
Getty Images
How to set up Windows Hello for Business, step by step
Licensing for Windows Hello for Business is a simple process, but the setup involves making several decisions, including how to host the service, authentication types and more.
If organizations want to deploy Windows Hello for Business, they need to make some key decisions before embarking on the actual setup process.
Everything from authentication methods and password/PIN complexity to trust type and deployment model. The most important decisions are the deployment model and the trust type that should be used. Both of which are dependent on the eventual use cases that should be supported.
As part of the deployment process, organizations should follow the setup process and ensure the Windows Hello for Business configurations match internal security best practices and regulations.
How to choose Windows Hello for Business deployment models
In the context of Windows Hello for Business, the deployment model is basically referring to the usage of Windows Hello for authentication toward applications. There are three different deployment models:
- Cloud-only. The cloud-only deployment model is for organizations that only have cloud identities and don't access on-premises resources.
- Hybrid. The hybrid deployment model is for organizations that have their identities synchronized from Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID -- also known as a hybrid identity, and need a single sign-on (SSO) experience toward on-premises and cloud resources.
- On-premises. The on-premises deployment model is for organizations that don't have cloud identities and that only need SSO experience toward on-premises resources.
The most commonly used deployment model is the hybrid deployment model. That is mainly due to the fact that many organizations still rely on a hybrid identity and want to have an SSO-experience toward on-premises and cloud resources.
Windows Hello for Business trust types
Besides the deployment model, it's also important to determine the trust type for the deployment. The trust type is basically referring to how Windows Hello for Business authenticates toward Active Directory. The trust type doesn't affect the authentication toward Microsoft Entra ID, so it's not applicable to the cloud-only deployment model of Windows Hello for Business. There are three different trust types:
- Cloud Kerberos. The Cloud Kerberos trust type enables users to authenticate with on-premises resources by relying on Microsoft Entra Kerberos and requesting a Kerberos ticket directly via Microsoft Entra ID.
- Key. The key trust type enables users to authenticate with on-premises resources by relying on a device-bound key that is created during the provisioning of Windows Hello for Business.
- Certificate: The certificate trust type users to authenticate with on-premises resources by relying on a certificate that was requested. It uses a device-bound key that is created during the provision of Windows Hello for Business.
The latter two options both rely on certificate-based Kerberos to request the required tickets for on-premises authentication. With that, the implementation for those trust types would require the implementation of a public key infrastructure (PKI), which would make the implementation more complex.
To simplify the hybrid deployment of Windows Hello for Business, Microsoft introduced the first option. That option removes the requirement to implement a PKI. The removal of that requirement also makes Cloud Kerberos trust the recommended deployment model for Windows Hello for Business hybrid, unless there are specific certificate requirements.
How to configure Windows Hello for Business basics with 2 methods
Windows Hello for Business configuration typically contains two levels of configuration options: the basic and advanced options. The basics are always required and are focused on the standard cloud-only deployment, while the advanced options are focused on configuring more specific deployment scenarios that might not apply to every organization.
That also means that it always starts with the basics. When looking at Microsoft Intune, there are two methods available to configure the basics. The first method is to configure Windows Hello for Business by default for all Intune-enrolled Windows devices, and the second method is to configure Windows Hello for Business only for specifically assigned Windows devices.
Method 1: Configure Windows Hello for Business via enrollment options
The first method to configure Windows Hello for Business is by using Intune device enrollment. These options allow IT administrators to configure Windows Hello for Business immediately during the enrollment process of Windows devices into Microsoft Intune via these steps:
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Enrollment > Windows > Windows Hello for Business.
- On the Windows Hello for Business blade that slides over the screen, as shown below in Figure 1, configure at least the following settings to enable Windows Hello for Business with the minimal required security and click Save.
- Configure Windows Hello for Business. Select Enabled to enable Windows Hello for Business by default on all enrolled Windows devices.
- Use a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). Select Required to add an additional layer of security on all Windows devices that have a TPM available.

IT can tweak the remaining settings to further customizing Windows Hello for Business based on organizations specific requirements. That can be related to the PIN requirements, and to the usage of biometrics, phone sign-in and security keys.
Method 2: Configure Windows Hello for Business via an account protection policy
The second method to configure Windows Hello for Business is by using an account protection profile, which allows IT to configure Windows Hello for Business for specifically assigned Windows devices only. That profile contains a template with configuration settings that are currently related to Device Guard and Windows Hello for Business. All the settings within that profile are coming straight from the settings catalog in Microsoft Intune.
The following steps show how to configure Windows Hello for Business for specifically assigned Windows devices:
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Endpoint security > Account protection.
- On the Endpoint security | Account protection page, click Create Profile > Windows > Account Protection.
- On the Basics page, provide a unique name to distinguish the Account Protection profile from other similar profiles and click Next.
- On the Configuration settings page, as shown below in Figure 2, configure the following settings to enable Windows Hello for Business with the minimal required security for all assigned Windows devices and click Next.
- Use Windows Hello for Business. Select true to enable Windows Hello for Business by default on all assigned Windows devices.
- Require Security Device. Select true to add an additional layer of security on all Windows devices that have a TPM available.

- On the Scope tags page, configure the applicable scope tags and click Next.
- On the Assignments page, configure the devices that should be assigned with this Account Protection profile and click Next.
- On the Review + create page, review the configuration of the Account Protection profile and click Create.
The remaining settings can further customize Windows Hello for Business with organizations specific requirements. That can be related to the PIN requirements, and to the usage of biometrics.
Configuring the advanced capabilities of Windows Hello for Business
The more advanced capabilities of Windows Hello for Business are mainly focused on the complicated deployment scenarios that require on-premises authentication. For those scenarios, the preferred and easiest route would be using Cloud Kerberos trust. That route requires two configurations.
First, the IT administrator must enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos in the environment, as that would enable Microsoft Entra ID to generate tickets that can be used to authenticate with the on-premises environment via Active Directory.
The second configuration would be telling Windows Hello for Business to use Cloud Kerberos trust for authentication to on-premises resources. To accomplish this, admins can use an Intune Settings Catalog profile, which contains the required settings to enable that configuration. The following steps walk through the process of creating a Settings Catalog profile to configure the usage of Cloud Kerberos trust for specifically assigned Windows devices.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration.
- On the Windows | Configuration page, click Create > New Policy > Windows.
- On the Basics page, provide a unique name to distinguish the Settings Catalog profile from other similar profiles and click Next.
- On the Configuration settings page, configure the Use Cloud Trust For On Prem Auth to enable the usage of Cloud Kerberos trust with Windows Hello for Business for all assigned Windows devices. Then click Next.
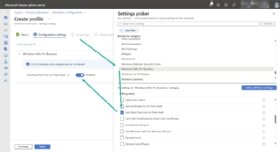
- On the Scope tags page, configure the applicable scope tags and click Next.
- On the Assignments page, configure the specific devices that should receive this settings catalog profile and click Next.
- On the Review + create page, review the configuration of the settings catalog profile and click Create.
Peter van der Woude works as a mobility consultant and knows the ins and outs of the ConfigMgr and Microsoft Intune tools. He is a Microsoft MVP and a Windows expert.







