What is compliance risk?
Compliance risk is an organization's potential exposure to legal penalties, financial forfeiture and material loss, resulting from its failure to act in accordance with industry laws and regulations, internal policies or prescribed best practices. Compliance risk is also known as integrity risk.
Organizations of all types and sizes are exposed to compliance risk, whether they are public or private entities, for-profit or nonprofit, state or federal. An organization's failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations can affect its revenue, leading to a loss of reputation, business opportunities and valuation.
Organizations must manage compliance risk effectively to avoid any of these potential consequences. By doing so, they can identify gaps in their current risk compliance framework and implement the necessary procedures to ensure compliance.
Types of compliance risk
An organization might be implicated in the following types of compliance risks:
- Corrupt and illegal practices. Legal compliance requires that organizations, agents and employees follow all laws and regulations relevant to their industry. Common compliance risks in this category include fraud, theft, bribery, money laundering and embezzlement. Recent regulatory changes have tightened enforcement in sectors including finance, healthcare and technology, increasing penalties for these violations.
- Privacy breaches. Privacy-related compliance risks have intensified with evolving data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act in the U.S. Noncompliance can lead to substantial penalties and legal action. Furthermore, companies handling sensitive data must implement cybersecurity protocols, including encryption and multifactor authentication (MFA), to protect against hacking and data breaches.
- Environmental concerns. These compliance risks deal with pollution and environmental damage an organization's operations can cause. Examples include the destruction of natural habitats, use of harmful chemicals, hazardous waste disposal and pollution of groundwater. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks encompass factors such as environmental impact, labor practices, corporate ethics and diversity policies. Organizations face ESG-related compliance risks if they fail to meet emerging standards in these areas, as regulatory bodies and stakeholders increasingly hold companies accountable for sustainable and ethical practices. In response to increasing regulatory requirements, many companies now integrate sustainability goals into their compliance strategies, aiming to reduce carbon footprints and promote eco-friendly practices.
- Process risks. A process risk is a failure to follow an established procedure for completing a task or a deviation from the standard process. For example, a company must have a documented procedure for accessing its network remotely. Failure to uphold these standards can expose the company to legal and financial penalties, especially in highly regulated industries like banking and healthcare.
- Workplace health and safety. Companies are legally required to follow specific health and safety protocols. For example, in the U.S., the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, OSHA, imposes standards that companies must meet to ensure a safe workplace, with stringent penalties for noncompliance. Likewise, the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) enforces workplace standards across the EU, focusing on employee well-being and injury prevention.
What is compliance risk management?
Compliance risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and mitigating potential losses that might arise from an organization's noncompliance with laws, regulations, standards, and both internal and external policies and procedures. Management practices are intended to help organizations maintain compliance with various regulations and laws. A strong compliance risk management program includes ongoing training, regular risk assessments and proactive monitoring to detect emerging threats and regulatory changes.
Organizations need to be aware of their compliance risk on several levels -- not just from the perspective of the chief compliance officer. While the CCO and other compliance staff are responsible for reviewing all aspects of the organization's compliance risk -- including its legal, regulatory, financial and technical risks -- the compliance risk extends to all levels of the organization, including IT. Incorporating IT and cybersecurity measures is increasingly critical, as data breaches and cyberattacks can lead to severe compliance violations.
Compliance risk management forms a portion of the collective governance, risk and compliance (GRC) discipline. GRC is a set of management practices and technologies designed to ensure that an organization is operating in a manner consistent with its values, mission and risk tolerance. GRC tools and technologies are evolving, enabling companies to automate compliance processes, generate real-time compliance reports and streamline regulatory change management. Industries such as finance and healthcare, which face intense regulatory scrutiny, have increasingly adopted these GRC measures.
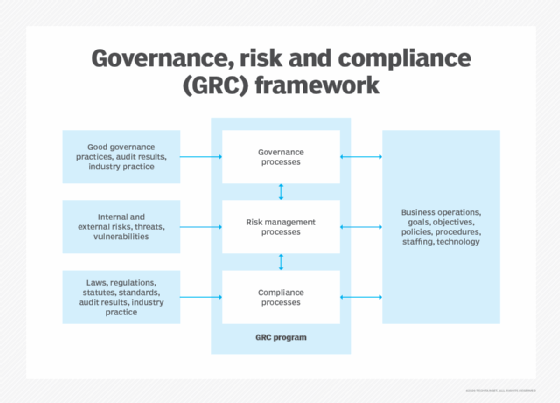
Compliance risk examples
In the U.S., corporate compliance is usually tied to applicable laws and regulations. For example, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) applies to publicly traded companies, whereas the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act pertains to companies that have publicly traded stock. Both FCPA and SOX are enforced by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and other authorities. Other compliance laws, such as the Anti-Money Laundering Act, demand transparency in financial transactions to prevent criminal activity. Compliance with these laws requires extensive record-keeping, periodic compliance audits and adherence to ethical standards.
There are also various compliance risks and requirements in healthcare. Enacted in 1996, HIPAA is a significant U.S. federal law that plays a vital role in safeguarding protected health information (PHI). Proposed amendments to HIPAA in 2025 include mandatory annual compliance audits for healthcare institutions and MFA for access to electronic PHI.
Cloud and data compliance
The adoption of cloud technologies has introduced new compliance challenges. Organizations must verify that cloud providers meet regulatory standards, particularly for data protection and privacy.
Compliance can be compromised if unauthorized employees access cloud data or if data residency requirements are neglected. The most reputable providers offer encryption and data localization options to address these concerns.
The importance of compliance training and culture
Creating a strong culture of compliance within an organization is essential for effective compliance risk management. This involves regular, comprehensive training programs that educate employees on the latest regulatory compliance standards, company policies and their specific roles in maintaining compliance.
A culture that prioritizes ethical behavior and accountability at all levels helps reinforce compliance standards and reduces the likelihood of violations. In addition, effective compliance training minimizes human errors, which are often a significant source of compliance breaches.
The International Organization for Standardization provides guidance on risk management and compliance in various industries, which can also be invaluable for employee training. As more countries adopt stringent compliance requirements, organizations must ensure their policies and practices align with these international standards to avoid legal repercussions and protect their global reputation.
What is a compliance risk assessment?
A key concept of compliance risk management is the risk assessment process, which includes identifying and evaluating the potential risks that threaten an organization's ability to ensure compliance with laws and regulations. A thorough compliance risk assessment involves analyzing external factors, such as regulatory changes, and internal factors, such as operational vulnerabilities. Furthermore, organizations can use compliance software tools to streamline risk assessment and monitor compliance in real time.
Following a compliance risk assessment, an organization can determine its level of compliance and reveal what changes need to be made to improve. It uses this information to create and implement a compliance risk management strategy that helps ensure compliance with laws.
For example, the assessment might reveal that the organization requires more secure procedures regarding remote work. The organization can plan to address this weakness by implementing more thorough remote work policies.
Developing a compliance risk mitigation strategy
A proactive compliance risk mitigation strategy enables organizations to manage risks systematically. Key elements of this strategy include the following:
- Establishing a strong compliance policy framework.
- Conducting regular audits and assessments.
- Implementing real-time monitoring systems.
- Ensuring ongoing employee training.
In addition, organizations should establish clear channels for reporting compliance issues and foster an environment where employees feel comfortable raising concerns. Developing a structured, adaptable compliance program ensures that the organization can navigate regulatory changes and mitigate risks effectively.
The role of technology in managing compliance risk
Technology plays a critical role in streamlining compliance risk management processes, particularly through the use of AI, machine learning and robotic process automation. These tools enable organizations to automate compliance monitoring, conduct real-time risk assessments and flag potential risks before they escalate.
Compliance management software also provides advanced reporting and analytics, helping compliance teams make informed, data-driven decisions. By using technology, organizations can better manage complex regulatory requirements and improve their response to emerging risks.
With persistent geopolitical and economic concerns, organizations are realizing they need stronger risk management initiatives. Learn more about the trends reshaping enterprise risk management.







