radiology information system (RIS)
What is a radiology information system (RIS)?
A radiology information system (RIS) is a networked software system for managing medical imagery and associated data. A RIS is especially useful for tracking radiology imaging orders and billing information, and is often used in conjunction with picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) and vendor neutral archives (VNAs) to manage image archives, record-keeping billing and electronic health records (EHRs).
The role of technology in healthcare has evolved dramatically, especially in the field of medical imaging. Radiology information systems stand at the forefront of this evolution, offering an indispensable tool for managing medical imagery and associated data.
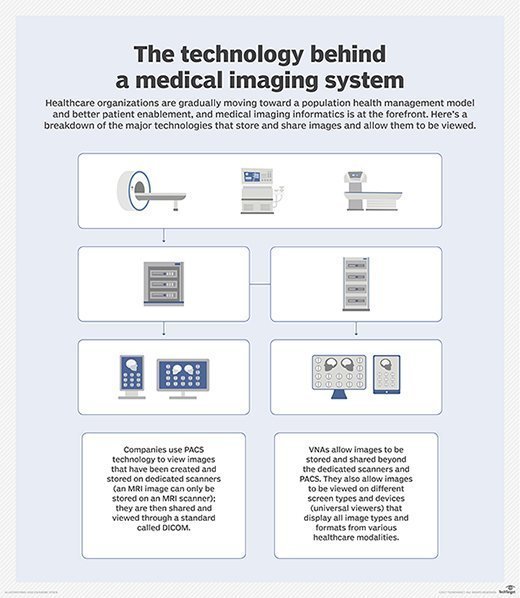
Key components of a radiology information system
A RIS has several basic functions:
- Patient management: A RIS can track a patient's entire workflow within the radiology department; radiology providers can add images and reports to EHRs, where they can be retrieved and viewed by authorized radiology staff.
- Scheduling: The RIS allows staff to make appointments for both inpatients and outpatients.
- Patient tracking: Using a RIS system, providers can track a patient's entire radiology history from admission to discharge and coordinate the history with past, present and future appointments.
- Results reporting: A RIS can generate statistical reports for a single patient, group of patients or procedures.
- Image tracking: Traditionally, radiology providers use RIS to track individual films and their associated data. But as EHRs have become standard across the healthcare industry and digitized images and PACS have been widely adopted, radiology departments and their RIS-PACS systems have been more drawn into the clinical workflow of the entire medical enterprise.
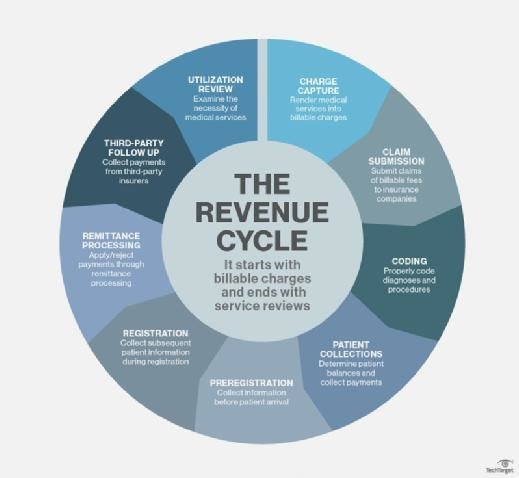
- Billing: Beyond basic financial record-keeping, modern RIS systems handle electronic payments and automated claims, increasingly merging these functions into broader EHR systems for revenue cycle management (RCM).
The benefits of a radiology information system
The evolution of radiology information systems has revolutionized healthcare management, particularly in the field of medical imaging. With the implementation of an updated RIS, healthcare facilities experience a significant uplift in operational efficiency including the following advantages:
- Enhanced efficiency: Automated scheduling and streamlined workflows reduce wait times and improve the overall efficiency of radiological services.
- Improved patient care: Quick access to patient history and reports leads to better-informed decisions, directly impacting patient care quality.
- Streamlined data management: Centralized data storage makes it easier to access and manage patient health information (PHI), reducing errors and improving data integrity.
- Optimized billing processes: Integrated billing systems within RIS ensure accurate and faster billing, reducing administrative burdens.

RIS vs. other medical systems
RIS, PACS, and hospital information systems (HIS) are all critical components of modern healthcare infrastructure and health IT, each serving a unique role. RIS specializes in the operational management of radiology departments, encompassing everything from patient scheduling to billing and report generation.
In contrast, PACS is primarily concerned with the storage, retrieval and distribution of medical images, serving as a digital archive that replaces the need for physical film storage. HIS, on the other hand, is a more overarching system that manages all the administrative and clinical information across the hospital, integrating various departments and their functions.
While each system has its distinct functionalities, they often work in tandem to ensure a smooth, efficient and integrated healthcare experience.
The future of radiology information systems
The future of RIS systems is closely intertwined with advancements in technology, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing. The integration of AI in RIS promises to not only automate certain processes but also enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. This could lead to breakthroughs in predictive analytics, aiding in early disease detection and treatment planning.
The shift toward cloud-based systems is another significant trend. By leveraging the cloud, RIS can offer greater scalability, flexibility and accessibility, making it possible for healthcare providers to access critical information remotely and securely.
This advancement is particularly relevant in today's increasingly digital and connected world, where the ability to access and analyze data on the go can significantly enhance the quality of patient care. As RIS continues to evolve and embrace these technological advancements, it stands at the cusp of revolutionizing healthcare delivery.
The ongoing development of RIS is not just an advancement in medical imaging technology; it's a step towards a more efficient, effective, and patient-centered healthcare system.
Learn about the uses of AI in medical imaging and how AI has cemented its role in telemedicine. Explore how generative AI could change healthcare and what four electronic health record vendors are doing to leverage generative AI in clinical workflows.






