email archiving
What is email archiving?
Email archiving is a systematic approach to saving and protecting the data contained in emails to enable fast retrieval. These tools play a vital role in organizations that prioritize data permanence.
Email communications are placed in a secure repository that resides outside of production environments. Incoming and outgoing messages are indexed, along with any document attachments. The contents of retained email are preserved in their original state in read-only format.
An email archive tool aids with compliance, knowledge management, litigation support and storage management. Aside from storing email, most content archiving products have evolved to encompass enterprise file sync-and-share data, instant messaging and corporate social media activities.
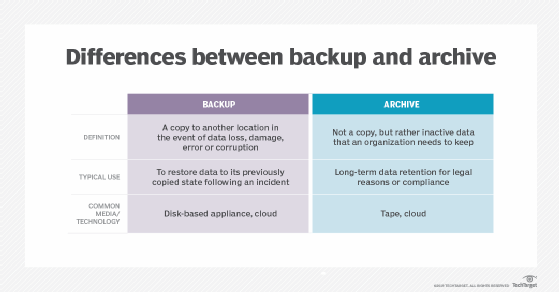
Email archiving vs. email backup
There is a noteworthy distinction between email archiving and backup. An email archive serves as a historical reference that exists outside the backup cycle. Because archived email is retained for indefinite periods, these systems require highly durable storage media and low total cost of ownership. High performance remains important for random read access. Data authenticity is of primary concern.
An email backup creates a backup image of the entire email system to facilitate recovery to its previously stored state. This creates cost and storage management headaches for companies that internally manage their own email backups. Email backup requires high-capacity storage media to handle a heavy stream of writes, while also minimizing the overall cost per gigabyte.
The evolution of email archiving
In the early days of email, companies often relied on users to maintain individual email archives. The IT department would back up a user's email but searching of messages was not automated. If IT needed to trace a specific email, it often took weeks to find it. The emergence of software with specialized email archiving services helps organizations curate data from thousands of mailboxes.
The archiving platform creates a searchable index that allows bulk email to be sifted in minutes. Customers usually obtain an email archive as part of an integrated software product for backup and disaster recovery, email governance or information lifecycle management. However, some vendors offer email archiving as a stand-alone product.
Email archiving: Compliance use cases
A content archiving application has two main functions. It indexes the email content and assigns it to a physical archive or other storage target. Second, it applies a policy engine that governs rules on data deletion and the length of retention periods. It automates data tiering to less-expensive storage media.
Policy-based email archiving enables IT managers to manage large email archives easier.
Email archiving services take on greater significance as companies strive to meet regulatory compliance. Preservation of business-related email is a mandate for companies in highly regulated industries such as financial services, government and healthcare.
Federal regulations passed by the U.S. Congress, such as the Dodd-Frank Act, Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP), HIPAA and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, place stringent requirements on how long an email is retained and the security measures surrounding it. Certain sections of FRCP, for example, require archived email to be preserved on write-once, read-many media to ensure data can't be altered or deleted.
An email archive is a necessity in organizations with hundreds or perhaps thousands of mailboxes, creating a virtual record to find email messages under subpoena for e-discovery or other litigation proceedings.
These regulations do not necessarily require that each email be archived. Spam and an employee's personal email correspondence typically are exempt. Nonetheless, any documents considered germane to the company's business activity could be subject to litigation requests under federal or state laws.
Email archiving to aid storage management
Archiving historical email correspondence has implications on storage capacity. Reducing the number of electronic messages stored on the mail server enables organizations to reclaim capacity on the production server. Another benefit is shorter backup times.
Physical storage capacity requirements for email archiving are less than that of centralized storage. If the same attachment recurs in multiple email messages, archiving software saves only one instance. Each archived message is affixed with a stub that points to the fully stored original email. The information is securely protected but still accessible for auditing its chain of custody.
The evolution of Microsoft Exchange Server points to this trend. Microsoft introduced In-Place Archiving in Exchange 2013, essentially creating an archive within a mailbox dedicated to storing historical messaging data. The enhancement eliminates the management of discrete PST file folders. The feature provides users with a consistent view from the Microsoft Outlook email program, Outlook web application or the integrated Microsoft 365 suite.
Cloud email archiving
Public cloud providers have fostered a services-based approach to delivering security, software and storage. The storage-as-a-service model lets an enterprise consume as few or as many resources as needed. Similarly, cloud-based email archiving may be an option for midsize businesses that want to avoid the cost of dedicated email servers and related infrastructure.
Using the cloud for email retention requires no special software or hardware. Cloud-hosted archives typically have strong search capabilities and high scalability. Users can specify archive policies that align with their corporate needs.
But there are reasons for caution when considering a cloud email archive. First is the issue of cost relative to the level of in-house management users must handle. Keep in mind that a managed service provider essentially leases hard disk space in a multi-tenant data center. Responsibility for managing the archive itself rests mostly with the user.
Additional fees may be charged for specialized services such as e-discovery sorting or consulting on which regulations may apply to content.
As with any vendor, it's important to get clarity regarding the service-level agreement. It should specify how quickly the data must be restored from the cloud, compensation if the vendor fails to meet its obligations and contingencies for data should the vendor go out of business. Encryption, data residency and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard bear attention as well.
Email archiving tools
There are numerous email archiving products available, including services integrated in backup software suites and storage management tools provided by storage array vendors. The following list is not exhaustive, but it highlights some notable vendors and products geared for email archiving and migration:
- Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office.
- Archive360.
- Barracuda Message Archiver.
- Commvault Cloud.
- Dell SourceOne.
- Google Vault.
- Microsoft Exchange Online Archiving.
- Rackspace Email Archiving.
- Veeam Backup for Microsoft 365.
- Veritas Enterprise Vault.
Editor's note: This article was revised in 2023 by TechTarget editors to improve the reader experience.








