
Getty Images
How to fix an iPhone Personal Hotspot that's not working
Connectivity issues, misconfigured settings and human error can all cause mobile hotspot problems. IT must know how to avoid and fix iPhone hotspot issues for remote workers.
Mobile hotspots provide essential connectivity for a mobile and hybrid workforce, but inconsistent performance or security misconfigurations can disrupt operations and create compliance risks.
When a user's iPhone hotspot isn't working as intended, there are various quick fixes they can try. If there's no internet connection, they can check their cellular data and reset the network settings. If they receive an error message saying the password is incorrect, they can verify and update the Personal Hotspot password. If they receive an error message saying a device is unable to join the network, they can restart the iPhone and the connected device.
However, sometimes the troubleshooting process is more complicated. IT managers should have a plan for proactive management and troubleshooting to handle iPhone Personal Hotspots in the enterprise.
What causes iPhone hotspot issues?
Several factors could cause an iPhone hotspot to fail. Frequent culprits include connectivity issues, misconfigurations and human error.
Connectivity issues
Connectivity issues are among the most common challenges when supporting iPhone hotspots in an enterprise environment. These issues show up as inconsistent performance, slow speeds and dropped connections. Resolving connectivity issues starts with troubleshooting cellular connection problems and ensuring the hotspot is set up correctly.
Another typical connectivity problem is with the Bluetooth on devices pairing to an iPhone hotspot. Bluetooth is generally slower than Wi-Fi, and therefore potentially more prone to performance issues.
Bluetooth connectivity issues tend to be related to two main factors. First, other nearby Bluetooth devices can sometimes interfere with the Bluetooth signal, degrading hotspot performance or even preventing connectivity altogether. Second, outdated software can cause pairing issues. If either the iPhone or the device connecting to it is outdated, the mismatch can result in poor performance or an inability to connect.
Misconfigurations
Even with the support of MDM tools, configuration problems can affect iPhone hotspot connectivity. If a user has connectivity problems, make sure that the iPhone is running the latest version of iOS. Then, check that the hotspot is configured correctly.
Human error
Human error is often a cause of mobile device issues. As an example, a user might forget their password or accidentally turn off the hotspot on their phone. In some cases, a user might mistakenly try to connect to someone else's iPhone hotspot rather than the one on their own phone.
How to fix Personal Hotspot issues on an iPhone
If the source of the problem isn't immediately clear or easy to solve, an admin might have to walk a user through fixing the iPhone hotspot. The following troubleshooting tips work with iOS 18.5 and later.
Step 1. Check cellular data on the user's iPhone
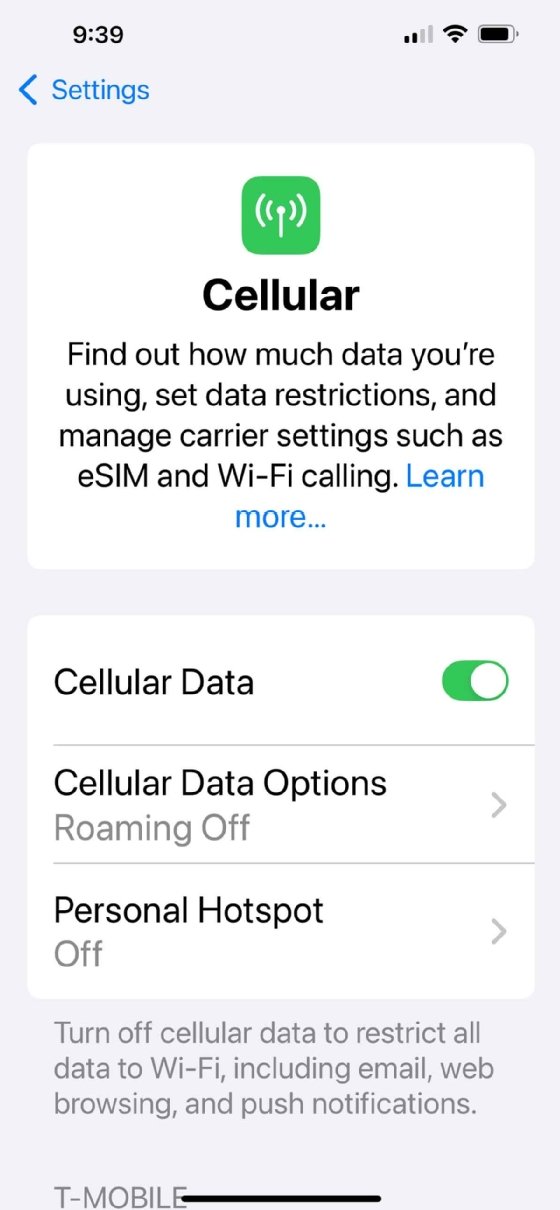
The first thing users should do is check whether their iPhone has a cellular data connection. They can do this by opening Settings > Cellular and seeing whether cellular data is toggled on, as shown in Figure 1. If the user's cellular data is turned off and can't be turned back on, then the user must contact their carrier to ensure their account is active and in good standing.
Step 2. Check Personal Hotspot settings on the user's iPhone
The user should also verify their Personal Hotspot feature is turned on and that the settings are configured correctly. They can do this by going to Settings > Personal Hotspot and checking that the feature is turned on.
The next step in the process is to make sure that the hotspot is configured correctly. To do so, tap on Personal Hotspot and then toggle on the Allow Others to Join option (Figure 2).
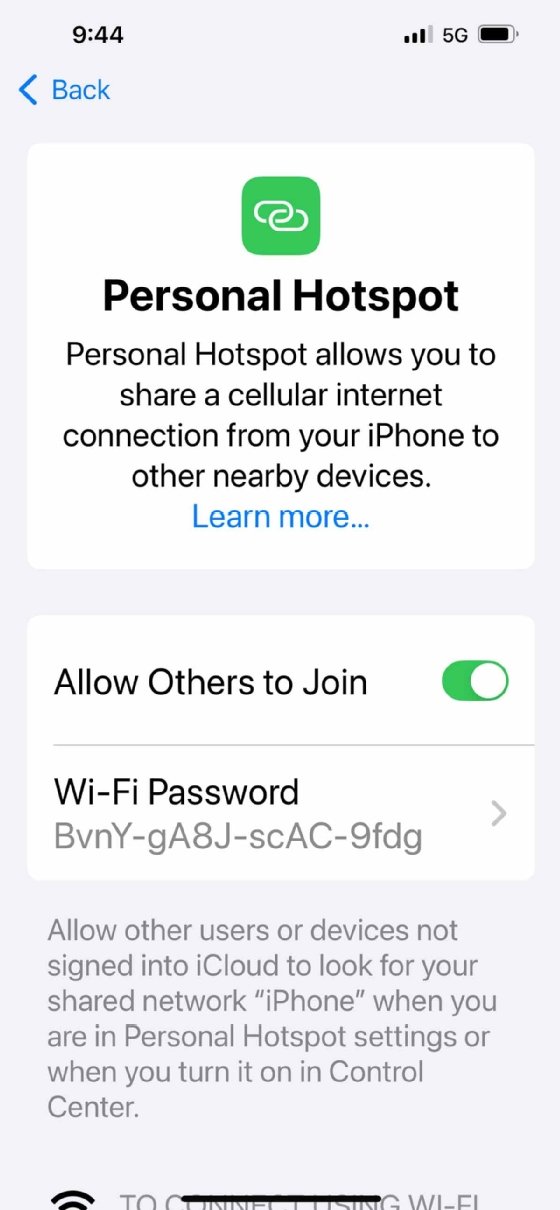
The iPhone automatically associates a random password with the hotspot. A user can change this password by clicking on it and then entering a new password. However, if the iPhone is being managed by the organization, the user might not have the necessary permissions to change the password.
On iPhone 12 and later devices, Apple provides a Maximize Compatibility option under the Personal Hotspot settings. Using this option can help some devices connect to the iPhone hotspot more easily. However, Apple warns that using this setting might diminish Wi-Fi security and performance for connected devices. As such, it's best to avoid using the Maximize Compatibility option unless the user cannot connect without it.
Step 3. Restart the iPhone and connected devices
As with many minor software glitches, sometimes the key to resolving a hotspot problem is to perform a full reboot of the iPhone. It's also a good idea to reboot the device that is trying to connect to the hotspot.
Step 4. Reset network settings
The best way to refresh an iPhone's network settings is to reboot the phone. However, another method is to enable Airplane Mode for a few seconds and then turn it back off.
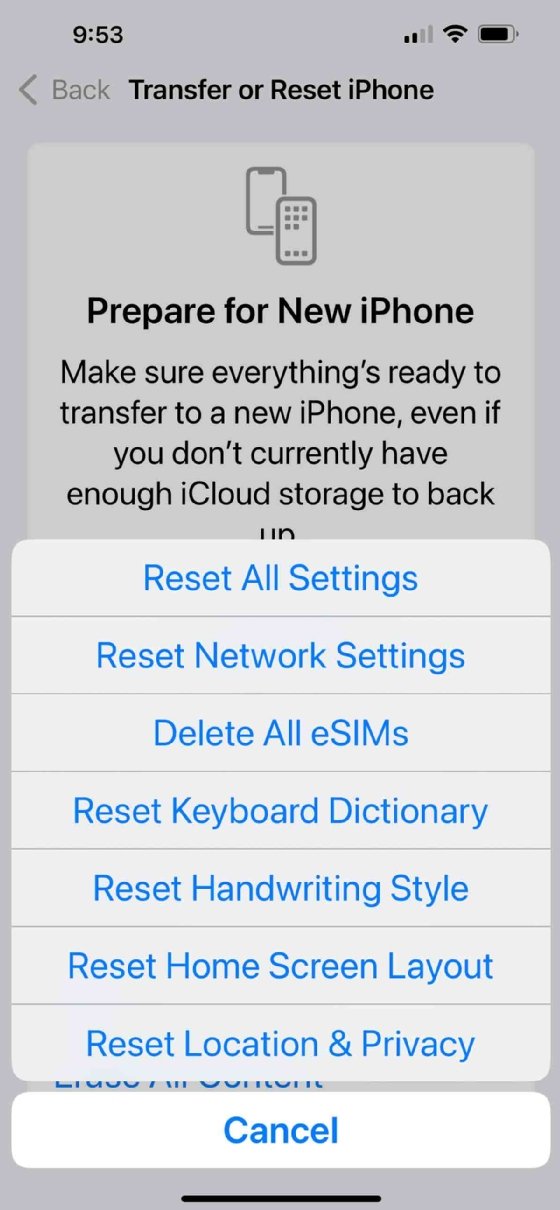
If the issue persists, the user can try resetting their iPhone's network settings. This step should be performed with extreme caution since it's easy to accidentally reset all of the phone's settings. To reset the phone's network connections, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset. At this point, the phone will display a menu containing various reset options (Figure 3). Choose the Reset Network Settings option. This will remove all network settings, including Wi-Fi passwords.
Step 5. Contact carrier support
If no other steps have worked, the last option is to contact the wireless carrier's support team for further assistance. If the user works in a BYOD environment and owns the phone themselves, they would need to call their carrier. With corporate-owned devices, the service desk might have to contact the organization's carrier support. If the organization uses a mobility MSP, the service desk can escalate the issue to them.
Common error messages when using an iPhone hotspot
When iPhone Personal Hotspot issues occur, it's often accompanied by an error message that can help determine the cause of the problem.
A common error message is "Personal Hotspot Not Available." This usually means that the cellular carrier has disabled the hotspot feature. As such, the user or organization should review their plan to make sure that the carrier has enabled hotspot use. If the plan does include hotspot access, check to make sure that the user hasn't exceeded their data allotment.
Another error users might encounter is "Unable to Join the Network." If this error message, or a variation of it, appears on the device that the user is trying to connect to the hotspot, make sure that the iPhone is powered on. Additionally, check that it doesn't have low battery power and hasn't gone into sleep mode. Users can also try toggling the hotspot off and back on again. Some iPhones might automatically turn off the hotspot when the screen is powered off.
If a user receives an error message stating that the hotspot password is incorrect, they should make sure they're connecting to their iPhone and not someone else's. If they are connecting to the correct phone, they can try temporarily changing the password to something less complicated to make sure they're typing it in correctly.
To troubleshoot a "No Internet Connection" error message, open a browser directly on the iPhone to make sure it can access the internet. If internet access is working on the phone, make sure that it's not using low data mode. If the user is in an area with spotty coverage, they should also check to make sure that roaming is enabled.
Users might also receive an error message indicating that the hotspot is not accepting new connections, or that it's hosting the maximum number of devices. This issue can occur with certain data plans, as some plans limit hotspots to a single connection. If the user isn't exceeding the connection limits, try disconnecting any unused clients to see if that makes the problem go away.
Editor's note: This article was originally written by Will Kelly in May 2023. Brien Posey updated this article in November 2025 to reflect changes in troubleshooting options and to improve the reader experience.
Brien Posey is a former 22-time Microsoft MVP and a commercial astronaut candidate. In his more than 30 years in IT, he has served as a lead network engineer for the U.S. Department of Defense and a network administrator for some of the largest insurance companies in America.
Will Kelly is a freelance writer and content strategist who has written about cloud, DevOps, AI and enterprise mobility.






