
Getty Images
A primer on hyperscale data centers
Hyperscale data centers can hold thousands of servers and process much more data than an enterprise facility. However, they can be difficult to build and maintain.
The number of hyperscale data centers is rapidly growing.
A hyperscale data center is almost exactly what it sounds like: a data center that can excessively scale and quickly meet the needs of new, massive growth.
These data centers are built to process more data than enterprise data centers and have a variety of features that make them unique. There are also some challenges in how to design and maintain them compared to enterprise or smaller data centers, such as advanced automation and large uptime demands.
What is a hyperscale data center?
By their nature, data centers are designed to operate at scale and often house dozens, if not hundreds, of physical servers and VMs. A hyperscale data center is essentially the next level up -- it can support thousands of servers and millions of VMs. An analyst report from The Business Research Company predicted that the global hyperscale data center market will grow from $35.72 billion in 2022 to $76.73 billion in 2027 at a compound annual growth rate of 16.5%.
Hyperscale computing takes a stripped-down approach to networking that combines compute, storage and virtualization layers into a single computing environment. The infrastructure networks servers horizontally to maximize the hardware, and a load balancer monitors the amount of data the facility needs to process.
Put simply, hyperscale data center architecture is designed to be exceptionally lean and agile. This enables the ability to share the processing load across the infrastructure and quickly add or remove servers or other resources as needed to meet capacity demands.
Key features of a hyperscale data center
The approach to hyperscale architecture may vary from provider to provider, especially as the big players experiment with what works best. Most hyperscale data centers share a few common features, including the following:
- Large site locations. Since hyperscale data centers can support thousands of servers, they tend to be much larger than the average data center. The typical facility is at least 10,000 square feet, according to IDC, with some of the truly massive facilities reaching hundreds of thousands or even millions of square feet.
- High-density server racks. More square footage isn't the only way to fit more servers into a hyperscale facility. Most also use specialized high-density server racks. These server racks are wider and can accommodate more components, like power suppliers and hard drives, with enough space for engineers to swap them out and customize them as needed. Most hyperscalers have at least 5,000 servers, according to IDC.
- Strong energy resources. With so much equipment to support, hyperscale facilities need a massive amount of power. Some facilities consume entire gigawatts of power, which is enough to power a small city. Hyperscalers invest in the most advanced power suppliers and HVAC systems for more efficient cooling. Hyperscale data centers are also often built in areas with cheap electricity, away from critical power grids.
- Disaggregation and modularity. The ability to customize and swap out components is key to the flexibility of hyperscale facilities and equipment. This requires a commitment to personalized configuration, which is expensive, but the result is highly improved modularity, which makes it easier to adjust infrastructure and equipment on short notice.
- Automation. Given the sheer scale of these data centers, manual monitoring is simply not feasible. Many hyperscalers heavily rely on automation tools to allocate assets, optimize workloads, monitor and repair systems, and more.
Benefits of a hyperscale data center
With these features, there are various ways they translate to practical benefits compared to traditional data centers:
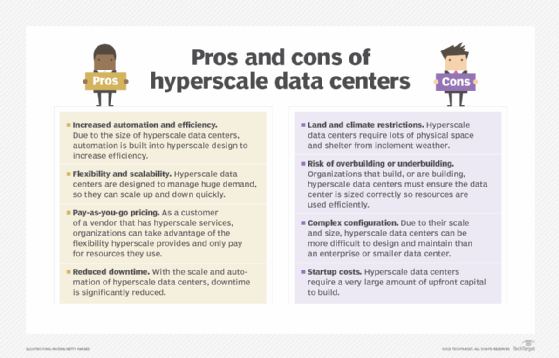
- Flexibility and scalability. The biggest advantage of hyperscalers is the ability to scale out horizontally but also to scale up vertically. This enables better balanced workloads and superior resource provisioning. As demand increases or decreases, it is easy for hyperscale data centers to adjust and match that demand, no matter the scale.
- Reduced downtime. Since hyperscalers have a considerable focus on automation and so many resources on hand, there is reduced downtime. The environments are so controlled that they can automatically recover from various issues. If there's a sudden spike in demand, the hyperscaler can meet those needs. Many redundancies are also in place to maintain uptime at all costs.
- Increased efficiency. From operations to cooling, hyperscale data centers are designed to operate at peak efficiency. And, thanks to increased automation, they may not require as much staff to manage.
- Advanced technology. As larger organizations evolve and iterate on hyperscale architecture, the technology and best practices they pioneer will hopefully trickle down to smaller data centers. This will, in turn, empower all data centers to use their physical space better, more rapidly provision resources and reduce their power usage.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing. For hyperscale customers, the services can be more flexible. A hyperscale data center can support large levels of service and scale with increased demand.
Challenges of hyperscale data centers
Many of the features of hyperscalers also represent the biggest challenges of hyperscaling, including space, power usage and advanced technologies.
Land and climate restrictions
For starters, hyperscale data centers require a lot of land in an area with cheap but reliable electricity. A hyperscale data center should also not be anywhere with severe inclement weather that could bring the whole place down -- not to mention the need for layered security to prevent cyber attacks and breaches that could do the same.
Difficulties in configuration
Customization is also a challenge. Hyperscale computing environments are still in their infancy. They require nearly every aspect to be personalized and configured, which takes a significant amount of expertise upfront. Organizations that build hyperscale data centers also need to invest in extensive R&D, in addition to advanced hardware and cabling. While they can remove the need for human expertise over the long term, modern automation tools can be expensive and difficult to implement.
Risk of overbuilding or underbuilding
It is possible to overbuild or underbuild a data center. In the former case, organizations could have idling resources, underused machines or even equipment that was new at the time but outdated by the time it is used. Underbuilding could result in overloaded machines and large-scale system failures.
Examples of existing hyperscale data centers
Nearly half of the world's hyperscale data centers are in the U.S. The largest facilities belong to cloud providers, including Microsoft, Amazon, Google, IBM and Meta. There were at least 700 hyperscale data centers in 2021, according to Synergy Research Group.
The Chinese market is also rapidly growing and currently has some of the largest hyperscale data centers. For example, the Inner Mongolia Information Hub facility in Hohhot, China, is 10.7 million square feet and is one of the largest data centers in the world. There's also the Range International Information Hub in Langfang, China, which is 6.6 million square feet.
Others that have or plan to build hyperscale facilities include Apple, Twitter, eBay, Tencent, Oracle and Alibaba. With the growth the market is seeing, more of these facilities -- potentially hundreds of them -- could open up over the next few years.
Keep up with developments to prepare for hyperscaling
There are considerable challenges to supporting hyperscale computing in data centers, which means only the biggest of players in the field will likely be able to afford, build and maintain these facilities. However, data center administrators should stay up to date on the latest advancements and trends in hyperscale computing as the technology and best practices trickle down.
Rapid growth accelerates the future of hyperscale, and by keeping up with its fast evolution, all data centers can benefit from the pioneers pushing the field forward.







