
carloscastilla - Fotolia
What SD-WAN devices do I need in an SD-WAN deployment?
Despite the software-centric nature of software-defined WAN, certain SD-WAN devices are still required to help transport traffic and complete network connections.
A software-defined WAN may sound like a software-only proposition, but the name obscures the fact that SD-WAN devices are still required. In reality, an SD-WAN needs underlying hardware because hardware is the target and transport for all SD-WAN operations.
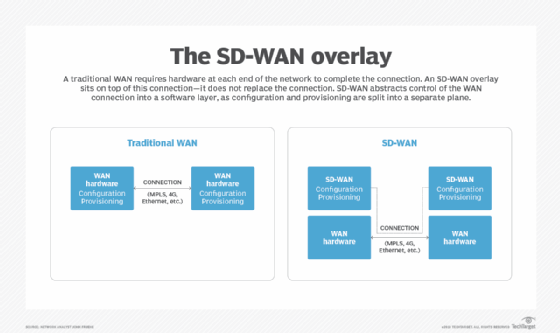
Any traditional WAN service requires hardware at each end of the network to complete the connection, and an SD-WAN sits on top of this connection -- it does not replace the connection.
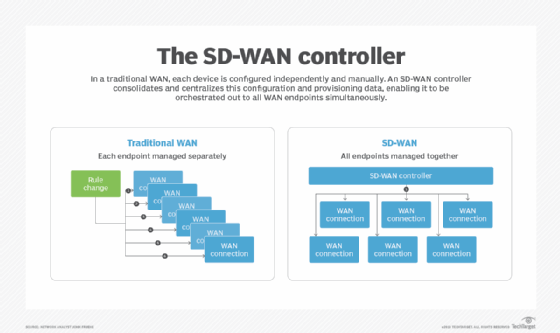
A traditional WAN maintains all control and provisioning information at the hardware level, and each device is configured independently and manually. An SD-WAN centralizes this configuration and provisioning data in a repository, enabling it to be orchestrated out to all WAN endpoints simultaneously.
By looking at the SD-WAN architecture, you'll see both an overlay (the SD-WAN) and an underlay (the WAN hardware). In this split of configuration and provisioning into a separate plane, SD-WAN abstracts the control of the WAN connection into a software layer that sits on top of the underlying hardware.
What is an SD-WAN controller?
At the center of any SD-WAN service is the SD-WAN controller. The controller is software that runs on a server -- not specialized networking hardware -- maintaining all the configuration, provisioning and business rules for managing the different WAN connections.
The SD-WAN controller enables the management of all WAN connections holistically across a network. This consolidation and orchestration strategy will enable the SD-WAN controller to maintain all of the WAN connections for better efficiency.
What are SD-WAN routers?
The traditional WAN connection is often a WAN line card or data center router on the enterprise side and typically a router at the branch location. An SD-WAN router is essentially a WAN endpoint that is specific to the SD-WAN service.
Technically, an SD-WAN can sit on top of traditional WAN infrastructure. But, for most providers to deliver all their special features, they ask customers to install the vendor-provided SD-WAN devices, which are sometimes called SD-WAN routers or SD-WAN appliances. These devices are more tied to the SD-WAN controller, giving the controller greater authority over the connection.
Some vendors, such as Cisco, deliver SD-WAN capability over a wide range of their standard routing products. Other vendors, such as Silver Peak or VeloCloud (now part of VMware), recommend using their specialized SD-WAN routers in order to take advantage of their additional special features.
The advantages of SD-WAN
A business would want to deploy an SD-WAN for several reasons. Some of the top SD-WAN benefits include the following:
- network automation by reducing repetitive tasks;
- consistent endpoint configuration that reflects the proper network rules; and
- added flexibility that eases deployment of multiple WAN endpoints at each branch site, which provides more cost-effective transport and better redundancy.







