What is a risk map (risk heat map)?
A risk map, or risk heat map, is a data visualization tool for communicating specific risks an organization faces. It helps companies identify and prioritize the risks associated with their business.
An important component of enterprise risk management, a risk map facilitates the following:
- Drives an understanding of an organization's risk profile and risk appetite.
- Clarifies thinking on the nature and impact of risks.
- Improves the organization's risk assessment.
How do risk maps work and what are they used for?
A risk map is often presented as a two-dimensional matrix in the enterprise. For example, the likelihood of a risk occurring is plotted on the horizontal or x-axis, while the impact of the same risk is plotted on the vertical or y-axis.
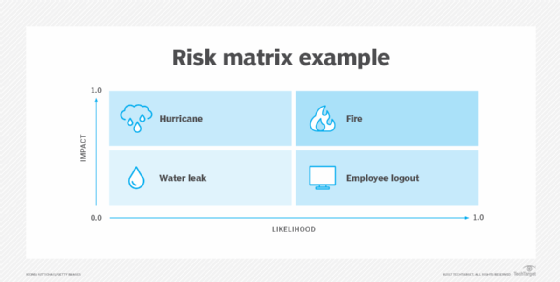
Identified risks in the high-likelihood and high-severity section typically demand attention. Suppose the organization is dispersed geographically, and certain risks are associated with particular geographical areas. In that case, risks might be illustrated with a heat map, using color to illustrate the levels of risk to which individual branch offices are exposed.
Organizations use risk heat maps to help identify the risks they are likely to encounter, see the varying levels of concern attached to each risk and depict their risk priorities in an intuitive, self-explanatory way. Risk maps help enterprise executives and their teams understand where to prioritize their risk mitigation resources.
In addition, the graphical representation of each risk's potential impact and likelihood makes risk management more tangible to employees, particularly those outside the executive ranks and the enterprise risk function with no special training in risk management. This enables organizational leaders to involve employees at all levels in discussions about risk and risk mitigation requirements.
What are the main benefits of a risk heat map?
Risk maps enable organizations to do the following:
- See the organization's total risk environment at a high level, providing a big-picture view.
- Ensure that risk mitigation priorities -- and resources -- are aligned to the most significant risks.
- Reduce insurance costs -- developing risk maps can help organizations demonstrate a comprehensive, well-aligned risk management strategy to insurance companies and get more favorable premiums.
- Support collaboration between the organization's risk function and other functional departments, which have greater visibility into risk due to the risk heat map.
- Encourage shared strategic decision-making on risk issues.
- Effectively focus on improving risk management and risk governance.
- Sharpen the enterprise's definition of its risk appetite and risk tolerance.
- Generate better integration of risk management activities across enterprise functions.
- Give teams throughout the enterprise a common language for discussing risk.
Why is it important to use a risk heat map?
Creating a risk map forces executives and their teams to identify the risks that could threaten the organization and rank their possible effects and likelihood. The exercise can clarify priorities for enterprise leaders and help them address issues before they threaten the organization's operations.
Creating a risk map facilitates interdepartmental dialogues about an organization's inherent risks. It forces greater collaboration between the risk function and other departments within an organization, as they must all work together to identify, prioritize and visualize risks. As such, a risk heat map can help the company visualize how risks in one part of the organization can affect the operation of other business units across the enterprise.
A risk map also adds precision to an organization's risk assessment strategy and identifies gaps in its risk management processes.
When should a risk heat map be used?
Risk heat maps can be used for the following use cases:
- Compliance audits. Heat risk maps visually indicate to regulatory bodies an organization's risk landscape and the effectiveness of its proactive risk management strategies.
- Proactive threat management. Organizations can quickly identify and address potential risks, focusing security resources on the most vulnerable systems and assets.
- Resource allocation. Risk heat maps can indicate high-risk areas where personnel, budget dollars or tools are needed.
- Communicate risks. Organizations can use risk heat maps to communicate with stakeholders about identified risks, helping them interpret the risk levels and make decisions across different teams.
What are the key considerations for creating a risk heat map?
Risk maps are most effective when organizations thoroughly consider the different categories of risk they face, the various risks within each category, and their potential probabilities and possible effect on the enterprise.
Organizations should also keep the following key considerations in mind as they develop risk maps:
- The specific systems and information assets that certain risks could affect.
- The type of impact -- monetary, operational, reputational -- each risk could have.
- Whether there's an acceptable level of impact and, if so, how much is tolerable for the organization.
- Existing internal controls and any additional controls that could or will be implemented.
- The organization's risk tolerance and risk appetite.
How to create a risk map
Organizations can implement the following steps to create an actionable risk heat map:
- Identify inherent risks. Risks can be broadly categorized into strategic, compliance, operational, financial, reputational and cybersecurity risks. Organizations should aim to chart their lists by considering specific factors that might affect them financially.
- Assess risks. Once an organization has identified risks, it should seek to understand what internal or external events drive them. It must evaluate those risks, estimate their potential frequency and impact, and identify the control processes to offset them.
- Plot risks on the risk map. Each risk should be plotted on the risk heat map according to its likelihood and impact scores. These data points should be ranked, focusing on managing risks with the highest potential for significant impact.
- Visualize and map risks. After gathering and evaluating the risk data, the risk manager must decide how to visualize that information in ways that make sense for their unique needs.
- Create a mitigation strategy. A risk manager must create a plan outlining specific actions to reduce the risk's impact or likelihood. They should assign responsibilities to stakeholders and set deadlines for implementing these strategies.
- Review regularly. The risk manager should regularly review and update the risk heat map to reflect emerging and changing risks.

Risk maps are typically square, but some are rectangular or circular. They're frequently graphs built on an x-y axes, but some are divided into quadrants with the upper-right block designating the most significant risks.
Many maps feature a red-yellow-green color code to indicate whether risks are significant, moderate or low-level concerns. However, some use varying shades of a single color to indicate risk levels. Additional presentation variations exist, such as creating a risk map as a bar graph.
Organizations can use the completed risk map to facilitate discussions and decision-making. However, they must recognize that risk maps are not static, so they must have a process for reviewing them regularly to ensure key risks are being managed effectively. They should also have a method for revisiting and adjusting their risk maps as threats evolve and vulnerabilities change.
An organization's reputation is critical to its success. Learn how organizations can manage reputational risk to avoid a reputational disaster.







