disaster recovery (DR) test
What is a disaster recovery (DR) test?
A disaster recovery test is the examination of each step in a disaster recovery plan to ensure that an organization can recover data, restore business critical applications and continue operations after an interruption of services.
A disaster recovery (DR) test is outlined and run as part of an organization's business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) planning process.
In many organizations, DR testing is neglected because creating a plan for disaster recovery can tie up resources and become expensive. Companies might consider having a DR plan as enough, even if there is no evidence that the plan will work correctly if disaster strikes.
If an organization doesn't invest time and resources into testing its disaster recovery plan, there's a real chance the plan will fail to execute as expected when it's needed. Communications, data recovery and application recovery are typically the focus of disaster recovery testing. Other areas for testing vary, depending on the organization's recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO).
Experts recommend conducting disaster recovery tests on a regular basis throughout the year and incorporating them into all planned maintenance and staff training. Once a test has been completed, audit logs and other data should be analyzed to determine what worked as expected, what didn't work as expected, what changes need to be made to the DR plan's design and what tasks need to be scheduled for retesting.
Goals of disaster recovery testing
One of the main goals of a disaster recovery test is to determine if a DR plan can work and meet an organization's predetermined RPO/RTO requirements. It also provides feedback to enterprises so they can amend their DR plan should any unexpected issues arise.
IT systems rarely remain static, so new and upgraded products need to be tested again. If storage systems and servers have been added or upgraded since the organization developed the DR plan, they must be included in new test. This also applies to new applications that have been deployed and older applications that have been updated. If the cloud -- private, public or hybrid -- begins to play a larger role in an organization's IT infrastructure, it must be incorporated into the test. A disaster recovery test helps to make sure a DR plan stays current in an IT world that changes constantly.
Types of disaster recovery tests
There are three basic types of disaster recovery testing:
- Plan review. Here, the DR plan owner and other members of the team behind its development and implementation closely review the plan, examining it in detail to find any inconsistencies and missing elements.
- Tabletop exercise. During a tabletop exercise, stakeholders gather to walk step by step through all the components of a disaster recovery plan. This helps determine if everyone knows what they are supposed to do in case of an emergency and uncovers any inconsistencies, missing information or errors.
- Simulation. Simulating disaster scenarios is a good way to see if the procedures and resources -- including backup systems and recovery sites -- allocated for disaster recovery and business continuity work in a situation as close to the real-world as possible. A simulation runs a variety of disaster scenarios to see if the teams involved in the DR process can restart technologies and business operations in a timely manner. This process can determine if there are enough people on staff to get the DR job done properly.
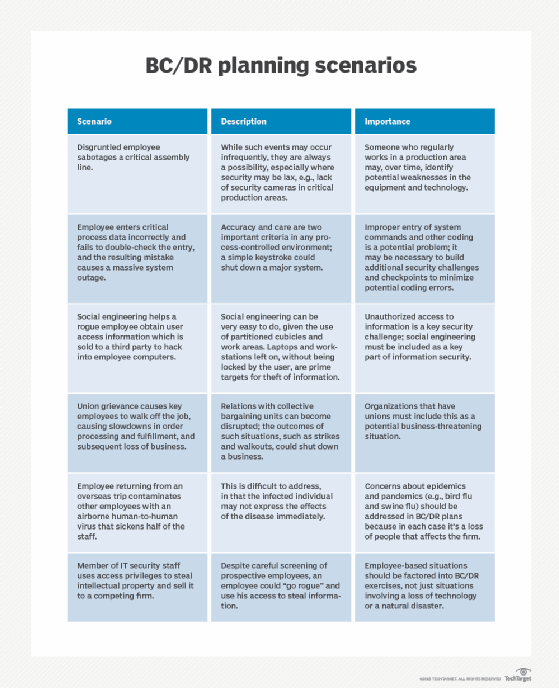
Important aspects of a DR test
Effective disaster recovery testing should take the following into consideration:
- Timing. When was the last time an application or system was tested? The longer the period between tests, the higher the risk that change or growth -- in data, hardware or software -- will result in DR plan failure. It is also important to measure and know how long a complete recovery takes from an RTO perspective as part of a DR test.
- Changes. Test to make sure backup/restore processes remain unaffected by any changes. Always perform a DR test after any major infrastructure changes -- for example, in storage hardware or upgrading of a hypervisor -- as these can lead to the need to rewrite disaster recovery processes.
- Impact. Organizations need to know if disaster recovery testing will impact a production environment. For example, tests can cause downtime because an application or hardware devices must be taken down or they will impact the live data. All data and software updates should be incorporated into a simulation to make sure it is a valid run-through and the impact of the tests are the same as if the DR plan was implemented in a real-world disaster.
- People. Use a DR test to minimize or completely remove the potential for human error from the disaster recovery process. Also, be sure to use a variety of people -- not just employees involved with directly supporting a particular application -- to better determine the validity of all the steps in a DR plan, either on a live system or during a paper exercise.
Disaster recovery plan template
Free, downloadable IT DR template helps facilitate the initiation, completion and testing of an IT DR plan.
Disaster recovery testing checklist
Testing will look different for every organization, but there are some templates and checklists that businesses can follow to conduct a thorough test of a BCDR plan. To get a testing strategy off the ground, consider implementing the following steps:
- Present a detailed DR testing plan when attempting to get approval and funding to run tests.
- Clearly identify goals, objectives, procedures and what to look for in post-testing analyses.
- Put together a test team -- including subject matter experts -- and make sure everyone is available for the planned testing date.
- Determine exactly what to test -- for example, backup and recovery, system and networks resumption or the employee notification system.
- Carefully document and be prepared to edit the DR plan and disaster recovery testing scripts.
- Review and confirm that all code in test scripts is accurate.
- Include all relevant technology elements and processes being tested in the plan -- no matter how seemingly insignificant.
- Ensure the test environment is ready, available and won't affect production systems before starting. Make sure testing doesn't conflict with any other activities or tests.
- Schedule a DR test, which can take hours, far in advance; notify and remind other IT managers of the coming test.
- Perform a dry run -- or a practice exercise -- before the disaster recovery test goes live to uncover and fix potential problems.
- Stop and review the test when issues arise. Continue if the problem can be bypassed; reschedule if necessary.
- Designate a timekeeper to record start and end times and a scribe to take notes to help prepare for the test's after-action report, which describes what occurred during the test, what did and didn't work and what has been learned.
- Update BCDR plans and other documents based on what's been learned from the DR test.






