What is risk identification? Importance and methods
Risk identification is a crucial first step in risk management, enabling organizations to document and prepare for potential threats and opportunities.
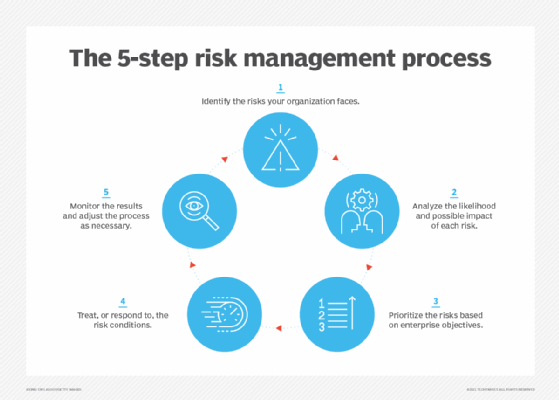
Risk identification is one of the first steps to a comprehensive risk management plan and involves searching for, identifying and documenting potential risks to an organization.
By identifying the various risk scenarios that could affect the business, organizations are better equipped to mitigate potential threats or negative risks, such as data breaches, accidents or business downturns. However, some risks can be positive and present opportunities, such as adopting new technology, hiring an inexperienced recruit and an unexpected surge in demand.
Why is risk identification important?
Risk identification is a core element of enterprise risk management. Identifying and assessing internal and external threats enables organizations to proactively prepare for future challenges.
Without risk identification, businesses become vulnerable to threats that can negatively affect several business areas, including profit, reputation and employee loyalty. By prioritizing risk identification and the next steps of risk management, organizations can ensure that risks are properly assessed and develop a plan before they occur, minimizing the likelihood of negative outcomes or taking advantage of possible opportunities with positive risks.
Benefits of risk identification
Risk identification can have several benefits for enterprise risk management, including the following:
- Mitigate adverse effects. By identifying risks early, organizations have time to develop strategies to mitigate negative outcomes. This can help reduce the likelihood of adverse risk effects or lessen their severity.
- Improve decision-making. When decision-makers have all the information about potential outcomes and risks, they can make more informed decisions about what will be best for the business. Proactively identifying risks also ensures that leaders are not caught off guard by complications and already have a strategy in place when crises arise.
- Identify opportunities. Risk identification enables organizations to identify potential threats to the business and uncover opportunities for improvement, helping organizations gain a competitive advantage and strengthen different areas of the business.
- Stay compliant. Risk identification can uncover potential compliance issues and regulatory requirements that aren't being met. By proactively flagging and addressing these issues, organizations can ensure they stay compliant and follow industry standards.
- Strengthen preparedness. When empowered with the knowledge of what risks may crop up, organizations can stay vigilant and prepared. This preparedness can help leaders proactively prepare with contingency plans, operational shifts, or better resource allocation. If an issue does arise, organizations that are already equipped to handle challenges can mitigate them quickly and effectively, reducing the impact on the business and employees.
- Improve organizational culture. An organization that prioritizes identifying and managing risk creates a stronger culture around risk preparedness and mitigation. A consistent culture of awareness also empowers employees to proactively identify risks and bring them up to leadership.
Types of risks to consider
Organizations can face several different types of risks. Understanding these risks is essential for ensuring that risk management encompasses all potential threats.
- Strategic risks. Strategic risks come from decisions made about the business and its strategic goals and direction, such as a new offering or a new business model. When the business strategy shifts, organizations are left vulnerable to strategic risks related to those decisions, such as profit loss or customer loss.
- Operational risks. Business operations—including internal processes and systems—are critical to an organization's success, so when operations are disrupted, it can lead to operational risk. Internal or external challenges, such as supply chain disruptions, technical difficulties or inefficient systems, can interrupt operations.
- Financial risks. Financial risks are threats that might affect the business's bottom line, such as market changes or economic downturns. Any type of financial disruption can significantly affect profitability and business operations, leading to negative outcomes if an organization is not prepared.
- Compliance risks. Organizations that are noncompliant with regulations or laws leave themselves vulnerable to compliance risks. Compliance risks can result in financial or reputational damage, including legal action and fines, especially in heavily regulated industries.
- Reputational risks. Reputational risks emerge when an individual, such as an employee or customer, reacts negatively to some part of the business, such as mistreatment from the company, a poorly managed public issue or poor customer experiences. Reputational risks can lead to organizations losing customers and ultimately lead to a loss of profit.
- Environmental risks. These risks come from environmental risk factors, such as changing weather patterns, natural disasters or new environmental regulations. Environmental risks can lead to issues with supply chains, business operations and production costs.
Common risk identification methods
There are several ways for organizations to identify risk accurately and effectively, including the following.
- Brainstorming. Brainstorming involves a group of business leaders or employees getting together to generate ideas and have open discussions about possible risks that may arise. It enables employees to think about the company's future, assess the impact of potential risks, and proactively identify solutions and strategies.
- SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that could affect a business, project, or objective. It enables leaders to examine all aspects of a new idea or strategy and identify the possible risks, good or bad, associated with it.
- Stakeholder interviews. One-on-one interviews with stakeholders or subject matter experts can uncover the biggest risks that are prominent in the minds of those who are the most knowledgeable or the most closely related to the project, uncovering risks and threats that may not be obvious.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Like interviews, surveys and questionnaires can help leaders understand the thoughts and ideas of a broad range of team members or stakeholders who are involved with different areas of the business, providing a diverse range of perspectives.
- Historical data or root cause analysis. Historical data analysis enables business leaders to review previous incidents, data, and audit reports that can give insight into potential future risks. Similarly, a root cause analysis looks at previous project risks and how they relate to the current project.
- Scenario planning. By assessing possible future scenarios and the risks associated with them, leaders can develop the best strategies and proactively prepare for any challenges that may arise.
Tips for effective risk identification
Risk identification can be a valuable tool for businesses to proactively address challenges and ensure the successful completion of projects and goals. Here are some tips for ensuring its success.
- Choose the right strategy. Depending on business needs, decide on how to begin the process. Consider a top-down or bottom-up approach, or combine elements of both.
- Use external research. Work with expert consultants to identify blind spots and oversights that an internal employee may have missed.
- Seek out diverse perspectives. Use methods such as SWOT analysis, interviews, and questionnaires to get a comprehensive view of potential risks. Internal feedback can also be a valuable tool to identify risks in different areas of the business.
- Invest in risk management tools. These tools, software and frameworks can streamline data collection, risk scoring, tracking and reporting. A solid risk management tech stack also provides a centralized home for all risk management elements.
- Incorporate industry news and market trends. Staying up to date on market trends and industry changes ensures that emerging risks are considered and mitigated, and new opportunities are identified early on.
- Assess competitor strategies and activities. By monitoring competitors' activities, organizations can identify market shifts and innovations that might spur new threats or opportunities.
- Recording findings in a risk register. Documenting risk identification findings—with sources, potential impacts and mitigation plans—is essential for informed decision-making and clarity across the organization.
Questions to help identify business risks
Identifying risk is all about being curious and asking the right questions. Here are some questions to start identifying business risks:
- What are the key business objectives? What could prevent the business from achieving them?
- Is the business making any upcoming shifts into a new market, new product, or new business model? Why? What is the plan to integrate these changes?
- What assumptions is the business making in its strategic plans? What happens if these assumptions are wrong?
- Is the business up to date with all applicable laws, regulations, and industry best practices?
- Are there emerging technologies or innovations that could disrupt the industry?
- What issues could damage the business's reputation or stakeholder trust?
What's the next step after risk identification?
After risks have been identified, the next step in the risk management process is risk assessment and risk analysis. This involves evaluating the identified risks to understand their likelihood of occurring, their effect, how quickly they would materialize, and how they may connect to other potential risks.
Alison Roller is a freelance writer with experience in tech, HR and marketing.






