining compliance requires diligent efforts to stay updated on regulations and adapt risk management practices accordingly.
- Resistance to change. Organizations adopting ERM often encounter internal resistance, as employees and departments must alter their perspectives and approaches to risk management. This challenge is compounded by ineffective change management practices. Change management is essential for successful transformation, but it can lead to operational disruptions when not properly executed.
- Lack of buy-in and support. Leaders might struggle to reach a consensus on risk severity and metrics across all units of an enterprise. Without a strong commitment from senior leadership and a risk-aware culture, ERM efforts can falter.
- Lack of qualified personnel. Establishing an ERM program requires specialized knowledge and expertise. A shortage of qualified personnel can hinder the development and execution of effective strategies. To build a strong ERM framework, organizations must invest in training and hiring skilled professionals.
- Inadequate risk metrics and monitoring. Effective ERM requires reliable and relevant data to assess and track risks. However, many organizations lack the necessary tools and advanced analytics, making it difficult to collect, analyze and interpret data. This can hinder their ability to measure risk exposure and make informed decisions.
Who should manage ERM in an organization?
The board of directors and executive management are both in charge of determining what ERM process should be in place, as well as how ERM across the organization should function. More specifically, an organization's top management is responsible for designing and implementing the ERM process, while the board of directors is responsible for providing oversight. This oversight includes the understanding and approval of ERM processes and overseeing identified risks to ensure responses are within the stakeholders' risk appetite.
The role of a chief risk officer (CRO) is central to overseeing ERM. The CRO is in charge of identifying, analyzing and mitigating risks that impact the organization as a whole. The CRO also ensures that an organization complies with any government regulations. More granular roles in the process fall on other C-level positions and staff.
Enterprise risk management in action
ERM takes a companywide view of risks and opportunities. It requires teamwork across departments and guidance from top leaders. The following are some real-world ERM examples:
- Financial services. Banks and insurance companies use ERM to manage credit, market and operational risks, ensuring they remain solvent and compliant with regulations. For instance, they might use scenario analysis to understand the effects of economic downturns on their loan portfolios.
- Healthcare. Hospitals apply ERM to address patient safety risks, regulatory compliance and operational disruptions. This could involve using protocols to prevent medical errors or having contingency plans for emergencies.
- Manufacturing. Manufacturing companies use ERM to manage supply chain risks, production disruptions and quality control issues. For example, a car manufacturer might monitor its suppliers' financial health and geographical locations to anticipate potential disruptions.
- Technology. Tech firms use ERM to handle cybersecurity risks, data privacy concerns and the risks associated with rapid innovation and market changes. This might include executing strong security measures or having incident response plans for data breaches.
- Energy. Companies in the energy sector use ERM to manage volatile commodity prices, environmental regulations and operational safety. For example, an oil and gas company could assess the risks associated with drilling in certain regions and plan for potential environmental effects.
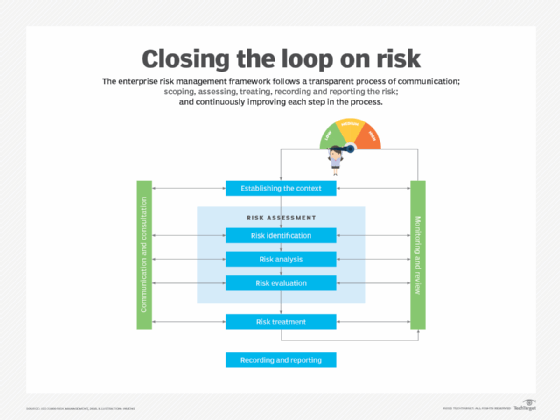
ERM frameworks
Enterprise risk management frameworks come in many formats. For some companies, adherence to ERM might be mandated by compliance and regulatory requirements. For other businesses, these frameworks might be useful in shaping and defining ERM in its early stages of development and implementation. Common frameworks include the following:
- COSO ERM framework. As mentioned previously, the COSO ERM framework defines essential ERM components, as well as key ERM principles and concepts, while also providing clear direction and guidance for ERM.
- ISO 31000:2018. ISO 31000:2018, the current version of ISO's standard, provides documents and principles, as well as a framework and a process for managing risk. The framework identifies opportunities and threats, as well as methods to effectively allocate resources for risk treatment. It applies to any organization and aims to integrate risk-based decision-making into governance, planning, management, reporting, policies, values and culture.
- BS ISO 31000:2018. This British Standard is the U.K. adoption of the ISO framework. Similarly, the American National Standards Institute offers a U.S. version of ISO 31000 that's published by the American Society of Safety Professionals.
- NIST Risk Management Framework. Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework outlines a seven-step process for organizations to manage information security and privacy risk. The RMF contains a suite of NIST standards and guidelines that support the implementation of risk management programs.
- COBIT 2019. Formally known as Control Objectives for Information Technologies, COBIT is an IT governance and management framework developed by the ISACA professional association. COBIT 2019, the current version, provides guidance and tools focused on managing IT-related enterprise risks in alignment with overall business goals and other ERM practices.
- RIMS Risk Maturity Model. Offered by the Risk and Insurance Management Society, this is a best-practice framework that helps organizations assess the maturity of their ERM capabilities across several key attributes. It provides a roadmap for improvement from an ad hoc to a leadership level.
ERM tools and software considerations
When evaluating an ERM tool, organizations should consider a product that provides the following features and attributes:
- Integration. The ERM tool should integrate with other technologies for real-time data exchange.
- Analytics. The right data analytics and reporting features are needed to identify relevant trends, patterns and anomalies in an organization's data sets.
- Customization. The tool should be customizable to align with the organization's risk management strategy.
- Regulatory compliance. Tools should update to changing regulations that might affect business operations.
- Cost-effectiveness. The chosen tool needs to remain financially viable, so check those factors as well.
Informa TechTarget's own research has identified the following often used ERM tools:
- Archer. This integrated risk management suite provides tools for enterprise, operational, IT, security and third-party risk management. It's also used for regulatory compliance; management of environmental, social and governance programs; and other risk-related functions. Archer Engage is a risk reporting and data collection application that provides a unified user experience for business users and risk management teams. Archer Insight is a risk quantification tool.
- AuditBoard. The core focus of this cloud-based platform has been to streamline audit and compliance processes for companies required to meet complex regulations. The company has expanded into other aspects of risk management. AuditBoard ITRM for IT risk management focuses on IT security risks and support for collaboration among security teams, risk managers and business users.
- IBM OpenPages. This AI-enabled governance, risk and compliance (GRC) platform supports risk management, regulatory compliance and data governance programs. IBM acquired OpenPages in 2010 to expand its business analytics offerings into compliance and risk management processes. It has since integrated the software into IBM Cloud Pak for Data, a set of cloud-based tools for organizing, managing and analyzing data. OpenPages is designed to help organizations centralize siloed risk management initiatives. It includes GRC and ERM tools for managing risks that might appear in IT governance, data privacy and financial controls.
- LogicManager. This cloud-based ERM tool is designed to help organizations understand, monitor and mitigate risks across the enterprise. Its features include a centralized platform for risk identification, assessment and analysis, as well as automated workflows for risk management processes. It also offers reporting and dashboards with insights into risk exposure, compliance and audit management tools, and the ability to connect risks to controls, policies and other business elements.
- MetricStream. Built on a scalable GRC platform, MetricStream streamlines risk management processes, enhances visibility into risk exposure and facilitates informed, risk-aware decisions. It provides a centralized platform for risk management, compliance management, audit management, and strong reporting and analytics with dashboards for real-time insights.
Learn more about the skills and roles involved in ERM, such as those in C-level roles.