infrared radiation (IR)
What is infrared radiation?
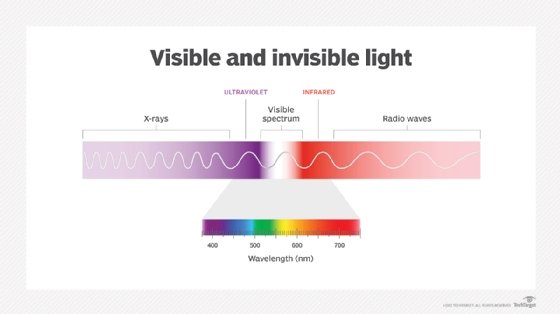
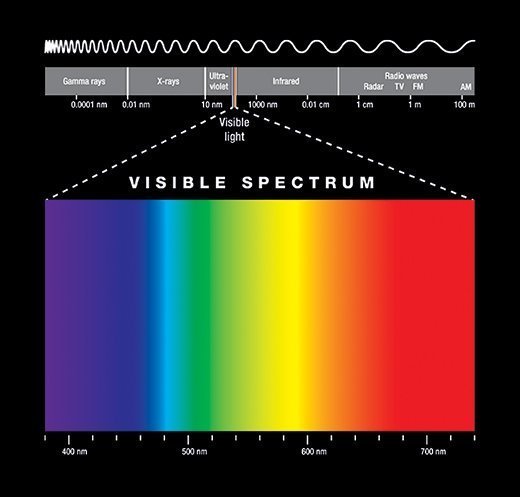
Infrared radiation (IR), sometimes referred to simply as infrared, is a region of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum where wavelengths range from about 700 nanometers (nm) to 1 millimeter (mm).
Infrared waves are longer than visible light waves but shorter than radio waves. Correspondingly, the frequencies of IR are higher than microwave frequencies but lower than visible light frequencies, ranging from about 300 gigahertz to 400 terahertz (THz).
Infrared light is invisible to the human eye, but heat sensors can detect longer infrared waves. Infrared shares some characteristics with visible light, however. Like visible light, infrared light can be focused, reflected and polarized.
Wavelength and frequency
Infrared is typically subdivided into multiple spectral regions, or bands, based on wavelength. However, there is no uniform definition of each band's exact boundaries.
Infrared is commonly separated into near-, mid- and far-infrared. It can also divide into the following five categories:
- Near-infrared.
- Short-wavelength infrared.
- Mid-infrared.
- Long-wavelength infrared.
- Far-infrared.
Near-IR, mid-IR and far-IR define as the following:
- Near-IR. The near-IR band contains the range of wavelengths closest to the red end of the visible light spectrum. Near-IR consists of wavelengths that range from 700 nanometers (nm) to 1,300 nm, or 0.7 microns to 1.3 microns. Its frequency ranges from about 215 THz to 400 THz. This group consists of the longest wavelengths and shortest frequencies, and it produces the least heat.
- Mid-IR. The intermediate IR band, also called the mid-IR band, covers wavelengths that range from 1,300 nm to 3,000 nm, or 1.3 microns to 3 microns. Frequencies range from 20 THz to 215 THz.
- Far-IR. Wavelengths in the far-IR band, which are closest to microwaves, extend from 3,000 nm to 1 mm, or 3 microns to 1,000 microns. Frequencies range from 0.3 THz to 20 THz. This group consists of the shortest wavelengths and longest frequencies, and it produces the most heat.
Infrared radiation uses
Infrared has a variety of uses and applications. Some common uses for IR include heat sensors, thermal imaging and night vision equipment.
In networking, wired and wireless operations use infrared light. Remote controls use near-infrared light, transmitted with LEDs, to send focused signals to home-entertainment devices, such as televisions. Fiber optic cables also use infrared light to transmit data.
In addition, astronomers extensively use infrared to observe objects in space that the human eye can't detect, such as molecular clouds, stars, planets and active galaxies.
History of infrared radiation technology
British astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered infrared in 1800. Herschel knew sunlight could separate into components, which occurs when light refracts through a glass prism. He then measured the temperatures of the different colors created.
Herschel found the temperature increased as the colors progressed from violet all the way to red light. Herschel then went a step further and measured the temperature in the portion beyond the red area. There, in the infrared area, he found the temperature was the highest of all.
Editor's note: This article was reformatted to improve the reader experience.






