lights-out management (LOM)
What is lights-out management (LOM)?
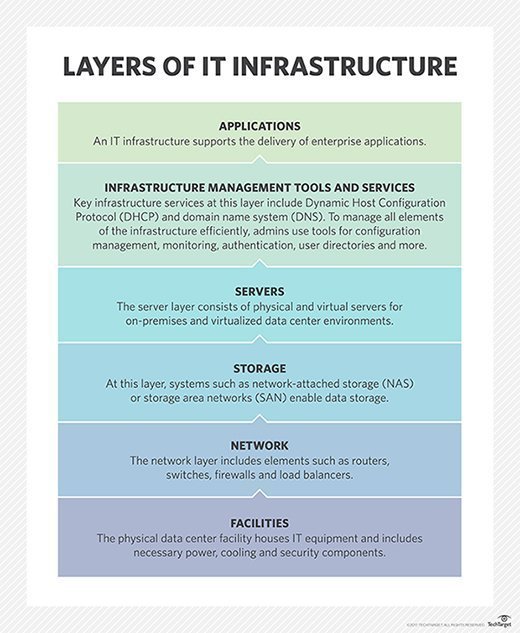
Lights-out management (LOM) is a form of out-of-band management. It enables system administrators to connect remotely to servers and other data center infrastructure to monitor and maintain those systems. With LOM in place, IT teams can keep their systems running and respond to potential problems no matter where they are located, even if they're on the other side of the world.
An LOM system enables data center administrators to manage infrastructure as though they're within physical proximity of the equipment. It lets admins carry out a variety of remote management tasks, such as starting and stopping systems, assessing problems, updating firmware and software, and viewing the event log.
How does lights-out management work?
With an LOM system in place, systems administrators can carry out a range of tasks from remote locations. Among the functionality LOM enables are the following:
- start a system even if it's powered off;
- stop or reboot a system;
- monitor a system's health;
- troubleshoot problems;
- respond quickly to downtime;
- control alarms, fans and other components;
- update firmware;
- reinstall the operating system; and
- view the system event log.
What are the main components of an LOM system?
LOM systems incorporate similar components, including hardware, dedicated communication ports, communication protocols and event logs.
Hardware component
An LOM system consists of a hardware component that carries out the management tasks. It also has an interface for accessing the component remotely to provide the necessary instructions. The hardware component is sometimes called the LOM module, but it might also go by other names. It is often integrated directly into the host system's hardware.
For example, Dell offers an integrated lights-out management system. Dell's Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller with its PowerEdge servers is an LOM hardware component that's attached to the server's motherboard. Dell also provides a web interface and command-line interface (CLI) for performing remote management tasks.
Cisco offers a similar component with its Unified Computing System (UCS) C-Series Rack Servers and UCS S-Series Storage Servers. The component -- referred to as the Integrated Management Controller (IMC) -- is a baseboard management controller (BMC) that provides embedded server management. A BMC is a specialized service processor that monitors a system's physical state. Cisco also provides a web interface, CLI and Extensible Markup Language application program interface for interacting with the IMC.
Dedicated communication port
An infrastructure system that supports LOM typically includes a dedicated port for enabling communications between the LOM module on the host system and the outside world. The port makes it possible to connect the host system to a management network that's separate from the primary data network.
Communication protocol
An LOM system also relies on a communication protocol to exchange messages between the client interface and the LOM module. The protocol enables the interface to send management commands to the module and the module to send its responses back to the interface.
Some vendors use their own proprietary protocols, but over the years, many have opted for the Intelligent Platform Management Interface, a standardized message-based interface that works in conjunction with a BMC.
Event logs
An IT team can use one LOM system to manage several data center systems. The LOM module on each managed system maintains an event log that tracks all operations. This makes it possible for administrators to instantly check any of several hundred recent system events.
What are the benefits of LOM?
LOM systems can be configured to provide a number of advantages, including the following:
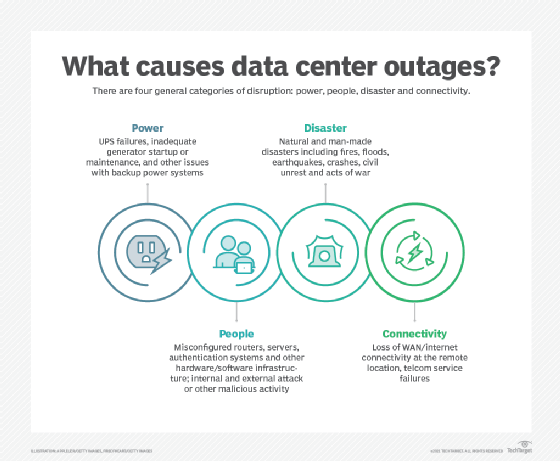
- Increased uptime. Using LOM, administrators can monitor data center metrics from afar, and diagnose and respond to issues faster. This approach increases overall uptime, while reducing the impact on supported workloads.
- Enhanced performance. An LOM system helps ensure that each monitored system is running within acceptable parameters, with optimal performance.
- Reduced disruptions. LOM systems make it possible for remote admins to track metrics such as processor temperatures. Such remote metric tracking cuts down on service disruptions and risks to the hardware.
- Fewer on-site personnel. LOM minimizes the number of people who must be physically present in a data center. It can be useful in times of impending natural disaster. For example, administrators can shut down servers remotely if a hurricane is threatening a facility. LOM has also proven beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic, when fewer admins can be present in the data center and remote access is more important than ever.
Learn more about the LOM tools that let admins do everything from turning servers off and on to remediating operational issues.






