
Gorodenkoff - stock.adobe.com
Data center safety checklist: 10 best practices to follow
Data center facilities pose various risks to those who operate them. Here are 10 best practices to follow when implementing data center safety.
Data center facilities pose various risks to the workers who operate them, so having a well-structured data center safety plan is crucial for protecting staff. Understanding proper data center safety, likewise, is essential for IT leaders, facilities managers, operations teams and employees.
Common risks in data centers include environmental hazards -- such as heat, cold and noise -- as well as malfunctioning fire suppression and electrical systems. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic sparked new and stringent protocols related to staff health.
Establishing best practices for data center safety, along with appointing a dedicated facility or safety manager, can help teams stay out of harm's way.
The importance of data center safety
Given the right conditions, data centers can be a high-risk environment. For example, high-voltage equipment can cause electrocution; combustible material, if placed near hot equipment or near hot work, can cause a fire; heavy racks can pose physical hazards if not properly secured; and a lack of training can lead to incidents caused by human error.
Ensuring data centers have proper safety protocols is an important aspect for both employee health and the data center itself. A well-implemented data center safety plan prioritizes the safety and well-being of humans, enhances the ability to maintain operational continuity, safeguards infrastructure and ensures continued compliance.
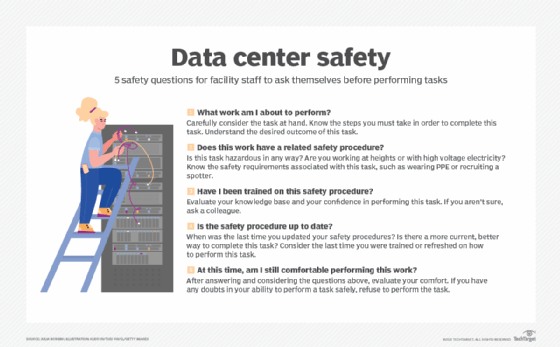
10-step data center safety checklist
A structured safety checklist will help an organization standardize procedures and reduce risk. The following 10 points cover different aspects that should be included in a data center safety plan.
1. Start with a detailed risk assessment
Conducting regular, comprehensive and detailed risk assessments is a core aspect of data center safety. A risk assessment not only helps identify physical, environmental and operational risks, but it also enables the organization to evaluate the severity of each risk. This acts as a base for controlling and minimizing potential safety hazards.
For example, a risk assessment might find poor airflow in a data center, which could cause equipment to overheat, potentially creating a fire hazard.
2. Revise lockout procedures
The term lockout refers to the practice of turning off or de-energizing equipment before performing maintenance or repair work. Having proper lockout procedures helps prevent accidental power-ups, electrical shocks or equipment damage.
Lockout procedures should be revised and standardized to ensure equipment status remains off until any maintenance is complete. Additionally, all operating staff should be trained to understand lockout practices for relevant equipment.
3. Implement electrical work training and supervision
Only qualified employees should work on electrical-based tasks. Electrical equipment and systems will heavily rely on power systems, which can become a potential hazard if not handled correctly. Electrical safety guidelines should be included in a data center safety plan to minimize the potential risks involved.
A data center safety plan should also include employee training and regular checks of the electrical infrastructure.
4. Specify strict rules around hot work
Hot work refers to any activity that involves fire, sparks or high levels of heat. Any activity considered as hot work -- such as welding, grinding or cutting -- should follow strict safety guidelines. Specific areas should be designated as hot work zones to minimize the risk of a fire. Fire suppression equipment, such as fire blankets or fire extinguishers, should also be within reachable distances for the same reason. Before performing any hot work, inspect the area for any flammable materials. Some organizations might also choose to ban hot work around IT equipment.
5. Appoint dedicated facility managers
A facility manager will help oversee daily data center operations, ensuring that the data center is run efficiently and safely. Facility managers monitor data center systems, such as those for power, security, HVAC and mechanical operations. The facility manager is also responsible for environmental health and safety, personnel management, emergency preparedness, change management, energy management and financial management.
The facility manager must collaborate with IT admins to ensure the data center runs smoothly. This individual should understand data center design principles, industry best practices, data center infrastructure management tools and emerging technologies. A facility manager should be thoroughly acquainted with all safety procedures and guidelines and be able to effectively communicate those procedures and guidelines to staff to ensure they are followed.
6. Ensure compliance with data center standards
Organizations should understand and adhere to relevant compliance standards. Data center compliance standards and similar relevant workplace safety standards, such as ISO 14001, OSHA regulations, ANSI/TIA-942 and NFPA 70, are all standards that help ensure worker and infrastructure safety.
For example, NFPA 70 is a standard that outlines safe electrical design, installation and inspection guidelines to protect workers and infrastructure from potential electrical hazards. Likewise, ANSI/TIA-942 is a standard designed by the Telecommunications Industry Association that specifies minimum requirements for telecommunications infrastructure in data centers.
Compliance must be a continuous effort, as it helps ensure ongoing alignment with changing security and safety regulations.
7. Implement emergency response procedures
There's always a chance something will go wrong; in such cases, organizations should have a prepared plan of action ready to go. This means developing plans for what to do in case of fire, flooding, earthquake or other emergency.
An organization might also choose to conduct emergency response drills to test its effectiveness and efficiency.
8. Ensure employees have the proper personal protective equipment
Some data center work -- such as electrical work, hot work, work at heights and heavy lifting -- might require personal protective equipment. PPE is essential to keeping employees safer in high-risk environments. Organizations should provide employees with proper gear to help ensure their safety.
Electrical work, for example, might require the use of insulated gloves and dielectric footwear to reduce the risk of shock. Hot work might require welding helmets and welding blankets.
PPE should also be inspected regularly to ensure it is still able to protect employees properly.
9. Conduct regular safety training sessions
Regular training sessions on safety procedures will help reduce the risk of accidents. This includes training employees on identifying risks, lockout and emergency procedures, compliance with safety standards, working at heights and ensuring proper use of PPE.
The training should be tailored to role-specific tasks, as not every employee faces the same risks. Conducting the training on a regular basis will also help ensure it training stays top of mind for each employee.
10. Regularly hold safety audits
Holding regular safety audits will help ensure all in-place plans and procedures are being followed properly. Schedule audits periodically to review safety systems, equipment and adherence to standards. If any flaws or opportunities for improvement are found, then corrective actions should be taken to update any plans or procedures. An organization might also benefit from using a third-party auditor for a more objective and independent review.
Alexander S. Gillis is a technical writer for WhatIs. He holds a bachelor's degree in professional writing from Fitchburg State University.








