What is a risk management specialist, and what does one do?
A risk management specialist is a role appointed within organizations to identify potential risks that might negatively affect the business. This role has traditionally focused on financial risks. But risk managers are increasingly being tasked with identifying potential risks affecting employees, third-party risks, cybersecurity threats and privacy-related issues. As a result, the scope of risk management has grown to include industries such as finance and IT, as well as the impact on employees, facilities, data and reputation.
A typical risk management specialist's job responsibilities include conducting risk assessments, analyzing data, monitoring risk factors, managing regulatory compliance and developing strategies to reduce risks.
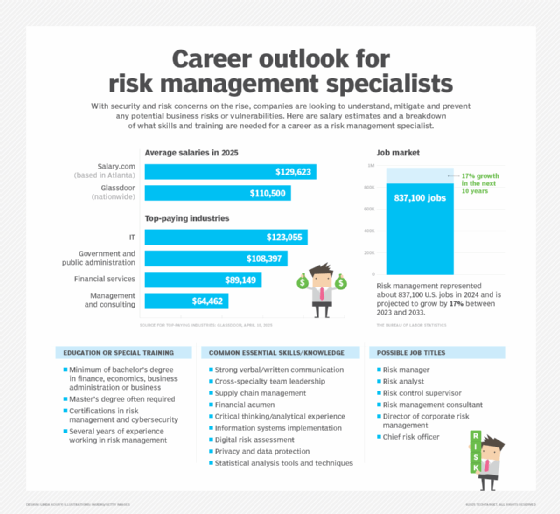
Despite the aspects of market risk that emerged in early 2020 with the COVID-19 pandemic, risk management was already one of the fastest-growing job markets in enterprise management. In the wake of recent regulatory changes and climate events, organizations are increasing the demand for risk management specialists. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which groups risk managers with financial managers, this field is expected to grow 17% by 2033, a much larger increase than many other industries.
Risk managers excel at identifying how things might break. They are also skilled at modeling and estimating the probabilities of different kinds of risks and setting up processes for addressing problems when they emerge.
Specialists can also prioritize risks to create a competitive advantage. For example, risk management officers can help product managers pursue new opportunities more efficiently by mitigating risks compared with competitors. They can also help business managers balance potential investments against potential risks.
Risk management specialists can also help implement systems to actively connect key risks to important alerts. This can help automate the execution of contingency plans when required. Tighter integration between business applications and decision-making can help improve the quality of risk management across the organization. The focus on blending IT and risk management also creates opportunities for other types of employees to earn risk management certifications.
Responsibilities of a risk management specialist
Risk managers wear a lot of hats. They engage in regular in-person discussions and email exchanges about all aspects of the company so they can proactively identify issues. They must be able to identify problems in a helpful way that supports morale and the growth of the enterprise. The following are some additional responsibilities assigned to risk management specialists:
- Connect financial data to specific risks and mitigations, such as insurance or policies.
- Curate data related to various types of risks from within the company and the industry at large.
- Identify and characterize risks through in-depth discussions with employees, customers, regulators and third-party experts.
- Identify risk indicators by considering how different scenarios could impact a business.
- Create risk management models and reports to assess and mitigate various aspects of risk exposure.
- Provide training and generate risk disclosure and risk maps to help guide employees, inform regulators and keep shareholders informed.
- Keep an eye on emerging regulations that might affect business risk positions.
- Translate the effect of new laws or regulations into practical advice for business leaders.
- Facilitate risk conversations between different areas of expertise within the organization, including legal, IT, finance, privacy, human resources, health and safety, supply chain management and operations teams.
- Develop and implement risk management plans to help reduce potential losses.
Essential skills
Aside from everyday tasks, risk management specialists and related positions require a lengthy set of skills.
An essential job for risk management specialists is effectively communicating with industry experts, frontline workers, managers and executives across the organization. These specialists need to be good at identifying potential problems without exacerbating them. They also must be able to strike a balance of cultivating awareness of problems without killing the enthusiasm for promising new opportunities.
One of the unique skills of risk managers is quickly understanding the greater context of events that affect the business. For example, a risk manager might think about the various ways the move to working from home could affect sales, employee morale, operations, regulations and other aspects of the business.
Other essential skills for a risk management specialist include the following:
- Financial acumen.
- Strong verbal and written communication.
- The ability to summarize complex situations.
- Familiarity with statistical analysis tools and techniques.
- The ability to organize information and implement systems.
- The ability to manage cross-specialty teams.
- Supply chain management fluency.
- Digital risk assessment capabilities.
- An understanding of privacy and data protection.
How to become a risk management specialist
Prospective risk management specialists need to do the following to succeed in the field:
- Earn a bachelor's degree. A bachelor's degree is typically considered the minimum educational requirement to be a risk management specialist. This could be an undergraduate degree in finance, business administration or accounting. An ideal starting point is a bachelor's degree in business management, which can be used in financial industries such as banking and insurance. Other types of professionals can cultivate risk management specialist skills by cross-training. Some positions might also require a master's degree in risk management or related fields.
- Gain experience. Individuals should gain the necessary foundational skills by getting experience in management, accounting or finance roles. Several years of work experience in these areas will help ensure these individuals have developed relevant technical and analytical hard skills.
- Earn certifications. Although certifications are not necessary, they can be beneficial. Certifications like the Certified Risk Management Professional or the Financial Risk Manager can also help individuals highlight their skills.
There are numerous other risk industry trade organizations that provide comprehensive education and certifications, including the following:
- Certified Risk and Compliance Management Professional from the International Association of Risk and Compliance Professionals.
- International Certificate in Enterprise Risk Management from the Institute of Risk Management.
- Certified Risk Manager from the Risk & Insurance Education Alliance.
- A certificate in Risk Management from the Organisation of Certified Risk Managers.
- Professional Risk Manager certification from the Professional Risk Managers' International Association.
- Chartered Enterprise Risk Analyst credential from the Society of Actuaries.
- A Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control certificate from the Information Systems Audit and Control Association, or ISACA.
Risk management crosses multiple business and technical domains. As a result, risk management specialists might also come from other business units that have equally strong skills in identifying problems and creating systems for mitigating their potential impact. Experts in legal, human resources, data protection, cybersecurity and supply chain management could consider a risk management career path.
Salary and career path outlook
According to Salary.com, the total pay range for a risk management specialist in Atlanta in 2025 is $117,053 to $142,193, or an average of $129,623 annually. However, according to Glassdoor, the average salary for a risk management specialist in 2025 is $110,500 per year, with a range between $79,000 and $142,000. However, these ranges are influenced by factors such as location, education, level of experience and industry.
Several skills are needed to be a competent risk management specialist. Learn about related risk management skills and why they're needed.






