session ID
What is a session ID?
A session ID, also called a session token, is a unique identifier that a web server assigns to a user for the duration of the current session. A session is a finite period of interaction between a web client and server. The session provides a structure for carrying out related operations between the user and the website. The session ID is integral to ensuring the continuity of operations throughout the session.
Web servers use sessions and session IDs because they typically rely on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to facilitate communications between the server and connecting web browsers. HTTP, along with HTTP Secure (HTTPS), are stateless protocols, which means they do not maintain state between requests and responses. Each request is independent of all other requests, even if those requests come from the same user on the same device and they occur one right after the other.
Sessions and session IDs provide a mechanism for tying those requests together, making it easier to carry out tasks such as filling out multipage forms or tracking items in an online-shopping cart.
Web servers that issue session IDs use various methods to persist the IDs throughout the life of the session. The most common approach is to store the session ID as a cookie on the user's browser. A cookie is a small amount of data that contains information about the user, session, environment or user's activity. A cookie that holds a session ID is typically deleted after the session has been terminated, although it might instead be configured to expire on a specific date and time.
In some cases, such as when cookies are disabled on the browser, the session ID might be appended to the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) rather than being stored in a cookie. However, the URL approach can increase the risk of exposing the session ID, making it easier to hijack the session. It can also skew search engine results because of the way the webpages are indexed. Another option is to include the session ID in a hidden form field that is persisted throughout the session, although that approach also has several limitations.
How do session IDs work?
Some web servers generate session IDs by simply incrementing static numbers, but that method leaves the site vulnerable to hackers who use prediction techniques to guess the session ID. Most web servers now use special algorithms to create more complex identifiers. For example, the session IDs might be much longer, include a mix of alphanumeric characters and symbols, or incorporate variables such as the date and time values.
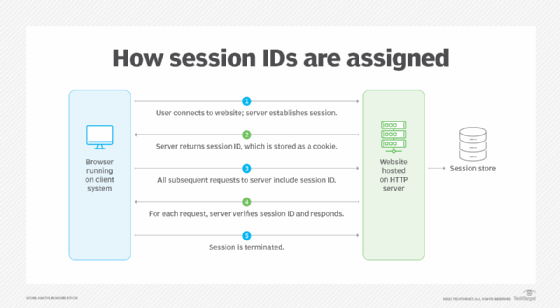
The process of assigning session IDs to unique user sessions generally follows a similar pattern from one website to the next:
- The user connects to the website on the HTTP server. After the connection is verified, the server establishes a session between the browser and the website. In some cases, the server does not create the session until the user logs into the site.
- The server tracks the session-related information and maintains it in a data store, such as a file system or database. The tracking process might involve creating a session object that defines the session's properties, depending on the technology used. The server also generates a session ID and transmits it to the user's browser. The identifier is usually stored as a cookie on that browser.
- For all subsequent requests to the server, the browser includes the session ID. In this way, the server can track all the state data associated with the current session.
- The server confirms the session ID for each request. If the session ID can be verified, the server carries out the requested operation.
- The session is terminated, which invalidates the session ID. Termination can occur in multiple ways. For example, the user might log out of the website or close the browser, or the session might time out automatically after a specified period of inactivity.
The illustration shows the five steps, from connection through termination. Note that step 3 can represent one or more consecutive requests and step 4 can represent the responses to each request.
Although most websites take a similar approach to assigning their session IDs, they do not follow the same strategy when it comes to reassigning identifiers. For example, some websites might assign a new session ID each time the user revisits the site, but only if the user closed the browser after the previous visit.
Other sites might maintain the session ID from one visit to the next, as long as the cookie has not expired and has not been deleted. Other sites might issue a new ID each time the user logs into the site, and still other sites might assign a new session ID after a few minutes of inactivity, which means terminating the first session.
Session IDs do not ensure secure communications between the browser and server. In fact, they can introduce security risks if not properly implemented and managed. Skilled hackers can intercept the session IDs and then masquerade as authorized users so they can hijack the sessions.
Web administrators and developers must use due diligence to protect session IDs so their users' sensitive information is not compromised. To this end, the IDs should be random, complex and fully protected in transit and while being stored.
Learn how to encrypt and secure a website using HTTPS and discover if long URLs are better than short URLs.







