Implementing SAP Enterprise Buyer and other SAP supply components
SAP components are the underlying technologies that enable the SAP business scenarios. In this section, learn to define SAP SRM by key SAP components, such as SAP Business Information Warehouse (SAP BW), SAP Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI), SAP Enterprise Portal (SAP EP).
 |
|
Enhancing supplier relationship management using SAP SRM
Chapter 2: SAP SRM -- An Introduction
SAP components such as SAP Enterprise Buyer, SAP Bidding Engine and SAP Enterprise Portal are the underlying technologies in SAP business scenarios. This section describes how SAP Enterprise Buyer (SAP EBP) is the execution hub for most supply processes in SAP SRM. It also discusses SAP Bidding Engine, SAP Enterprise Portal (SAP EP) and other SAP SRM-related components.

Enhancing supplier relationship management using SAP SRM, Ch. 2
Table of contents:
![]() The benefits of SAP supplier relationship management (SRM)
The benefits of SAP supplier relationship management (SRM)
![]() Understanding supply processes and concepts in SAP SRM
Understanding supply processes and concepts in SAP SRM
![]() Implementing SAP Enterprise Buyer and other SAP supply components
Implementing SAP Enterprise Buyer and other SAP supply components
2.5 SAP Components
SAP components are the underlying technologies that enable the SAP business scenarios. The key SAP components are listed below and described in some detail in the remainder of Section 2.5:
- SAP Enterprise Buyer (SAP EBP)
- SAP Bidding Engine
- SAP Supplier Self-Services (SAP SUS)
- SAP Catalog Content Management (SAP CCM) or SRM-MDM Catalog
- SAP Business Information Warehouse (SAP BW)
- SAP Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI)
- SAP Enterprise Portal (SAP EP)
Let´s explore these in more detail now.
2.5.1 SAP Enterprise Buyer (SAP EBP)
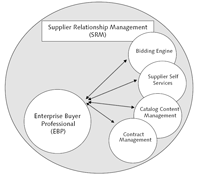
SAP EBP promotes self-service procurement. It is a Web-based solution that provides the complete procurement process for the procurement of both direct and indirect goods and services. The process begins with the creation of a shopping cart and ends with the entry of an invoice. SAP EBP is the execution hub for the majority of processes within SAP SRM, as shown in Figure 2.6.
Most organizations initiate their supplier-relationship management journey with implementing the EBP component in SAP SRM. Once implemented, EBP acts as a catalyst for all the other components. For example, the SAP CCM component is not used by itself; instead, users creating shopping carts or purchasing professionals creating purchase orders in EBP use catalogs to quickly search for and order products and services.
2.5.2 SAP Bidding Engine
|
||||
The Bidding Engine is an Internet solution that provides organizations the ability to strategically source and obtain optimal prices for goods and services. Tools such as RFx, Auctions, Reverse Auctions, and Bid Evaluation enable organizations to create and process bid invitations and Auctions to source products and services. Suppliers access the bid invitations using a Web browser where they can submit bids and access all the details of the bid.
As an example of how organizations might use the Bidding Engine capabilities is as follows, let's say your company wants to replace all the existing computers because they're getting outdated and wants to purchase state-of the-art laptops for all 5,000 users in the organizations.
This type of a purchase could cost an organization anywhere from $75,000 -- $100,000 just in equipment purchase, apart from the services and maintenance cost. Organizations could use the SAP Bidding Engine to invite a select group of suppliers such as Dell Corporation, IBM Corporation or HP. to a Bidding Event where they would get competitive bids electronically. Your company can then evaluate the bids received in an electronic manner based on a number of different criteria and select the most suitable supplier to contract the purchase.
2.5.3 SAP Supplier Self-Services (SAP SUS)
Supplier Self-Services, or SUS, is a hosted Internet solution that provides an integrated application for organizations to collaborate with their business partners. A Web browser such as Internet Explorer is all that is required for accessing SAP SUS. This offers smaller and mid-sized suppliers the opportunity to electronically integrate the procurement processes without the need for their own sales systems. SUS provides hosted order-management capabilities, including purchase-order processing, goods-receipt confirmation, invoice entry and the ability to view the payment status.
Organizations can invite strategic suppliers that are smaller in size and those that do not have the capability to exchange business documents electronically using XML or EDI. By enabling smaller suppliers with supplier self-services capabilities, your organization can ensure that documents are delivered to the supplier electronically via a hosted solution. Supplier organizations can assist in order collaboration and can acknowledge the PO receipt and delivery of the goods and services electronically, alleviating the manual efforts required by your purchasing department.
Also, suppliers can enter invoices electronically using SUS, and these can then be sent to the appropriate individuals in your organization for proper approvals using workflow prior to payment. This can reduce the manual efforts for your accounts payable department to enter invoices.
2.5.4 SAP Catalog Content Management (CCM)
SAP CCM is a new solution offering as of release SAP SRM 4.0 that enables organizations to manage enterprise and supplier content. Users can search for products and services using a robust search tool with added flexibility to search cross-catalogs, comparisons, and get detailed information on products or services. SAP CCM is a competitive offering to the widely used BugsEye and Emerge products offered by Requisite. SAP support for Requisite products expired in 2005. This means that organizations that have been using the Requisite applications with the previous SRM releases will have to decide whether to implement SAP CCM or enter into a new independent contract with Requisite.
Additionally, your organization might need to evaluate whether it will implement SAP CCM or NetWeaver Master Data Management (MDM), given that SAP has announced the strategic shift in content-management strategy in May 2006. SRM- MDM Catalog will be the strategic content-management offering by SAP beginning in Q4 2006, and all new SRM customers are being advised to implement SRM-MDM catalog instead of SAP CCM. There will be some confusion for customers on the selection of the right catalog solution. Chapter 6 will help clarify this for you.
2.5.5 SAP Business Information Warehouse
Business Information Warehouse (sometimes shortened to Business Warehouse or BW) is a packaged, comprehensive business-intelligence (BI) product centered around a data warehouse that is optimized for (but not limited to) the R/3 environment from SAP. SAP BW is an integral component of the SAP suite of applications with an added advantage of being a software package that can be used in both SAP and non-SAP environments.
It is important to note that all analytics in SAP SRM are powered by the business warehouse. This is one reason why SAP´s BI solution is integrated as a component within the SAP SRM solution offering; organizations really need to implement to enable analytics in SRM. The positive aspect for organizations is that they can quickly use more than 100 reports and queries that are provided via the standard content in BW for SAP SRM. SAP pre-delivers these reports for SAP SRM that can be used out of the box.
2.5.6 SAP Exchange Infrastructure (SAP NetWeaver Exchange Infrastructure)
SAP NetWeaver Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI) provides open integration technologies that support process-centric collaboration among SAP and non-SAP applications, both within and beyond enterprise boundaries. SAP XI is a middleware solution that organizations can use to exchange data between SAP SRM and business partner systems or electronic marketplaces, over the Internet. SAP XI is used in SAP SRM, to integrate processes between SAP EBP, SAP SUS, and SAP CCM.
Organizations that want to exchange business documents such as purchase orders, acknowledgements, and invoices electronically via XML or EDI with their suppliers need to implement the SAP XI component.
2.5.7 SAP Enterprise Portal (SAP NetWeaver Portal)
SAP NetWeaver Portal unifies key information and applications to give users a single view that spans IT siloes and organizational boundaries. With the SAP NetWeaver Portal, you can quickly and effectively integrate SAP solutions, third-party applications, legacy systems, databases, unstructured documents, internal and external Web content, and collaboration tools.
2.6 Summary
Thus far, we have talked about supplier relationship management in general and have briefly defined the SAP SRM solution. In this book, we will try to describe in detail the functionality available in SAP SRM. Chapters 3, 4, and 5 focus on SAP supply core processes: operational procurement, strategic sourcing, and supplier enablement respectively.
In Chapter 3, we discuss in detail operational procurement, which is primarily enabled using the EBP component. We will introduce the concept of the shopping cart in SRM, which is similar to a requisition in SAP R/3. In addition, we discuss in detail the business scenarios: Self-Service Procurement, Plan-Driven Procurement, and Services Procurement.
You can download a pdf of this chapter. You can also visit SAP Press to purchase a copy of Enhancing Supplier Relationship Management using SAP SRM.
You'll find more downloadable excerpts from books by SAP experts in our SAP chapter download library.