persistent storage
What is persistent storage?
Persistent storage is any data storage device that retains data after power to that device is shut off. It is also sometimes referred to as non-volatile storage.
Magnetic media, such as hard disk drives and tape, are common types of persistent storage,. Persistent storage systems can be in the form of file, block or object storage.
For the most part, storage persistence is a basic requirement of any storage system, whether it refers to a single drive, a shared networked storage system or a cloud storage service. It is rare that it is even mentioned among the technical specifications for storage devices and systems.
Persistent storage and containerization
There is, however, one exception related to recent developments in virtualized computing that has helped raise storage persistence as an issue.
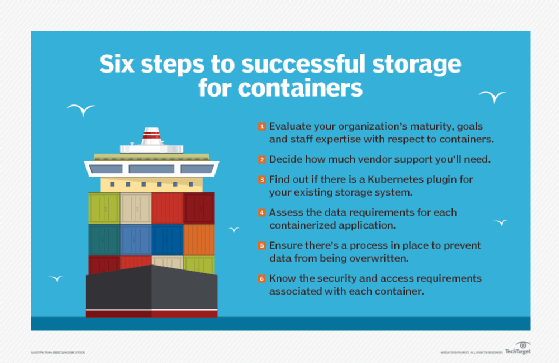
In recent years, containerization has become a popular way to bundle applications with their operating systems into discrete, transportable modules that can be created and destroyed as often as needed. But containers initially didn't support persistent storage, which meant that the data created with a containerized app disappeared when the app finished its work. The container was then destroyed.
Recently, however, a number of software and storage vendors have developed methods to retain the data created by container applications and maintain it in familiar storage volumes. Storage volumes are usually associated with Stateful applications, such as databases, that remain available even if the application is shut down or finishes its processing. These advances in storage for containers solve the problem of retaining the more ephemeral storage volumes that live and die with the stateless apps that are run from containers.
Persistence and solid-state storage
Solid-state drives (SSDs) differ from the other forms of persistent media in that they do not have any moving parts, either internally or with the drives required to access the media.
Some types of solid state storage, notably the chips used for RAM and cache systems, are typically nonpersistent (volatile) storage devices. The data they hold is erased when continuous power ceases to flow into the devices.
However, certain types, such as non-volatile RAM and flash-based RAM, are persistent. Typically, they rely on battery power when the main source of electricity is cut off. Administrators can also achieve a degree of persistence by using supercapacitors that store an electrical charge rather than a battery backup. RAM holds active work that IT may not yet have saved to a disk drive or SSD, so persistence may prevent data loss in the event of a crash or reboot.
Volatile or nonpersistent storage resources have at least one advantage. They generally present less of a security risk compared to persistent storage equipment because they lose all their data when power is cut off.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2024 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.








