
ra2 studio - Fotolia
6 multi-cloud storage challenges that affect strategic plans
Using multiple cloud storage providers can affect more than just how and where your data is stored. Discover the areas you need to consider to improve performance and costs.
Before implementing a multi-cloud storage strategy, it's crucial to determine what data will be stored, how it will be stored, the amount of data to be stored and how the data will be moved and transformed along the way. Doing all of this entails a number of challenges.
For instance, how do issues such as security, privacy and management come into play? Privacy and security are a particular concern for any aspects of cloud management that involve data, such as storage. Other areas that can raise potential issues include cloud services integration, slow or unreliable data networks, application delivery and workflow management, costs and a shortage of cloud skills.
In spite of these challenges, a multi-cloud storage strategy can increase flexibility, improve application performance and, if done properly, lower costs. Here are six areas you must factor into your multi-cloud to ensure the safety of your organization's cloud data storage, maximize performance, keep costs under control and ensure adequate staffing.
Challenge No. 1. Privacy and security
A multi-cloud storage strategy must consider a variety of security and privacy concerns. The use of multiple cloud services increases the number of attack surfaces and the potential for compromised data.
The more cloud storage services you employ, the greater the risks. Complicating matters even further is the increase in regional compliance and privacy laws, such as the European Union's GDPR.
The cloud platforms you choose should properly secure data -- using advanced encryption algorithms, for example -- as well as authenticate users, control access levels and safeguard against malware and other attacks.
Cloud providers offer limited visibility into their systems while taking different approaches to data protection, making multi-cloud security even more complex. In addition, traditional security tools were not designed for a multi-cloud infrastructure, while newer tools are not yet mature enough to provide an all-encompassing security offering.
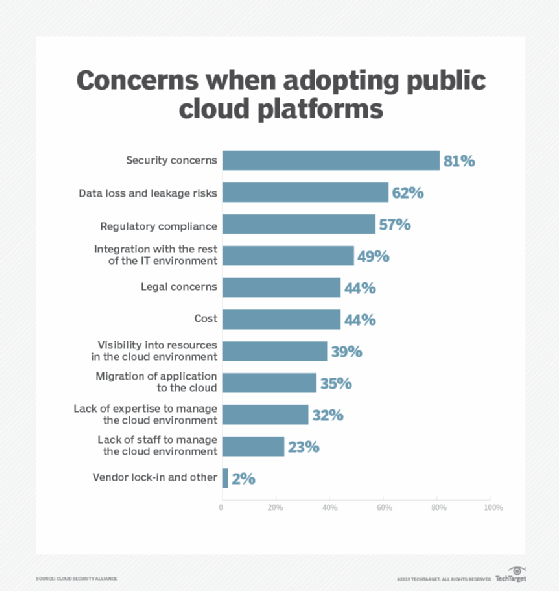
These security issues point to the larger management concerns that come with a multi-cloud strategy. Each service takes a unique approach to management, supporting different portals, tools and processes. Here, too, third-party tools are playing catch-up, which is made all the more difficult by the cloud's dynamic nature. System monitoring also becomes more complicated with each added service, especially given the cloud's abstracted nature.
Challenge No. 2. Integration of cloud services
The disparate systems that make up a multi-cloud infrastructure must communicate seamlessly with one another so data can effectively and safely move across environments. Unfortunately, cloud services use diverse methodologies and programming languages and offer different APIs that can conflict with one another, making it difficult to connect and manage systems in a unified way.
To avoid these issues, evaluate the tools offered by the cloud platforms and their efficacy and limitations. In addition, assess the platform's available APIs to ensure they're standards-based and support the functionality necessary to provide seamless integration with other platforms and systems.
Challenge No. 3. Latency inherent in data networks
The data networks that connect users and applications with stored data can be a problem. If connections are slow or unreliable, they can lead to high latency rates that can negatively affect application performance.
Even with reliable networks, distance can lower performance thresholds. If the data stores are hundreds or even thousands of miles from users or applications, performance can slow to a crawl.
Challenge No. 4. Application delivery and workflow management
A multi-cloud storage strategy also complicates application delivery and workflow management. Because platform configuration settings vary among providers, deploying the same application to different platforms requires provider-specific configurations.
In addition, not all services support the same functionality, further complicating application deployment. Migrating data can be more challenging, even with only a minimal number of services.
Although the focus might be on the storage component, all aspects of application delivery are affected by your choices. To this end, tools should provide a high degree of flexibility and integration. The challenge here is that multi-cloud technologies and tools are still in their infancy, although the list of options continues to grow.
Another consideration is how your multi-cloud storage strategy will affect other systems and processes. For example, if your organization follows a DevOps methodology for building and deploying apps, the multi-cloud infrastructure should enhance those application delivery capabilities. The storage services must seamlessly integrate with the DevOps tools that support the delivery pipeline.
Challenge No. 5. Cost issues
Another challenge with a multi-cloud storage strategy is maintaining effective cost controls. Although a multi-cloud approach can potentially lead to reduced costs, multiple platforms can translate into multiple fee structures and all the complexities and confusion that go with them.
The greater the number of cloud services involved, the more difficult it becomes to assess the different pricing structures, especially when weighing issues such as performance, functionality and compliance.
Challenge No. 6. Skilled professionals
Organizations must ensure their staffs have the skills necessary to develop, customize and maintain systems and applications that will accommodate the different and evolving cloud storage environments. Finding professionals with these skills can be difficult and expensive, increasing overall costs even more.
You will need to determine what it will take to manage and monitor the multi-cloud environment. Then, evaluate which tools and skills you have on hand and what you'll need to acquire.
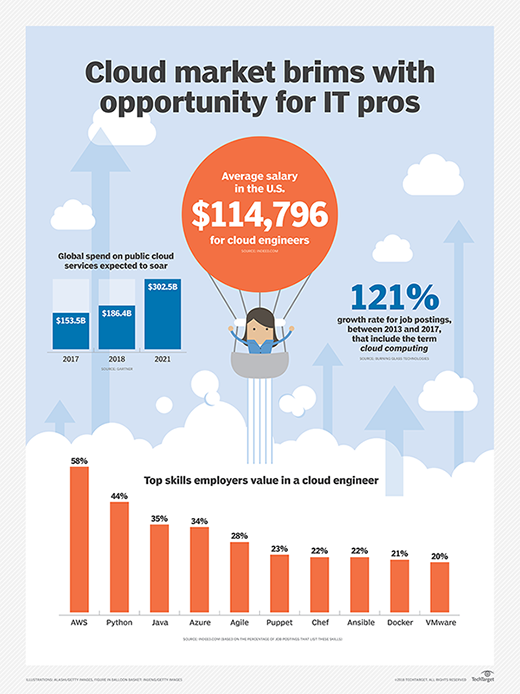
Going forward, your IT staff will need to be knowledgeable in a number of areas, such as cloud architecture, coding and data analysis. Ensure you have the right skills and infrastructure in place before you deploy your workloads to the cloud.







