What is CloudOps (cloud operations)?
Cloud operations (CloudOps) is the management, delivery and consumption of computing resources (e.g., software, hardware, virtual machines) in a computing environment where the visibility into the infrastructure varies based on the type of arrangement. There are several cloud configuration alternatives, and CloudOps activities vary with each.
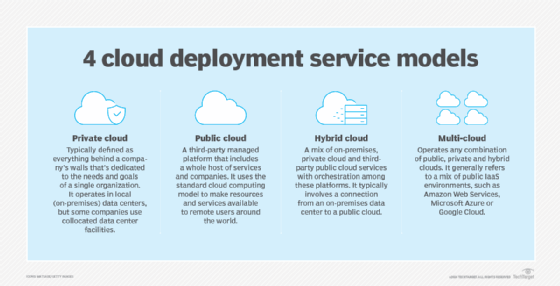
In a private cloud, all computing resources are dedicated to the organization that deploys the arrangement. The "cloud" can be in the firm's data center or in an alternate location, perhaps facilitated with the help of a third party. Cloud operations in this arrangement are focused exclusively on the organization and its requirements.
Public cloud arrangements eliminate all company-operated data center resources and transfer those assets to a cloud service provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Third-party managed service providers (MSPs) may also deliver the same kinds of service as cloud vendors. The services an organization uses may be shared with other cloud vendor customers, and CloudOps activities are managed mostly by the cloud vendor or MSP. Service level agreements (SLAs) are essential to ensure that the cloud service/MSP knows what is expected by the customer and that the customer has remedies if the agreed-upon services and performance criteria are not delivered.
In a hybrid cloud arrangement, the customer and the third-party provider agree on which activities will be delivered and managed by each. For example, the customer may manage high-priority systems that may have specific regulatory and compliance requirements, whereas the third party will manage other, less critical functions. CloudOps becomes a process of directly managing the "private" elements and using SLAs and other arrangements to monitor and manage the "public" elements.
At the enterprise level, CloudOps uses DevOps (development operations) principles of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) to achieve high availability (HA), strong security and procedures for incident management and disaster recovery. These issues are especially important in public and hybrid service configurations.
A CloudOps team's responsibilities typically include:
- Monitoring operations, especially of third-party vendors
- Automation of specific operational tasks
- Configuration management (CM)
- Resource allocation
- Optimizing performance
- Monitoring and managing costs
- Capacity management
- Cybersecurity management
- Disaster recovery (DR) and data backups
- Managing compliance requirements
- Using service management tools and frameworks (e.g., ITIL) to manage cloud operations
- Ensuring service-level agreements are met
Because of the continued deployment of cloud-based services, CloudOps has become an essential activity within many organizations, regardless of the type of service configuration.
What is addressed in CloudOps?
As noted, CloudOps is the performance of tasks needed to manage and maintain a cloud environment, including the automation of tasks associated with cloud operations. CloudOps team responsibilities vary based on the type of cloud arrangement and customer requirements. Regardless of the cloud type, CloudOps team goals are to facilitate, manage operations and provide governance.
Facilitation. Facilitation is the preparation and execution of tasks needed to manage cloud workflows and supporting activities. Task automation is a key activity, especially in situations where multiple tasks must be coordinated to achieve a specific goal.
Facilitation activities include:
- Identification of the most appropriate mix of cloud services for business requirements; this applies to public and hybrid cloud services
- Arranging for the deployment and removal of various cloud services, including those that deal with infrastructure, platforms, security and code
- Ensuring that all elements needed in the cloud infrastructure, such as networking and security, are coordinated for optimum performance; this applies to public and hybrid configurations
- Coordinating migration arrangements to plan, execute, test and deploy user computing resources (e.g., systems, workloads, infrastructure, data) from a private environment to a cloud service
Manage operations. This activity involves the day-to-day management and maintenance of a user's IT resources after they have been migrated to a cloud. Automation plays an important role in such activities.
Tasks associated with managing operations may include:
- Monitoring the performance of each system to ensure it is running properly
- Using automation to identify problems, troubleshoot them and fix them with minimal disruption to production
- Ensuring that cloud-based systems are properly deployed
- Using continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) resources to optimize performance.
- Scheduling and deploying patch management activities
- Using data from system monitoring tools to ensure that systems are properly configured and to update configurations as needed
- Monitoring security platforms to ensure that malware, ransomware and other malicious code is blocked or mitigated if it is detected
Governance. Effective cloud performance requires rules that define how the cloud is to perform and how users use cloud resources. Governance activities include establishing policies and procedures to manage cloud performance and ensure that users know how to use cloud services properly.
Governance activities may include:
- Establishing a framework of management activities, including policies and procedures, that define how the cloud environment is to operate.
- Creating service level agreements that define how cloud services are to be delivered, and penalties if they are not.
- Establishing technology disaster recovery plans that delineate the steps to take when a cloud service disruption occurs; most cloud vendors offer such plans
- Ensuring that critical systems and data are properly backed up and that backed-up data is periodically tested to ensure that it can be retrieved and activated if needed.
- Ensuring that data management processes are followed for data storage, data classification, data movement, data usage, data protection, and data storage and destruction.
- Define and periodically test business continuity (BC) plans, which may need to be coordinated with the cloud vendor's BC offerings.
- Periodically reviewing cloud resources and altering their status (e.g., reconfiguring the service or turning it off) based on business requirements.
- Where compliance with specific regulations and legislation is required, ensure that all governance activities, such as policies and procedures, are designed to demonstrate compliance.
- Document all relevant governance activities for potential audits.

Benefits of CloudOps
Migrating applications to the cloud brings its own benefits, such as freeing up internal infrastructure and controlling costs. However, whatever is moved to the cloud still must be managed, and the work around maintaining cloud-based applications and data is relatively the same as managing them on-site.
CloudOps benefits include:
- Cost-effectiveness.
- Easier to use than traditional in-house approaches.
- Flexible in terms of how resources can be organized and used.
- May require fewer resources than traditional approaches.
- Many steps can be automated.
- It can scale out and automatically provision servers.
- A cloud can abstract infrastructure from an application.
- Services are generally reliable.
- Advanced services such as artificial intelligence (AI) may be available.
Challenges of CloudOps
Challenges associated with cloud services, such as reduced user control and security risks, mean that a cloud migration -- even a partial or hybrid arrangement -- needs to be carefully evaluated with proper due diligence.
Challenges to the use of cloud services include:
- User direct control and access may be limited by the cloud vendor.
- It is possible to overspend on overprovisioned servers or other services.
- There may be limited governance abilities.
- Security with public cloud providers can be risky
- Cloud vendors may not be willing to accommodate a customer's compliance requirements.
- Cloud service disruptions could be catastrophic to a business
- Lock-in to a single vendor may make it difficult to migrate to a different cloud vendor.
What is the difference between CloudOps and DevOps?
DevOps is a collaborative approach that seeks to blend tasks traditionally performed by either the organization's application development or IT operations teams. An important goal of DevOps is to promote better communication between the two teams and build development pipelines that allow for continuous integration.
In contrast, CloudOps focuses on HA and continuous operation in a public or hybrid cloud. Whereas DevOps-based systems can work in any environment, e.g., in-house or cloud-based, CloudOps technicians focus on the delivery of systems using cloud platforms and services exclusively.
CloudOps is often considered a subset or part of DevOps, as it leverages DevOps principles but within a cloud-based architecture to increase the speed and efficiency of business processes. CloudOps also depends on the availability of continuous operations, which is a key part of the DevOps philosophy.
CloudOps management best practices and trends
When using CloudOps techniques and technologies, several important practices should be considered and put into play, including:
- Ensure that cloud activities are aligned with business requirements and that objectives for costs, security and performance are identified.
- Use resources efficiently by monitoring and analyzing performance and automating tasks such as backups, resource scaling and cloud security management.
- Security is an essential activity that can be assured by using encryption, multi-factor authentication and role-based access; periodic security audits are also essential.
- Continuous performance monitoring ensures that application and infrastructure elements are performing properly and that problems are identified and remedied.
- Automation can be leveraged to schedule and run repetitive processes to save time and minimize human error.
- Ensure that disaster recovery plans are in place and regularly tested.
- Establish and test data backups to protect critical systems and data.
- Proactively manage costs by using tools that analyze cloud expenses and by setting cost controls and budgets.
- Leverage DevOps principles of collaboration across various teams to speed up deployment and improve service quality.
- Provide training for technical teams and users.
- Select a vendor that accommodates SLAs and whose services are consistent with customer needs; be careful about vendor lock-in.
- Maintain flexibility and adaptability to handle business changes and be aware of the most appropriate cloud services.
Perhaps the most important trend impacting CloudOps is the use of AIK, which can dramatically improve CloudOps performance and effectiveness. Some of the ways that AI supports CloudOps are:
- Automation and optimization. AI can automate repetitive processes and use predictive analytics to optimize cloud performance.
- Security performance. Virtually all aspects of cybersecurity management, ranging from threat detection and analysis, can be optimized using AI.
- Cost control. AI-based financial tools can analyze expense trends and recommend ways to improve resource utilization and reduce costs.
- Improving performance. By monitoring all operations and using specific algorithms, AI can identify potential performance and maintenance issues and recommend improvements.
- Enhanced scalability. Again, by monitoring and analyzing specific performance metrics, AI can recommend ways to scale resources based on demand and other factors.
- New service innovation. AI can spur the development of new cloud services and applications, such as services to support edge computing.
By integrating AI into CloudOps (and DevOps), organizations can generate better performance and value from their cloud investments.
To maximize the benefits of cloud computing, establish a structure that aligns the right people with the right roles by getting to know core cloud team roles and responsibilities.






