Microsoft Windows Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
What is Microsoft Windows Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)?
Microsoft Windows Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) is a service in Microsoft Windows operating systems (OSes) that allows download from and upload of files to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) web servers and Server Message Block (SMB) file servers.
BITS uses idle network bandwidth to transfer files in the background or foreground so a user's foreground experience is minimally impacted. Disabling the service prevents all applications that depend on BITS from automatically downloading programs and other important information.
BITS takes unused or idle network bandwidth to perform file transfers -- downloads or uploads -- from or to HTTP web servers and SMB file servers. The file transfers -- say, between a client machine and server -- are asynchronous and happen in the foreground or background. This means that, when an application requests BITS for a file transfer, it can freely perform any other task.
BITS includes PowerShell cmdlets for creating and managing transfers and the BITSAdmin command-line utility for creating download or upload jobs and monitoring their progress. The service also includes a queue administration facility to prioritize file transfer requests from applications.
If a disruption or interruption occurs on the network, BITS automatically reconnects and resumes the file transfer when the network or machine returns to service. BITS can pause and resume transfers automatically even after a reboot. It also transfers files when the machine is plugged in and in Modern Standby mode, thus remaining mindful of power usage.
Lifecycle of a Background Intelligent Transfer Service job
A BITS job is a container that holds one or more files to be transferred to or from HTTP web servers and SMB file servers. A job has properties that specify how BITS transfers the files and interacts with the application.
The job's lifecycle begins with its creation. This is when the user specifies the job's priority, whether it is an upload or download and for which events they want to receive notification(s). Once the job is created, files can be added to it -- with a maximum of one file for upload jobs. The job properties can also be changed depending on the application. When adding one or more files to the job, it's important to specify the file's local (client) and remote (server) name.
When jobs are created, BITS automatically suspends jobs. The user must resume the job to activate it in the transfer queue, i.e., to move it from the suspended state to the queued state. It remains in the queued state until the BITS scheduler determines its turn to transfer files. At this point, the job moves to the connecting state, and BITS connects to the remote server. It then moves to the transferring state and remains there until one of four conditions occurs:
- The time slice ends.
- The transfer is complete.
- There is an error.
- The application suspends the job.
The job moves to the transferred state when BITS transfers all its files. The transferred files will only become available to the client when the application calls the IBackgroundCopyJob::Complete method and file ownership is transferred from BITS to the user.
How BITS preserves user experiences
Depending on the idle network bandwidth available, BITS increases or decreases the rate at which files are transferred. If an application starts consuming more bandwidth, BITS automatically decreases the file transfer rate, thus maintaining the user's overall experience and ensuring that background transfers are optimal.
As long as the user who initiated the file transfer remains logged on to the network and a network connection is maintained, BITS continues to transfer files, even if the application itself exits. That said, BITS does not force a network connection if it is lost or if a user logs off. Instead, it first suspends the transfer job and then resumes it after the lost connection has been reestablished or after a logged-off user logs back in.
BITS always considers the cost of the file transfer and the network usage, as well as network congestion. Also, it uses app-specified transfer policies to prevent the transfer of files on costed network connections. These considerations particularly matter on roaming networks where costs can go up quickly. BITS also helps minimize the impact on -- or interference with -- the user's foreground work, ultimately helping to preserve their experience working with the system.
Applications of Background Intelligent Transfer Service
BITS is most useful for system administrators looking to download files from or upload files to HTTP web servers and SMB file shares. In addition, it provides a Component Object Model interface that is useful for C, C++ and .NET programmers. Microsoft does not recommend the BITS application programming interface (API) for Universal Windows Platform programmers. They should use the Windows.Networking.BackgroundTransfer API instead.
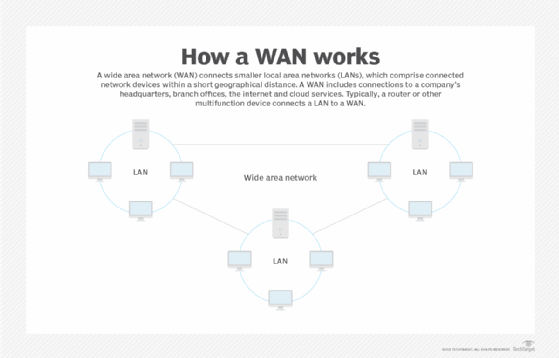
Windows uses BITS to download updates to a user's local system. Many other applications also use BITS, including applications that need to download from or upload files to an HTTP or representational state transfer web server or SMB file server. Applications that need to automatically resume file transfers after network disconnects or computer restarts also use BITS. Finally, BITS can be used to optimize wide area network traffic when used with BranchCache, a WAN optimization technology that is included in some editions of Windows and Windows Server OSes.
Types of transfer jobs and job states in BITS
BITS supports three types of transfer jobs:
- Download job. It downloads files to the client. Also, all files are transferred asynchronously in the foreground or background.
- Upload job. It uploads a file from the client to the server.
- Upload-reply job. It first uploads a file to the server and then receives a reply file from the server application that the upload has been completed.
A BITS job can be in one of four states:
- Starting. By default, the starting state is SUSPENDED. From this state, a user can add files to the job and also set job and file properties.
- Action. Multiple action states are possible that show the current internal activity of the job, such as QUEUED, CONNECTING and TRANSFERRING. Another action state is TRANSIENT ERROR, which indicates that the job failed to transfer the file.
- Transferred. This state happens when the transfer has succeeded and there's no more transferring to be done.
- Final. The job is ACKNOWLEDGED and all completed downloaded files are available.
As a BITS job runs, it transitions between states in the different state classes. But, once it reaches a final state, it won't move out of that state, meaning it's not possible to call any state-changing methods. It also won't show up in a job enumeration. If an error occurs, the job moves to the fatal error state (BITS cannot recover from it) or to the transient error state (the error may resolve itself and BITS retries the job until the transfer is successful or until the job times out within the application-specified period). If a job times out in the transient error state, BITS moves it to the fatal error state.
Background Intelligent Transfer Service priority levels
BITS can intelligently pick which transfer jobs to run and when. This is because the application can use different priority levels: one for the foreground and three for the background. A priority level determines when a transfer job is processed relative to other jobs in the transfer queue, so therefore:
- A higher-priority job takes precedence over a lower-priority job.
- Lower-priority jobs do not receive transfer time until all higher-priority jobs are transferred or are in an error state.
- Jobs at the same priority level share transfer time, so no large job can block the transfer queue and cause delays.
To schedule jobs at the same priority level, BITS uses round-robin scheduling, where each job is given a slice of time to process its files. If a particular job does not complete during its allotted time slice, it automatically goes back to the queued state, and the next job in the queue gets activated on a first-in, first-out (FIFO) basis. Here, it's important to note that BITS does not guarantee FIFO processing, although it does its best.
In BITS 1.5 and earlier, foreground jobs are prioritized over background jobs. In fact, foreground jobs have the highest priority, and BITS only processes one job at a time. In later BITS versions, multiple foreground transfers can happen simultaneously, but multiple files in the same job are always transferred sequentially or serially.
The history of Background Intelligent Transfer Service
Microsoft has updated BITS a number of times:
- Microsoft introduced version 1.0 of BITS in Windows XP in 2001.
- Version 1.2 arrived in mid-2002 to add the Automatic Updates service to Windows 2000.
- Version 1.5 came in late 2003 with Windows Server 2003 and brought command-line support, more upload features and security improvements.
- Version 2.0, released in mid-2004 as an update for multiple OS deployments, added more download features, bandwidth throttling and support for SMB.
- Released in mid-2007, BITS 2.5 added support for IPv6 and custom HTTP headers and better HTTP security.
- BITS 3.0, included with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, added peer caching, notifications, temporary file access, HTTP redirect handling, additional Group Policy controls and event logging.
- BITS 4.0, released in mid-2009 with Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, brought token-based security, standalone file server features, refined bandwidth throttling and revised peer caching.
- BITS 5.0, included with Windows 10 in mid-2016, added improvements to background copy jobs, support for older background copy jobs and the ability to use BITS through APIs and PowerShell cmdlets.
- Version 10.1 of BITS, part of Windows 10 version 1703, also known as the Windows 10 Creators Update, refined download and notification features.
- Version 10.2 of BITS, part of the Windows 10 October 2018 Update, added default proxy ordering, as well as support for Modern Standby and mobile device manager policies and group policies.
- Version 10.3 of BITS, part of the Windows 10 May 2019 Update, enabled the ability to mark HTTP headers as write-only and server certificate validation callback.
Learn how to upload and download files with PowerShell File Transfer Protocol script, and read about eight secure file transfer services for the enterprise.





