
Getty Images
Manage resource use with VMware Horizon application pools
Load balancing is challenging in any environment, but with virtual desktops, uniformity of user experience is high priority. Use VMware Horizon to distribute vital resources.
VMware Horizon is known for its virtual desktop infrastructure, which offers Windows desktops to end users on many types of devices. However, there is another component: Remote Desktop Session Hosts also provide a single point of maintenance, a singular installation process and easier configuration workflows.
With an RDS host, end users access a desktop as a session and launch individual applications from any device. The screen output is on the user's device, but the executable runs on the RDS host. With an RDS host, each user can have their own individual VM without increased work for the virtualization admin.
How to deploy RDS hosts
RDS host deployments are referred to as a farm. The farm is a collection of Windows Servers with the RDS role installed. Each collection should have the same configurations and applications, and an automated pool of instant-clone RDS hosts that share one common golden image. Running clones on one machine guarantees they will all be identical. Clones must also deploy with the same amount of CPU and RAM resources. If one host is equipped with more capacity, it creates an imbalance in session placement. If the hosts are created equally, clones can -- by default -- support the same number of users.
After IT admins create a farm, they must configure the load balancing settings, as these are not preconfigured in Horizon. That doesn't mean sessions are not balanced on hosts. It means the server load is unaccounted for.
Figure 1 shows the default load balancing settings of a farm. The checkbox Include Session Count is enabled by default.
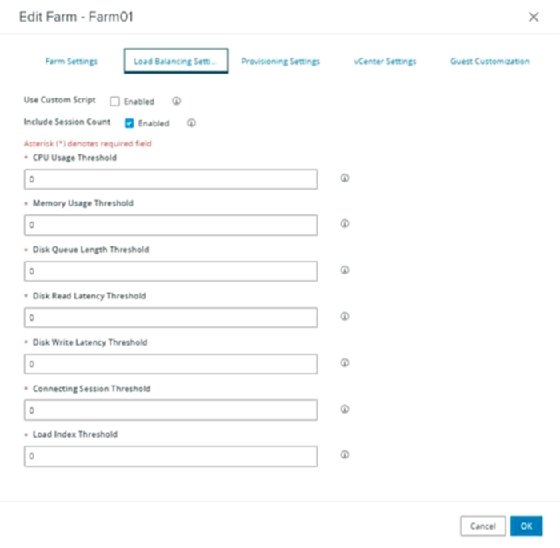
To place new sessions on hosts, first look at the number of sessions already connected. Disconnected sessions are taken into account because those users will reconnect. Over time, the same number of users will connect to each host. For homogeneous environments, this might be a sufficient placement method. If all sessions consume the same amount of CPU resources and memory, the user experience will be the same for all. That might not meet expected or required performance levels, but at least the uniformity yields an equal experience. But if all hosts are created with sufficient resources, performance should be OK for all users.
Load balance configured hosts
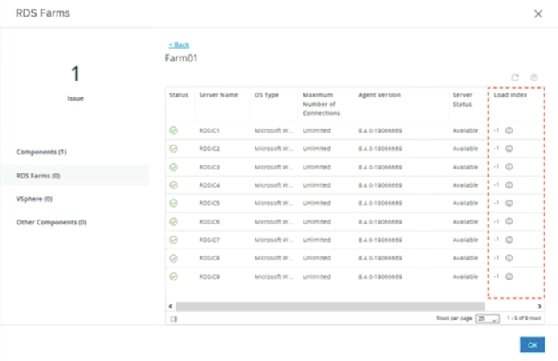
With the defaults configured, the monitoring dashboard's output shows a load index of -1 for each host, as seen in Figure 2, depicting a nine-host farm. The -1 indicates no load balancing settings are configured.
If loads appear different on all hosts, and user experiences vary depending on which host they are connected to, reconfigure the load balancer thresholds. This can be done in the farm settings. Figure 3 shows the same settings page as in Figure 1, with the recommended thresholds configured. The checkbox for session count is still enabled because if no selection is made based on the resource use, the selection is based on session count.
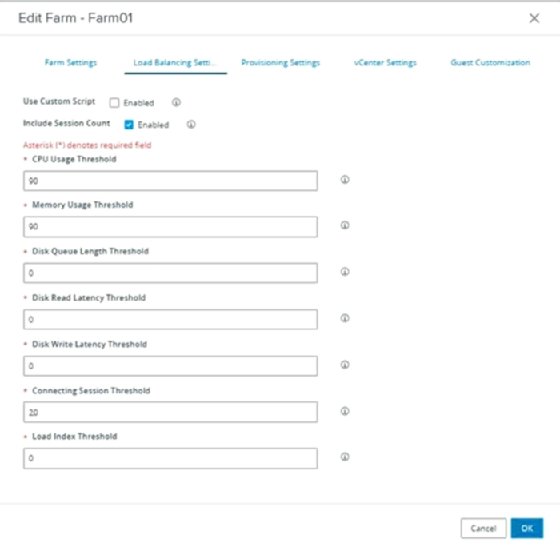
VMware configures the CPU and memory usage thresholds with the recommended value of 90%. Any value higher than 0 enables the count of these resources to calculate new session placement. The software's default load sampling interval is per 30 seconds. There's a possibility that resource use will increase -- sometimes abruptly. This could be a problem because the algorithm that chooses a host bases its decision on older information.
The new threshold -- added in version 8.4.0 (2111) -- prevents excessive sessions from being added to a host. This is the Connecting session threshold. The recommended value is 20: If there are pending sessions for host placement, hosts can support no more than 20 sessions.
Choose a number here that is suitable for the number of hosts and user sessions. In a larger environment with more than 10 hosts, a lower number will work. With fewer hosts, 20 or higher might be better.
In this example, thresholds are not enabled for storage disk queue length and latency. There are no recommended values for thresholds, and there are only realistic options if applications are storage I/O intensive, but most RDS hosted applications will consume most CPU and memory.
After IT admins enable the load balancing settings, the load index will generate every 30 seconds. This is listed on the Horizon Administrator Console dashboard. Figure 4 shows the same nine hosts as before, but with generated loads and configured load balancing thresholds. All hosts generate a load index that ranges from 0 to 100. Two hosts have a load index of 97. In this situation, no new sessions will be connected to the hosts.
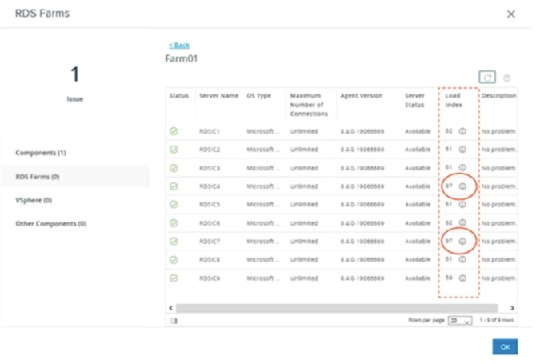
Version 8.4.0 (2111) added the load index threshold setting. This setting enables admins to configure the load index value that will stop new session placement on hosts. For example, if the setting is configured at 90, all hosts would have a load index of 90 or higher, so no new session would be placed on any host in the farm.
Previous user sessions that were disconnected from the Horizon display protocol remain logged into the Windows session and will reconnect to the same server -- even if new sessions are not allowed on the host. If a disconnected user's applications and files are still open, they must connect to that environment.
Users aren't limited to the thresholds Horizon creates to calculate the load index. The first checkbox in the settings page enables users to create a custom script. To create a script on each RDS host, enable the VMware Horizon Scripting host service and register your script, which the scripting host service will run. The VMware View Agent provides sample scripts in the installation directory on each RDS host. The created script must generate the load index based on an IT team's own formulas.







