What is financial risk management?
Financial risk management is the continuous process of recognizing, evaluating and mitigating potential threats to an individual's or organization's financial health.
How does financial risk management work?
A complex, multi-step financial risk management system that guards against unexpected loss involves the following actions:
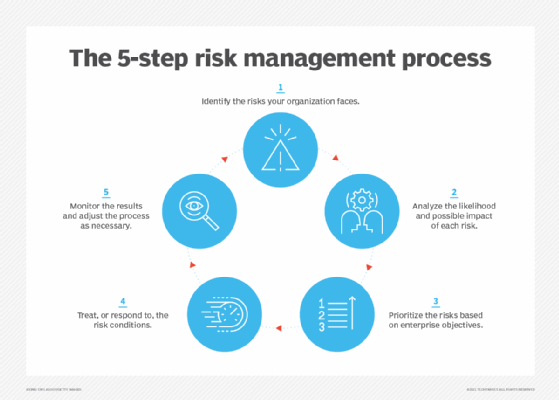
- Identifying risks. First, pinpoint potential financial risks. They vary based on the nature of the business or entity and its market.
- Assessing and quantifying risks. After identification, a risk assessment evaluates potential impact and probability. This process often includes statistical techniques, such as calculating standard deviations or applying regression models, to estimate exposure.
- Developing appropriate strategies. Organizations must determine their risk appetite, choosing to avoid, accept, transfer or mitigate each risk. Risk avoidance eliminates any high-risk activities, while risk acceptance indicates that the potential reward outweighs the downside for a company. Some risks are shared among business partners, while risk transfer shifts liability to another entity through insurance or contractual agreement.
- Initiating mitigation and loss prevention plans. Risk mitigation adds controls and procedures designed to minimize the likelihood of loss and the effect of realized risks.
- Monitoring and reviewing. Whether avoiding, accepting or mitigating risks, loss prevention plans require regular review and adjustment as needed.
Why is financial risk management important for organizations?
No company has money to lose. Yes, some loss is inevitable, but it must be minimized using every means available. Financial risk management leverages its structured flexibility to deliver several organizational benefits:
- Covering all financial bases. Monetary loss takes many forms: Lost income due to market volatility or theft, credit defaults harming business operations, operational failures undermining business continuity and loss of intellectual property are all under the umbrella of financial risk management. Ultimately, minimizing any loss boosts the bottom line.
- Preserving reputation. Companies lose more than money in a data breach; they lose face and many customers who won't soon return. No company or entity wants a reputation for lackadaisical financial management.
- Stabilizing operations. Effective financial risk management protects a company's capital and other assets, minimizing financial concerns through periods of uncertainty.
- Enabling informed decision-making. Knowing potential risks attached to an activity or decision gives business leaders clearer insight into the investment's risk-reward ratio.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance. Noncompliant entities face both penalties and damaged reputations. Competent financial risk management maintains an organization's regulatory compliance.
What are the different types of financial risk management?
Applicable across industries, financial risk management takes many available forms depending on the type of organization, its market and its greatest risks. The following are among the varied management choices:
- Market risk management. This process addresses the variables a company faces while doing business within its market.
- Credit risk management. This applies to any business with significant credit elements in its operational model, including credit assessments, credit limits and credit derivatives.
- Operational risk management. This involves risks related to internal operations, from equipment to company policy and staffing, as well as any external activities that heighten operational risk, including human error and malicious intent.
- Legal and regulatory risk management. This process identifies risks from regulatory changes or noncompliance with laws and their potential business impact.
- Liquidity risk management. This process tackles scenarios in which an organization has difficulty meeting short-term financial obligations due to insufficient cash reserves or a lack of easily liquidated assets.
- Foreign exchange risk management. This involves potential losses incurred from foreign currency exchange rates and is especially important for companies engaged in international trade.
How will AI affect financial risk management?
The rise of AI has a significant impact on financial risk management, regardless of industry. In particular, agentic AI -- used primarily to automate business processes and thereby eliminate human error -- has gained notoriety across fields.
That's due to agentic AI's many positive effects on business operations and outcomes, including the following:
- Processing large data sets. By design, AI algorithms analyze massive and complex data sets, providing insight into transactional history or social media presence, for example. Businesses use this data to identify patterns and trends before they become unmanageable.
- Improved forecasting accuracy. Through machine learning, models gain insight by recognizing and absorbing patterns, trends and complex data relationships, improving market predictions.
- Real-time monitoring. Transaction processing already continuously monitors transactional behavior and trends, but AI enhancements search for market fluctuations and emerging trends in real time.
- Advanced anomaly detection. Anomaly detection is another technology currently in use, typically to detect intruders into an internal system. Because of its ability to learn, AI recognizes normal behavior patterns and quickly identifies deviations that signal possible fraudulent or malicious activities.
- Behavioral analysis. Concurrent with anomaly detection, behavioral analysis and transactional patterns help expose unusual, potentially fraudulent activity.
- Enhanced regulatory awareness. AI assists with analyzing regulatory changes, automating compliance checks and detecting noncompliance.
However, AI in financial risk management also has shortcomings:
- Data quality questions and bias. The accuracy and fairness of an AI model depend on the quality of its data set. Bad, incomplete or biased data leads to bad, incomplete or biased decisions, sometimes known as "garbage in, garbage out." (Learn more about machine learning bias, or AI bias, here.)
- Lack of transparency. Some AI models, particularly deep learning algorithms that are the intellectual property of the developer, are understandably closed source. However, a lack of transparency is often problematic in the areas of compliance and governance.
- Regulatory uncertainty. As AI's influence grows, the regulatory landscape in finance continues to evolve, requiring care and vigilance from financial institutions seeking regulatory compliance in a shifting environment.
Best practices for financial risk management
Any organization's growth and profitability -- its continued existence, in fact -- requires the often routine but necessary work that underpins competent financial risk management. These essential best practices include the following:
- Performing comprehensive risk assessments regularly. Thorough risk assessments identify and evaluate all potential financial risks -- credit, market, liquidity and operational. These evaluations must be done regularly.
- Establishing a risk management framework. Enterprise risk management is a guideline for establishing and executing a risk management policy. Two popular frameworks, COSO ERM and ISO 31000, have commonalities and differences in achieving this goal. Part of the process, done through a committee or a chief risk officer, includes assigning roles and responsibilities to develop the framework.
- Integrating risk management policies into business practices. A comprehensive approach manages financial risks by meshing risk management policies with an organization's current operations and goals.
- Emphasizing regulatory compliance. Regulatory noncompliance carries significant long-term penalties, especially in heavily regulated fields such as finance and healthcare. Prioritize compliance to avoid financial, legal and reputational damage.
Every business, without exception, faces financial risk. Managing and mitigating these risks daily is foundational to its survival and eventual success.
This must be impressed upon everyone in an organization, from the C-suite down to rank-and-file employees, because everyone has a part in financial risk management, whether that involves approving company policy or recognizing -- but never clicking -- an email attachment from an unknown source.







