What is risk management? Importance, benefits and guide
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and controlling threats to an organization's capital, operations and financial performance. These risks stem from various sources, including economic fluctuations, financial uncertainties, legal liabilities, technology issues, management errors, workplace accidents and natural disasters.
A successful risk management program helps an organization consider the full range of risks it faces. Risk management also examines the relationship between different types of business risks and the cascading impact they could have on an organization's strategic goals.
Because of its emphasis on understanding and managing risk across an organization, this holistic approach is called enterprise risk management. In addition to a focus on internal and external risk threats, ERM emphasizes the importance of managing positive risks. These are opportunities that could increase business value or, conversely, damage an organization if not taken, as the companies disrupted by Amazon, Netflix and other born-digital powerhouses can attest.
Indeed, the aim of any risk management program is not to eliminate all risk but to make smart risk decisions.
"We don't manage risks so we can have no risk. We manage risks so we know which risks are worth taking, which ones will get us to our goal," said Forrester Research principal analyst Alla Valente, who specializes in ERM; governance, risk and compliance (GRC); and other risk-related topics.
This guide to risk management provides a comprehensive overview of the key concepts, requirements, tools and trends driving this dynamic field. It also offers guidance for risk and business leaders on the risk management process and how to implement an ERM program. Throughout, hyperlinks connect to other articles that deliver more in-depth information on the topics covered here.
Why is risk management important?
Risk management is critical to business success -- arguably more so now than ever before. The risks that modern organizations face have grown more complex, fueled by the rapid pace of globalization. New risks constantly emerge, often related to the now-pervasive use of technology. Climate change has been dubbed a "threat multiplier" by risk experts. Many organizations are still grappling with some of the risks posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. That includes the ongoing need to manage remote or hybrid work environments and what can be done to make supply chains less vulnerable to disruptions.
As a result, a risk management program should be intertwined with organizational strategy. To link them, risk management leaders must first define the organization's risk appetite -- that is, the amount of risk it's willing to accept to realize its business objectives. Some risks will fit within the risk appetite and be accepted with no further action necessary. Others will be mitigated to reduce the potential negative effects, shared with or transferred to another party, or avoided altogether.
In many companies, business executives and the board of directors have recognized the need for more effective risk management and are taking a fresh look at their programs. Organizations are reassessing their risk exposure and risk appetite, examining risk processes and reconsidering who should be involved in risk management. Companies that previously took a reactive approach to risk management -- guarding against past risks and changing practices only after a new risk causes harm -- are seeking the competitive advantages of a more proactive ERM approach. There's heightened interest in supporting business sustainability, resiliency and agility through risk management initiatives. Companies are also exploring how AI technologies and sophisticated GRC platforms can improve risk management.

Risk management in financial services vs. other industries
Many experts note that managing risk is a formal function at companies that are heavily regulated and have a risk-based business model. Banks and insurance companies, for example, have long had large risk departments typically headed by a chief risk officer (CRO), a title still relatively uncommon outside of the financial industry. Moreover, the risks that financial services companies face tend to be rooted in numbers. Therefore, they can be quantified and effectively analyzed using known technology and mature methods. Risk scenario modeling and scenario analysis can be done with some precision.
For other industries, risk tends to be more qualitative. That increases the need for a deliberate, thorough and consistent approach to risk management, said Gartner practice vice president Matt Shinkman, who leads the consulting firm's risk management and audit practices. "Enterprise risk management programs aim to help these companies be as smart as they can be about managing risk."
Risk management process
One of the best-known risk management resources is the ISO 31000 standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization, which goes by the acronym ISO worldwide. ISO 31000:2018, the standard's current version, outlines a risk management process that can be used by any type of entity and includes the following core steps:
- Identify the risks faced by your organization.
- Analyze the likelihood and possible impact of each one.
- Evaluate and prioritize the risks based on business objectives.
- Treat -- or respond to -- the risk conditions.
- Monitor the results of risk controls and adjust as necessary.
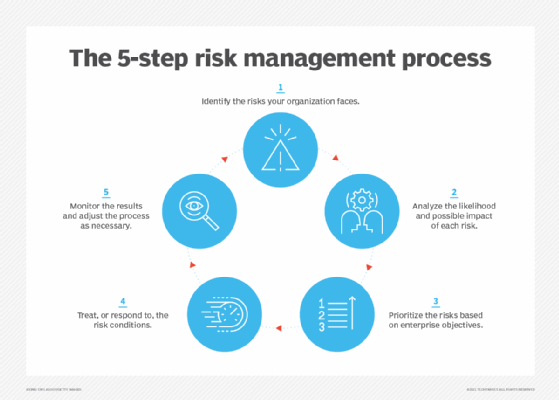
These steps sound straightforward, but risk management committees set up to lead initiatives shouldn't underestimate the work required to complete the process. For starters, a solid understanding of what makes the organization tick is needed. To obtain that, the ISO 31000 process also includes an upfront step to establish the scope of risk management efforts, the business context for them and a set of risk criteria. The goal is to know how each identified risk relates to the maximum risk the organization is willing to accept and what risk management actions should be taken to preserve and enhance organizational value. Developing an internal communication plan is another key foundational step.
Document business impacts and create a risk register
By definition, something is only a risk if it has a potential business impact, said Greg Witte, president of advisory services firm Palydin LCC and an architect of frameworks developed by NIST on cybersecurity, privacy, workforce and other risks.
In identifying risk scenarios, many risk management committees find it useful to take a combined top-down and bottom-up approach, Witte said. In the top-down exercise, leadership identifies the organization's mission-critical processes and works with internal and external stakeholders to determine the conditions that could impede them. The bottom-up perspective starts with the threat sources -- cyberattacks, economic downturns, earthquakes, etc. -- and considers their potential impact on critical assets.
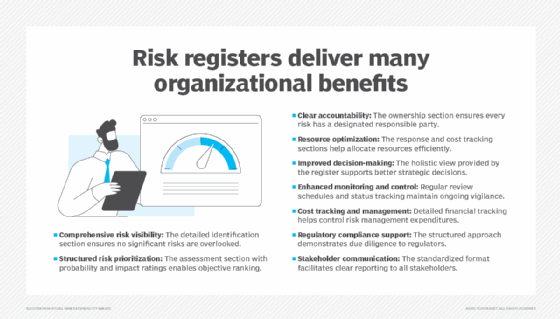
Organizations typically record their findings in a risk register, which helps track the risks through the subsequent steps of the risk management process. Risk registers include information about the likelihood of different risks affecting an organization and their potential business impact. They also document risk response plans, risk owners and stakeholders, and the cost of managing risks. A downloadable risk register template can be found in the article linked to above.
Risk management standards and frameworks
As government and industry compliance rules have expanded over the past two decades, regulatory and board-level scrutiny of corporate risk management practices have also increased. That makes risk analysis, internal audits, risk assessments and other risk management functions a major component of business strategy. How can an organization put this all together?
Risk management frameworks developed by standards bodies and other entities can help. Here's a sampling of them, starting with brief descriptions of the two most widely recognized ones, ISO 31000 and the COSO ERM framework offered by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, better known as COSO:
- COSO ERM framework. Launched in 2004, this was updated in 2017 to address the increasing complexity of ERM and highlight the importance of embedding risk considerations into business strategies and of linking risk management and operational performance. It's part of a group of complementary COSO frameworks that also includes an internal control one, first published in 1992, and a new corporate governance framework that's currently in draft form. The risk management one defines key ERM concepts and principles, suggests a common ERM language and provides clear directions for managing risk. Developed by consulting firm PwC with input from COSO's five member organizations and external advisors, the updated framework is a set of 20 principles organized into these five interrelated components of a risk management program:
-
- Governance and culture.
- Strategy and objective-setting.
- Performance.
- Review and revision.
- Information, communication and reporting.
- ISO 31000. Released in 2009 and revised in 2018, the ISO standard includes a list of ERM principles, a framework to help organizations apply risk management mechanisms to operations, and the process detailed above for identifying, evaluating and mitigating risks. Developed by ISO's risk management technical committee with input from ISO national member bodies, ISO 31000:2018 is a shorter and more concise document than its predecessor and includes more strategic guidance on ERM. The newer version also emphasizes the important role of senior management in risk programs and the integration of risk management practices throughout the organization.
Some national standards bodies and groups have also released country-specific versions of ISO 31000. For example, the American National Standards Institute offers a version that's overseen by the American Society of Safety Professionals. Likewise, the British Standards Institution offers a U.K. version along with BS 31100, a risk management code of practice that provides a process for implementing concepts described in ISO 31000:2018 -- including functions such as identifying, assessing and responding to risks, and then reporting on and reviewing risk management activities.
Other frameworks that focus specifically on IT and cybersecurity risks are also available. They include NIST's Risk Management Framework, which details a seven-step process for integrating information security and data privacy risk management initiatives into the system development lifecycle. There's also the ISACA professional association's COBIT 2019, an information and technology governance framework that supports IT risk management efforts.
In addition, various risk maturity models can be used to benchmark risk management capabilities and assess their maturity levels. The most prominent one is the Risk and Insurance Management Society's Risk Maturity Model (RMM), which was developed in 2005 with software vendor LogicManager and updated in 2022. The revamped RMM helps risk professionals assess their programs in five categories: strategy alignment; culture and accountability; risk management capabilities; risk governance; and analytics. Other risk maturity models are available from the ProSight Financial Association and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development's Forum on Tax Administration.
The three lines model developed by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) offers another type of standardized approach to support governance and risk management initiatives. Originally called the three lines of defense before being renamed in 2020, the IIA's model outlines the different roles that business executives, risk and compliance managers and internal auditors should play in risk management efforts. It also calls for a governing body to provide oversight and accountability.
Traditional risk management vs. enterprise risk management
Traditional risk management often gets a bad rap compared to enterprise risk management. Both approaches aim to mitigate risks that could harm organizations. Both involve buying insurance to protect against a range of risks, from losses due to fire and theft to cybersecurity liability covered by cyber insurance. Both adhere to guidance provided by major standards bodies. But traditional risk management, experts argue, lacks the mindset and mechanisms required to understand risk as an integral part of enterprise strategy and performance.
Risk averse is another trait of organizations with traditional risk management programs. For many companies, "risk is a dirty four-letter word -- and that's unfortunate," Valente said. "In ERM, risk is looked at as a strategic enabler versus the cost of doing business."
"Siloed" vs. holistic is one of the big distinctions between the two approaches, according to Shinkman. In traditional programs, managing risk has typically been the job of the business leaders in charge of the units where the risk resides. For example, the CFO is responsible for managing financial risk, the COO for operational risk, the chief compliance officer for compliance risk and so on.
Departments and business units might have sophisticated systems in place to manage their various types of risks. But Shinkman explained that a company can still run into trouble by failing to see the relationships among risks or their cumulative impact on business operations. It's difficult to successfully manage strategic risks that could prevent the organization from achieving its overall business goals. Traditional risk management also tends to be reactive.
In enterprise risk management, managing risk is a collaborative, cross-functional and big-picture effort. An ERM team debriefs business unit leaders and staff about risks in their areas and helps them think through the risks. The team then collates information about all the risks and presents it to senior executives and the board. Having credibility across the enterprise is a must for ERM leaders, Shinkman said.
These types of risk managers increasingly come from a consulting background or have a "consulting mindset," he said, and they possess a deep understanding of the mechanics of business. In addition, the chief risk officer or other head of an enterprise risk management team commonly reports to the CEO -- an acknowledgement that managing risk is part and parcel of business strategy.
Forrester makes a distinction between the "transactional CROs" typically found in traditional risk management programs and the "transformational CROs" who take an ERM approach. The former work at companies that see risk management as an insurance policy, according to Forrester. Transformational CROs focus on their company's brand reputation, understand the horizontal nature of risk and view ERM as a way to enable the "proper amount of risk needed to grow," as Valente put it.
Risk management glossary
Many terms are used to define the various aspects and attributes of risk management. Click on the hyperlinks below to learn more about some useful terms to know.
What is residual risk? How is it different from inherent risk?
What is a risk profile? Definition, examples and types
What are the benefits of risk management?
Effectively managing risks brings many benefits to an organization, including the following:
- Increased risk awareness across the organization.
- More confidence in organizational objectives and goals because risk is factored into strategy.
- Better and more efficient compliance with regulatory and internal mandates.
- Improved operational efficiency through more consistent application of risk processes and controls.
- Improved workplace safety and security.
- A competitive advantage over business rivals with less mature risk management programs.
What are the challenges of risk management?
Risk initiatives also present various challenges, even for companies with mature GRC and risk management strategies. The following are some of the challenges risk management teams should expect to encounter:
- Expenditures go up initially, as risk management programs can require expensive software and services, plus the hiring of risk management practitioners.
- The increased emphasis on risk governance also requires business units to invest time and money to comply with the risk management policy.
- Reaching consensus on the severity of risk and how to treat it can be complicated and contentious, sometimes leading to risk analysis paralysis.
- It's difficult to demonstrate the value of risk management to executives without being able to give them hard ROI numbers.
- The breadth of the risk categories managed in an ERM program can be daunting. Some other examples include data risk, which involves sensitive information that needs to be safeguarded, and conduct risk, which covers potential illegal or unethical actions by a company and its employees. Human risk management addresses another category that's related to conduct risk but aims to prevent cybersecurity incidents caused by the behavior of executives or workers.
How to build and implement a risk management plan
A risk management plan describes how an organization will manage risk. It lays out the organization's approach to identifying, assessing, responding to and monitoring risks. Other common elements include the roles and responsibilities of risk management teams, resources that will be used in the risk management process, documentation measures, and internal risk policies and procedures. Organizations that don't develop a formal plan for managing risk "essentially leave their success to chance," said Donald Farmer, principal at advisory services firm TreeHive Strategy.
ISO 31000's overall seven-step process is a useful guide to follow for developing a plan and then implementing an ERM framework, according to Witte. Here's a more detailed rundown of its components:
- Communication and consultation. Raising risk awareness is an essential part of risk management. The communication plan developed by risk leaders must effectively convey the organization's risk policies and procedures to employees and other relevant parties. This step sets the tone for risk-related decisions at every level.
- Establishing the scope and context. This step requires defining both the organization's risk appetite and risk tolerance. The latter term refers to how much the risks associated with specific initiatives can vary from the overall risk appetite. Factors to consider here include business objectives, company culture, regulatory requirements and the political environment, among others.
- Risk identification. This step defines the risk scenarios that could have a positive or negative impact on the organization's ability to conduct business. Effective risk identification is a crucial part of proactively managing risks. As noted above, the resulting list should be recorded in a risk register and kept up to date.
- Risk analysis. The likelihood and potential impact of each risk are analyzed to help sort the various risks for management. Making a risk heat map can be useful here. Also known as a risk assessment matrix, it provides a visual representation of the nature and impact of risks. An employee calling in sick, for example, is a high-probability event that has little or no impact on most companies. An earthquake is an example of a low-probability event with high-risk impact.

- Risk evaluation. Here is where the organization assesses risks and decides how to respond to them through the following approaches:
- Risk avoidance, when the organization seeks to eliminate the potential risk.
- Risk mitigation, in which the organization takes actions to limit or optimize a risk.
- Risk sharing or risk transfer, which involve contracting with a third party (e.g., an insurer or a supplier) to bear some or all costs of a risk, if it occurs.
- Risk acceptance, when a risk falls within the organization's risk appetite and tolerance levels and is accepted without taking any risk reduction measures.
- Risk treatment. This step involves applying the risk controls and procedures agreed upon during the evaluation phase.
- Monitoring and review. Are the risk controls and treatment actions working as intended? Can they be improved? To answer those questions as part of an ongoing review process, risk monitoring activities should measure the performance of risk management efforts and examine key risk indicators that might trigger a change in strategy.

Risk management best practices
ISO 31000's eight principles of risk management are also a good starting point for organizations on best practices for managing risk. According to the ISO standard, a risk management program should meet the following objectives to help create and protect business value:
- Be integrated into overall organizational processes.
- Be systematic, structured and comprehensive.
- Be based on the best available information.
- Be tailored to individual projects.
- Account for human and cultural factors, including potential errors.
- Be transparent and all-inclusive.
- Be dynamic and adaptable to change.
- Be continuously monitored and improved upon.
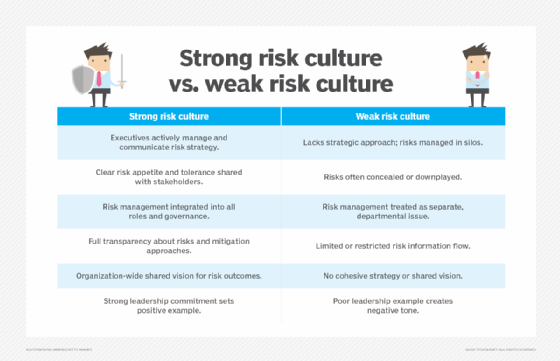
A key first step is creating a strong risk culture in an organization. Doing so shapes how risks are managed enterprise-wide and helps ensure that everyone, from senior executives to operational workers, knows their risk management responsibilities. Actions to take in developing a risk culture include setting an overall risk management strategy, integrating risk considerations into strategic planning and business operations, training employees on the risk management process and rewarding them for successful risk initiatives.
Writing a risk appetite statement for the organization is another important to-do item. Such statements document acceptable risk levels in different risk categories, commonly using a low-medium-high format or a variation on those terms. They also explain how the designated risk levels align with business goals and priorities. The article linked to above includes a downloadable template that can be used as a guide for structuring a risk appetite statement.
Increasingly, organizations are also using AI and other advanced technologies to automate inefficient and ineffective manual processes. For example, Farmer said AI can identify risk-related issues in real time or predict them before they arise, helping to enable proactive risk management. In addition, risk monitoring and reporting tasks can be automated, freeing up risk managers to do higher-level work. ERM and GRC platforms that include AI tools and other features are available from various risk management software vendors. Organizations can also take advantage of open source GRC tools and related resources.
Examples of risk management mistakes and failures
Risk management failures are often chalked up to willful misconduct, gross recklessness or a series of unfortunate events no one could have predicted. But an examination of common risk management failures shows that risk management gone wrong is more often due to avoidable missteps -- and run-of-the-mill profit-chasing. Here's a rundown of some mistakes to avoid.
Poor governance
The tangled tale of Citibank accidentally paying off a $900 million loan to Revlon's lenders in 2020 when only a small interest payment was due shows how even one of the largest banks in the world can mess up risk management -- despite having multiple controls and updated policies for COVID-19 pandemic work conditions in place. While human error and clunky software were involved, a federal judge ruled that poor governance was the root cause. An appeals court later overturned the judge's order that the bank wasn't entitled to refunds from the lenders. Nonetheless, two months after the erroneous payment, Citibank was fined $400 million by U.S. regulators for "longstanding" governance failures and agreed to overhaul its internal risk management, data governance and compliance controls.
Inadequate oversight
A lack of attention from senior executives and the board can also result in risk management shortcomings with serious business consequences. After Silicon Valley Bank failed in 2023, a report by the inspector general for the Federal Reserve System's Board of Governors said the bank's management "emphasized growth and failed to implement the controls necessary to effectively mitigate the risks associated with significant growth and concentrations." The latter referred to the bank's narrow customer base and large numbers of both uninsured deposits and investments in long-term securities. The board and senior management "failed to appreciate the significance of the multiple layers of risks," the report added. It might not have helped that the bank's CRO position was vacant for the last eight months of 2022.
Overconfidence on risk initiatives
Having too much faith in risk management processes is another big mistake. Misjudging how effective they are can come back to bite a company if risk isn't properly managed and an unexpected business crisis develops. Overconfidence can also manifest itself in another way: business managers and other workers putting too much stock in their ability to avoid or deal with risks. A common example is financial traders thinking they can handle risky trading strategies that blow up in their face -- and their employer's.
Overemphasis on efficiency vs. resiliency
Greater business efficiency can lead to bigger profits when all goes well. However, doing things quicker, faster and cheaper can result in a lack of resiliency. "When we look at the nature of the world … things change all the time," Forrester's Valente said. "Efficiency is great, but we also have to plan for all of the what-ifs."
Lack of transparency
Hiding data, a lack of data and siloed data can all cause transparency issues in risk management. A prominent example involves software vendor SolarWinds: Following the massive backdoor attack against its customers that was discovered in 2020, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filed a lawsuit in 2023, charging that the company and its CISO misled investors by understating or failing to disclose known security risks. In July 2024, a federal judge dismissed the SEC's claims about post-attack disclosures but ruled that charges related to statements before the attack could proceed. Twelve months later, the SEC said the parties had agreed in principle to settle the case, which would eliminate the threat of legal consequences for SolarWinds. Avoiding transparency problems requires an ERM strategy with common risk terminology, documented processes, and centralized collection and management of key risk data.
Risk analysis limitations
Many risk analysis techniques, such as creating a risk prediction model or a risk simulation, require gathering large amounts of data. Extensive data collection can be expensive and isn't guaranteed to be reliable. Furthermore, the use of data in decision-making processes can have poor outcomes if simple indicators are used to reflect complex risk situations. In addition, applying a decision intended for one aspect of a project to the whole project can lead to inaccurate results. Software programs developed to simulate events that might negatively affect a company can be both helpful and cost-effective, but they also require highly skilled personnel to accurately understand the generated results.
Illusion of control
Risk models can give organizations the false belief that they can quantify and regulate every potential risk. This could cause an organization to neglect the possibility of novel or unexpected risks.
Risk management for career professionals
The following articles provide resources for risk management professionals:
What is a risk management specialist, and what does one do?
Risk management trends: What's on the horizon?
A look at the trends reshaping risk management shows that the field is brimming with new ideas and requirements. Prominent among the latter is the growing need to manage AI-related risks in organizations -- the flip side of AI's growing role in risk management. Those risks include the following notable examples:
- Potential bias in AI algorithms.
- Delusional results, such as the hallucinations that generative AI tools often produce.
- Unethical or illegal use of AI tools.
- Unintended consequences from AI applications.
- Potential liability for AI-driven errors.
Because of incidents such as the SolarWinds attack as well as the supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic, recent wars and the Trump administration's tariff policy, there's also an increased focus on third-party risk management. It involves managing risks that stem from an organization's interactions with -- and reliance on -- various business partners providing products or services.
The third-party category encompasses both supply chain risk management, which deals with risks at suppliers, and vendor risk management, which focuses on IT vendors and other companies that sell finished goods. There's also fourth-party risk management, which addresses risks associated with the suppliers, vendors, subcontractors and service providers used by third parties.
More organizations are connecting their risk management initiatives and environmental, social and governance (ESG) programs, too. That's making sustainability risk management and efforts to address other kinds of ESG risks a higher priority for companies looking to make their operations more sustainable and ensure that they're acting in responsible and ethical ways.
In addition, organizations are exploring other new techniques, technologies and processes for managing risk. More are adopting a risk maturity model to evaluate their risk processes and better manage interconnected threats across the enterprise. They're looking anew at GRC platforms to integrate their risk management activities, manage policies, conduct risk assessments, identify gaps in regulatory compliance and automate internal audits, among other tasks. Newer GRC features that risk management experts said should be considered include the following:
- Analytics for geopolitical risks, natural disasters and other events.
- Social media monitoring to track changes in brand perception as part of managing reputational risk.
- Security tools to assess the potential impact of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Companies are also taking a fresh look at risk appetite statements. Traditionally used as a means to communicate with employees, investors and regulators, risk appetite statements are now being used more dynamically to replace check-the-box compliance exercises with a more nuanced approach to risk scenarios. The caveat? A poorly worded risk appetite statement could hem in a company or be misinterpreted by regulators as condoning unacceptable risks.
This article was updated in June 2025 for timeliness and to add new information.
Linda Tucci is an executive industry editor at Informa TechTarget. A technology writer for 20 years, she focuses on the CIO role, business transformation and AI technologies.
Craig Stedman is an industry editor at Informa TechTarget who creates in-depth packages of content on analytics, data management and other technology areas.






