cloud data management
What is cloud data management?
Cloud data management is a way to manage data across cloud platforms, either with or instead of on-premises storage. The cloud is useful as a data storage tier for disaster recovery, backup and long-term archiving.
With cloud data management, organizations can purchase resources as needed. They can also share data across private and public clouds, as well as in on-premises storage. A cloud-based data management system takes on the function of a traditional data management system tailored to the needs of the cloud.
How does cloud data management differ from traditional data management?
Although some platforms can manage and use data across cloud and on-premises environments, cloud data management considers that the data stored on premises and the data stored in the cloud can be subject to completely different policies. Data stored in the cloud has its own rules for data integrity and security. Traditional data management methods might not apply to the cloud, so having management in place designed for the cloud's unique requirements is vital.
The following are some key differences between traditional and cloud data management:
- Traditional data management focuses on on-premises storage, whereas cloud data management uses a cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud data management offers greater scalability and flexibility, as storage can be easily scaled up or down, depending on business requirements, without the need for upfront hardware investments. With traditional storage management, organizations must purchase hardware to scale storage.
- Cloud data management offers easy access to data from any location with network connectivity. It offers dynamic file sharing and collaboration, letting numerous users access and work on the same data at the same time. Traditional data management, on the other hand, can require physical access to the storage infrastructure or rely on more limited sharing options.
- In conventional data management, organizations handle tasks such as storage maintenance, backup, disaster recovery and security. Cloud data management shifts many of these responsibilities to the service provider, easing operational burdens for organizations. However, the organization remains accountable for data management and compliance with protection regulations.
- Traditional data management often involves substantial upfront costs for equipment, software licenses and maintenance. Cloud data management, on the other hand, is often based on a pay-as-you-go approach in which organizations only pay for the storage and data management services they use. This can result in cost savings, particularly for enterprises with changing storage requirements.
What are the benefits of cloud data management?
The numerous benefits of cloud data management often mimic those of cloud services in general. Some of the benefits commonly associated with cloud data management include the following:
- Pay-as-you-go pricing. Cloud service providers generally bill subscribers on a per gigabyte, per month basis. This means that organizations don't have to purchase storage hardware. Instead, they pay only for the cloud storage they consume.
- Scalability. One of the challenges associated with on-premises storage is that storage consumption must be closely monitored to avoid running out of space. When the available storage is depleted, the organization must purchase additional storage hardware that meets its anticipated future needs. In contrast, cloud storage providers have a nearly unlimited amount of storage that's readily available at any time. Organizations never have to worry about running out of storage or engaging in complex capacity planning tasks.
- Anywhere access. The very nature of the cloud means that data is accessible from anywhere.
- Zero maintenance. Public cloud providers handle all required maintenance, meaning that organizations never have to worry about replacing failed hard disks, performing hardware refreshes or installing firmware updates.
- Security. Cloud providers invest tremendous financial resources in data security and keeping their platforms secure. The result is that cloud storage is likely to be more secure than an organization's on-premises storage. But the security of data that's stored in the cloud comes down to the security policies the organization puts in place.
- Automated backups. Some -- but not all -- cloud providers automatically back up data stored in the cloud. Some cloud backup services even provide immutable point-in-time data backup capabilities, which can help keep data protected against ransomware.
- Improved data quality. Many cloud data management platforms are designed to centralize data, thereby letting a single data set be used throughout the organization. This approach helps eliminate duplicate data, driving down storage costs while also eliminating the inconsistencies that often exist across data sets.
- Disaster recovery. Cloud storage offers a dependable data backup option. Data saved in the cloud can be swiftly restored in the event of hardware failure, natural catastrophes or other emergencies, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
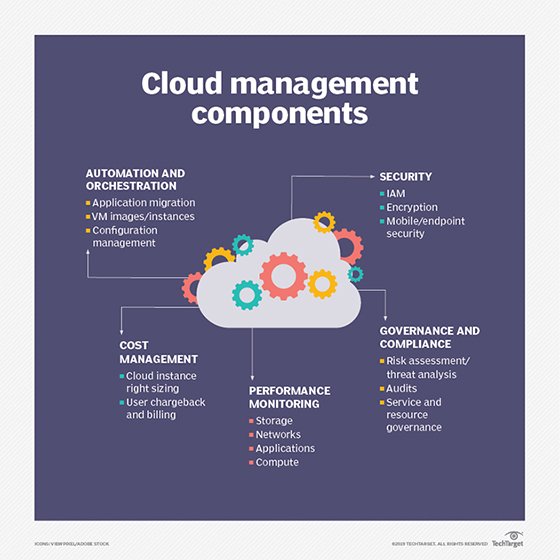
What are the challenges of cloud data management?
Most cloud data management challenges are the same drawbacks cited for cloud technologies. These challenges include the following:
- Cost. Even though the cloud is often marketed as being an inexpensive data storage option, storing large amounts of data in cloud data lakes or cloud databases can be expensive.
- Data egress fees. Most cloud providers charge a data egress fee if customers decide to move data out of the cloud. These fees apply whether the data is being moved back on premises or to another cloud. Data egress fees are designed to discourage organizations from removing their data from the cloud where it currently resides, and therefore, tend to be expensive.
- Data integrity. Similar to on-premises copy data management platforms, cloud-based systems need a way of ensuring integrity. This often means avoiding duplication and resolving conflicts between contradictory records and taking other steps to ensure data accuracy.
- Security. Although cloud security has improved dramatically over the last several years, it's ultimately up to each organization to establish data access policies that ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Vendor lock-in. When relying on a single cloud service provider, businesses can encounter vendor lock-in issues. Switching cloud providers or migrating data to an on-premises environment can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Complexity and skills gap. Cloud data management can be complicated, requiring particular knowledge and abilities. Organizations can face difficulties managing complex data landscapes, putting in place data governance frameworks and ensuring effective data management processes.
Cloud data management use cases
There are countless use cases for cloud data management for businesses. Common use cases of cloud data management include the following:
- Deployment. Cloud data management can simplify the process of provisioning test and development environments because test environments can easily be spawned from production data sets.
- Sharing data between multi-cloud environments. Cloud data management also makes it easy to share data among multiple cloud applications. Because a single data set is shared, that data can act as a single source of the truth rather than each app using its own siloed data set.
- Data backup and recovery. Cloud data management offers a dependable and flexible alternative for the backup and recovery of data. Organizations can safely store their data on the cloud, assuring data security and enabling speedy recovery in the event of data loss or system failures.
- Data analytics and business intelligence. Cloud data management lets businesses use cloud-based analytics services and tools to process and analyze enormous amounts of data. Organizations that store data on the cloud can easily access and study data to get useful insights and make data-driven choices.
- Data integration and extract, transform, load. By providing scalable and flexible infrastructure, cloud data management streamlines data integration and ETL operations. Data from diverse sources can be integrated, transformed and loaded into cloud-based data warehouses or analytics platforms for further processing and analysis.
- Data governance and compliance. Cloud data management assists enterprises in meeting data governance and compliance needs. It helps enterprises build data governance frameworks, enforce data security and privacy rules and ensure compliance with requirements such as General Data Protection Regulation or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
- Long-term storage and data archiving. Cloud storage provides a cost-effective option for data archiving and long-term storage. Organizations can use the cloud to offload infrequently accessed data, lowering storage costs while assuring data durability and availability.
Best practices for managing data in the cloud
Cloud data management is different from cloud storage, although cloud storage is an underlying requirement for cloud data management. Cloud data management is more about managing data integrity, data access and data growth. As such, there are several best practices to consider, including the following:
- Define the goals of the project. The first step in any cloud data management project is to define what the organization hopes to accomplish. Without clear goals, it's impossible to implement a cloud data management strategy that's well-suited to the organization's unique needs.
- Decide what data sets will benefit from being moved to the cloud. Although a case can be made for migrating all data to the cloud, there might be benefits to leaving certain data sets in on-premises data centers. For example, an application that's sensitive to latency will likely need the data to remain near the application, which might rule out the use of cloud services.
- Automate data protection. Many cloud providers automatically back up data, but if the provider's data protection practices don't comply with an organization's service-level agreements, then they must set up their own automated data protection strategy.
- Ensure data security. Deploy strong security measures to protect data in the cloud. This involves employing strong access controls, encryption and multifactor authentication. Monitor and audit data access regularly and adopt security best practices provided by the cloud service provider.
- Aggregate and centralize data. Data aggregation and centralization on the cloud can improve data accessibility and simplify data management processes. This entails gathering data from multiple sources and storing it in a centralized repository.
- Set up backup and disaster recovery plans. Set up backup and DR policies to promote business continuity and minimize data loss in the event of a disaster. This involves regular backups, off-site storage and recovery procedure testing.
Cloud data management companies and products
There are numerous cloud data management products available on the market. However, it's important to evaluate specific requirements when selecting providers.
Examples of cloud data management providers include the following:
- Actifio. Actifio, acquired by Google in 2020, enables copy data management in multi-cloud environments as well as native application integration. This means that data that previously resided on premises can be immediately reused in the cloud. Additionally, the Actifio automation platform is accessible through the REST API, meaning that it's easy to integrate.
- Amazon Web Services. AWS provides scalable and affordable cloud computing services, as well as data management options.
- Box. Box offers safe cloud workflow and content management options that guarantee data residency, privacy and industry compliance.
- Cohesity Data Management as a Service. DMaaS is designed to eliminate mass data fragmentation by eliminating data siloes and bringing all of an organization's data together in a single platform. This platform can be used for disaster recovery, long-term retention and archival and ransomware recovery.
- Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud. Informatica offers a cloud platform for data management powered by artificial intelligence (AI). It provides open and flexible options, supports multi-cloud and hybrid settings and uses AI and machine learning to enable low-code and no-code data management.
- NetApp. NetApp provides enterprise cloud services such as cloud storage and data management tools. Its services attempt to boost productivity by simplifying data administration.
- Rubrik. The Rubrik Cloud Data Management scale-out platform uses a single interface to manage data across public and private clouds. In addition to offering ransomware recovery, Rubrik's platform was the first to support hybrid cloud environments.
What is the future of cloud data management?
The following key aspects and events are likely to shape the future of cloud data management:
- AI and machine learning integrations. Cloud data management systems that incorporate AI and machine learning will improve automation, analytics and decision-making. This will enable more intelligent data processing and insights, leading to better-informed business strategies. Having most or all of an organization's data in one place helps organizations tap into hidden business insights by making it easier to use machine learning-based big data analytics.
- Management of supply chain disruptions. Because cloud data management can be used to create a single source of truth, it lets organizations act on data in near real time. For example, a well-crafted cloud data management strategy might help an organization better respond to disruptions in its supply chain before they cause a significant problem.
- Data fabric. The concept of data fabric is on the rise, seeking to connect data across diverse storage systems without requiring data duplication or relocation. Using semantic knowledge graphs, metadata management and machine learning, data fabric establishes connections and integration among data sets, enhancing accessibility while ensuring compliance with governance regulations.
- Edge computing integrations. Edge computing is becoming more popular due to the proliferation of internet of things devices and the demand for low-latency computing. Cloud data management will continue to extend its reach to the edge, helping bring data processing closer to the source and reducing latency.
Modern businesses depend on cloud storage because it provides cost-effective, flexible and accessible data management and security. Discover the many benefits and drawbacks of cloud data storage.






