TheSupe87 - Fotolia
How to manage cookies across web browsers
There are pros -- saved login credentials -- and cons -- privacy concerns -- to cookies. Either way, IT should understand how to manage cookies across web browsers.
Users like to think they can be somewhat anonymous on the internet, but the reality is, cookies monitor almost every move a user makes.
In the enterprise, limiting users' access to certain sites, data and applications may seem like a good security move, but there are risks when keeping cookies and when removing them.
As an IT professional, you can, at least to some degree, manage cookies, including removing and stopping them. The methods for how to manage cookies vary depending on the web browser. Most browsers contain similar functionality, although some have more manageable options. You can create custom lists of websites to block in some browsers, but not in others.
No matter how the browser works, you likely cannot dictate which browser users work with, so it's important to know how to manage cookies across some of the most popular browsers.
The good and bad of cookie management
Before you make any changes to how cookies work, you should understand that there are risks in doing so. Deleting and managing cookies will affect users.
Removing or otherwise restricting cookies could:
- prevent users from accessing certain sites that help them do their jobs;
- hurt users' productivity by forcing them to take the time to enter account information, such as usernames and passwords, each time they visit a site;
- affect users' experience within a site by not allowing the browser to remember frequently visited pages; and
- hinder search performance and, thus, impede performance on the job because sites take longer to load.
Failing to manage, delete or restrict cookies, however, can be:
- a security risk, leaving the user vulnerable to attacks such as a cookie tossing attack where cookies are transferred to another computer, compromising user data;
- an annoyance to users by tracking their online habits; and
- a personal security risk for users via location services.
How to manage cookies in Google Chrome
In the upper-right corner of the Chrome browser, click the tools ellipsis.
In the tools section, go to Settings, scroll to the bottom and click Advanced. The Privacy and Security section includes the following options:
- Clear Browsing Data, which allows you to manually clear browsing history, cookies, site data, and cached images and files. This will sign the user out of most sites.
- Content Settings, where you can click Cookies to reveal the cookie management dialog box. Here, you can turn the first option off to prevent cookies from saving and reading data. Blocking all third-party cookies is also an option on this page, or you can block, clear or allow cookies on specific sites.
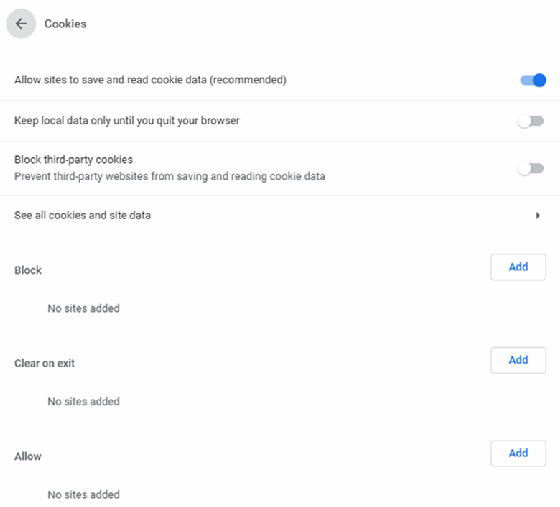
How to manage cookies in Internet Explorer
In Internet Explorer, click the Tools icon in the upper-right corner and move the cursor over to Safety. Several options appear, including Delete Browsing History -- which includes cookies -- Turn on Tracking Protection, and Turn on Do Not Track requests. Clicking on Delete Browsing History produces a number of options, as shown in Figure B. Unlike Chrome, there is an option to purge or not purge saved passwords.

Tracking Protection may be enabled, similar to Chrome, which will prevent websites from sharing cookie data. This is an important feature you can use to prevent user data from being shared among disparate websites.
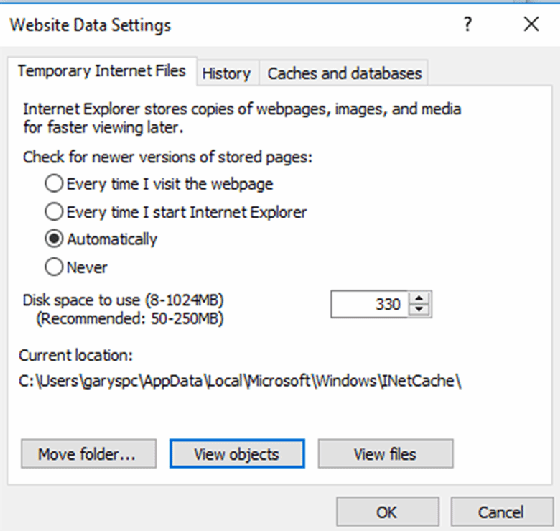
From the Tools menu, select Internet options, and from the General tab, under Browsing history, select Settings. Here, you can control temporary internet files -- including disk space usage -- as well as view and delete files (Figure C).
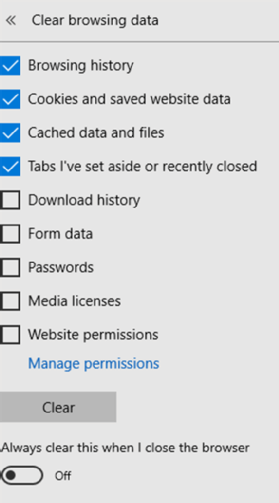
How to manage cookies in Microsoft Edge
Managing cookies in Microsoft Edge is a bit different than in IE. After opening the browser, click the three-dot icon in the upper-right corner and choose Settings. In the drop-down menu, under Clear browsing data, select Choose what to clear to reveal the options in Figure D. Note that cookies and website data are cleared by default. You can also clear cookies without clearing passwords or website permissions.
Back on the Settings menu, scroll down to Advanced Settings to access additional security settings, including an option to block only third-party cookies.
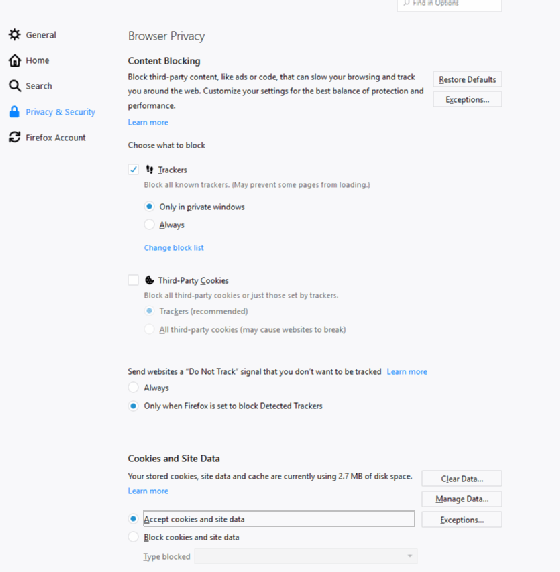
How to manage cookies in Mozilla Firefox
In a Firefox browser, open the icon with three lines in the upper-right corner and select Options. In the Options menu on the left, select Privacy & Security. In this menu, there are several options to block cookies and take related actions, including the following:
Content Blocking
- Trackers: Blocks trackers for private windows only or always. You can also create and manage a custom block list.
- Third-Party Cookies: Blocks all third-party cookies or only those cookies set by the trackers.
- Do Not Track: Prevents sharing of information with other websites.
Cookies and Site Data
- Clear and manage cookie data.
- Accept or block cookie and site data.
- Users define the blocked sites.
Login & Password Management