
What is data quality and why is it important?
Data quality measures a data set's condition based on factors such as accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, uniqueness and validity. Measuring data quality can help organizations identify errors and inconsistencies in their data and assess whether the data fits its intended purpose.
Organizations have grown increasingly concerned about data quality as they've come to recognize the important role that data plays in business operations and advanced analytics, which drive business decisions. Data quality management is a core component of an organization's overall data governance strategy.
Data governance ensures that the data is properly stored, managed, protected and used consistently throughout an organization.
Why is data quality so important?
Low-quality data can have significant business consequences for an organization. Bad data is often the culprit behind operational snafus, inaccurate analytics and ill-conceived business strategies. For example, it can potentially cause any of the following problems:
- Shipping products to the wrong customer addresses.
- Missing sales opportunities because of erroneous or incomplete customer records.
- Being fined for improper financial or regulatory compliance reporting.
According to the 2023 Monte Carlo report "The Annual State of Data Quality Survey," data quality issues in many organizations are on the rise, and their negative effects are growing. Average monthly data quality incidents per organization rose from 59 in 2022 to 67 in 2023; data quality-related issue resolution increased from less than four hours on average in 2022 to more than four hours; and the average percentage of impacted revenue rose from 26% in 2022 to 31%.
In addition, according to the report "2025 Outlook: Data Integrity Trends and Insights," published by Drexel University in partnership with data integrity vendor Precisely, 64% of organizations surveyed rate quality as the top data integrity issue, and distrust of data for decision support has risen from 55% in 2023 to 67%.
Corporate executives' and business managers' lack of trust in data is commonly cited among the chief impediments to using business intelligence (BI) and analytics tools to improve organizational decision-making. At the same time, data volumes are growing at staggering rates, and the data is more diverse than ever. Never has it been more important for an organization to implement an effective data quality management strategy.
What are the six elements of data quality?
Low-quality data can lead to transaction processing problems in operational systems and faulty results in analytics applications. Such data needs to be identified, documented and fixed to make sure that business executives, data analysts and other business users are working with good information. High-quality data should possess the following six characteristics:
- Accuracy. The data correctly represents the entities or events it is supposed to represent, and the data comes from sources that are verifiable and trustworthy.
- Completeness. The data includes all the values and types of data it is expected to contain, including any metadata that should accompany the data sets.
- Consistency. The data is uniform across systems and data sets, and there are no conflicts between the same data values in different systems or data sets.
- Timeliness. The data is current (relative to its specific requirements) and is available to use when it's needed.
- Uniqueness. The data does not contain duplicate records within a single data set, and every record can be uniquely identified.
- Validity. The data conforms to defined business rules and parameters, which ensure it is properly structured and contains the values it should.
A data set that meets all of these measures is much more reliable and trustworthy than one that does not. However, these are not necessarily the only standards that organizations use to assess their data sets. For example, they might also consider qualities such as appropriateness, credibility, relevance, reliability or usability. The goal is to have trusted data that fits its intended purpose.
Benefits of good data quality
Maintaining good data quality produces a broad range of positive results, including the following:
- It enables organizations to reduce the costs associated with identifying and fixing bad data when a data-related issue arises. Maintaining data quality also helps to avoid operational errors and business process breakdowns, which can increase operating expenses and reduce revenue.
- It increases the accuracy of analytics, including those that rely on AI technologies. This can lead to better business decisions, which in turn can lead to improved internal processes, competitive advantages and higher sales. Good-quality data also improves the information available through BI dashboards and other analytics. If business users consider the analytics to be trustworthy, they are more likely to rely on them instead of basing decisions on gut feelings or simple spreadsheets.
- It frees up data teams to focus on more productive tasks, rather than on troubleshooting issues and cleaning up the data when problems occur. For example, they can spend more time helping business users and data analysts take advantage of the available data while promoting data quality best practices in business operations.
Data quality vs. data integrity vs. data profiling
The terms data quality and data integrity are sometimes used interchangeably, although they have different meanings. At the same time, some people treat data integrity as a facet of data quality or data quality as a component of data integrity. Others consider both data quality and data integrity to be part of a larger data governance effort, while some consider data integrity to be a broader concept that combines data quality, data governance and data protection into a unified effort for addressing data accuracy, consistency and security.
From a broader perspective, data integrity focuses on the data's logical and physical validity. Logical integrity includes data quality measures and database attributes such as referential integrity, which ensures that related data elements in different database tables are valid.
Physical integrity is concerned with access controls and other security measures designed to prevent data from being modified or corrupted by unauthorized users. It is also concerned with protections such as backups and disaster recovery. In contrast, data quality is focused more on the data's ability to serve its specified purpose.
Data profiling adds a wrinkle; while data quality ensures that data is usable, and data integrity ensures that it is trustworthy, data profiling specifies what is actually in the data. It includes examining, analyzing and summarizing data to understand its structure and content.
It is useful to think of data quality as the end goal, data integrity as the guiding principle, and data profiling as the diagnostic process used to realize the other two.
How to assess data quality
The following essential steps must be part of a data quality assessment:
- Define data quality requirements. What does high-quality mean to the organization? What dimensions matter most and how will they be measured?
- Inventory the data assets. Conduct baseline studies to measure the relative accuracy, uniqueness and validity and each data set. The established baselines can then be compared against the data on an ongoing basis to help ensure that existing concerns are being addressed and to identify new data quality issues.
- List and prioritize data sources. Map all databases, application programming interfaces and other sources that fall within the scope of the quality assessment.
- Profile the data. Analyze the structure and content of all data, with attention to completeness, value distributions, format consistency and outliers.
- Score and report on data quality. Measure against selected dimensions, assign scores and rank identified issues that surface.
- Investigate root causes of issues. Once issues have been identified, trace them back to workflows and entry points to determine root causes for remediation.
- Implement continuous monitoring. After problem areas are identified, keep an eye on them.
Various methodologies have been developed for assessing data quality. For example, data managers at UnitedHealth Group's Optum healthcare services subsidiary created the Data Quality Assessment Framework (DQAF) in 2009 to formalize a method for assessing its data quality. The DQAF provides guidelines for measuring data quality based on four dimensions: completeness, timeliness, validity and consistency. Optum publicized details about the framework as a possible model for other organizations.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF), which oversees the global monetary system and lends money to economically troubled nations, has also specified an assessment methodology with the same name as the Optum one. Its framework focuses on accuracy, reliability, consistency and other data quality attributes in the statistical data that member countries must submit to the IMF. In addition, the U.S. government's Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology has detailed a data quality framework for patient demographic data collected by healthcare organizations.
How to improve data quality
Assessment is important. But continuous data improvement should become a priority. The following are the essential steps in improving data quality:
- Establish clear goals. A central question in assessing data quality is: What does high-quality data look like to the organization? The answers to that question should be used to align business objectives with the data quality requirements that will be put in place for ongoing data improvement. The prioritized dimensions -- accuracy, completeness, timeliness and validity -- will be central.
- Prioritize the issues. Once data quality issues in the organization have been surfaced, it is important to rank them according to their effect on the organization's processes and efficiency, to effectively remediate the most important problems. This could change over time and should thus be periodically revisited.
- Establish remediation standards. For the sake of consistency and efficiency, ensure that remediations are known, understood and adhered to across the enterprise.
- Implement data governance. Establishing data roles -- owners, stewards and custodians -- is a good idea. Data policies and standards should be formally published and maintained, and metadata, data definitions and transformation logic should be documented.
In many organizations, analysts, engineers and data quality managers are primarily responsible for fixing data errors and addressing other data quality issues. They are collectively tasked with finding and cleansing bad data in databases and other data repositories, often with assistance and support from other data management professionals, including data stewards and data governance program managers.
A data quality initiative might also involve business users, data scientists and other analysts to help reduce the number of data quality issues. Participation might be facilitated, at least in part, through the organization's data governance program. In addition, many companies provide training to end users on data quality best practices. A common mantra among data managers is that everyone in an organization is responsible for data quality.
To address data quality issues, a data management team often creates a set of data quality rules based on business requirements for both operational and analytics data. The rules define the required data quality levels and how data should be cleansed and standardized to safeguard accuracy, consistency and other data quality attributes.
After the rules are in place, a data management team typically conducts a data quality assessment, documenting errors and other problems -- a procedure that should be repeated at regular intervals to ensure the highest data quality possible.
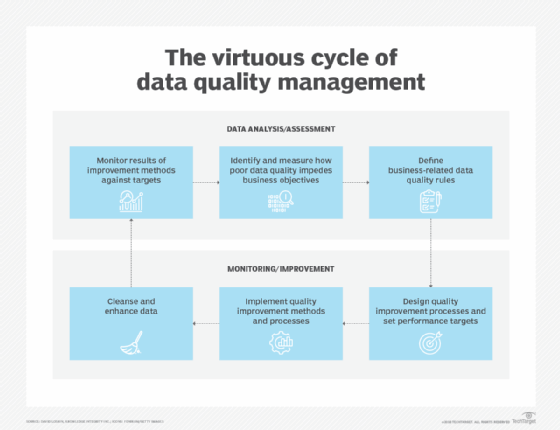
However, not all data management teams approach data quality in the same way. For example, data management consultant David Loshin outlined a data quality management cycle that begins with identifying and measuring the effect that bad data has on business operations. The team then defines data quality rules and sets performance targets for improving data quality metrics.
Next, the team designs and implements specific data quality improvement processes. These include data cleansing or data scrubbing, fixing data errors, and enhancing data sets by adding missing values or providing more up-to-date information or additional records.
The results are then monitored and measured against the performance targets. Any remaining deficiencies in data quality serve as a starting point for the next round of planned improvements. Such a cycle is intended to ensure that efforts to improve overall data quality continue after individual projects are completed.
Data quality management tools and techniques
Organizations often turn to data quality management tools to help streamline their efforts. These tools can match records, delete duplicates, validate new data, establish remediation policies and identify personal data in data sets. Some products can also perform data profiling, which examines, analyzes and summarizes data sets.
Many of these tools now include augmented data quality functions that automate tasks and procedures, often through the use of machine learning and other AI technologies. Most tools also include centralized consoles or portals for performing management tasks. For example, users might be able to create data handling rules, identify data relationships or automate data transformations through the central interface.
Data quality managers and data stewards might also use collaboration and workflow tools that provide shared views of the organization's data repositories and enable them to oversee specific data sets. These and other data management tools might be selected as part of an organization's larger data governance strategy. The tools can also play a role in the organization's master data management initiatives, which establish registries of data on customers, products, supply chains and other data domains.
The following are examples of data quality platforms:
- Acceldata.
- Ataccama.
- Bigeye.
- Great Expectations GX Cloud.
- Informatica Data Quality.
- Monte Carlo Data + AI Observability Platform.
- Qlik.
- SAP Data Services.
- SAS Data Quality.
- Soda Core.
Some current data quality management techniques include AI-augmented quality management, in which platforms automatically create and enforce quality rules, and stream-first quality monitoring, which supports real-time validation and anomaly detection for unbounded data streams. Note that some of these platforms are open source.
Emerging data quality challenges
For many years, data quality efforts centered on structured data stored in relational databases, which were the dominant technology for managing data. However, data quality concerns expanded as cloud computing and big data initiatives became more widespread. In addition to structured data, data managers must now also consider unstructured data and semi-structured data, such as text files, internet clickstream records, sensor data and network, system and application logs.
The following factors play a role in data quality, adding to the complexity of managing data:
- Many of today's organizations work with both on-premises and cloud systems.
- Data source proliferation is rampant, as organizations integrate more external data into their processes.
- Modern data stacks are increasingly complex.
- A growing number of organizations are incorporating machine learning and other AI technologies into their operations and products; the quality requirements for data used in these operations are generally very high.
- Many organizations have implemented real-time data streaming platforms that continuously funnel large volumes of data into corporate systems.
- Many organizations lack unified governance.
- Data scientists are implementing complex data pipelines to support their research and advanced analytics.
Data quality concerns are also growing due to the implementation of data privacy and protection laws, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act. Both measures give people the right to access the personal data that companies collect about them. This means organizations must be able to find all the records on an individual in their systems without missing any because of inaccurate or inconsistent data.
Clean data is critical to data quality. Learn the advantages of good-quality data and how it differs from unclean data.







