wireless ISP (wireless Internet service provider or WISP)
What is a wireless internet service provider (ISP)?
A wireless internet service provider (WISP) is an internet service provider (ISP) that allows subscribers to connect to the internet at designated hot spots or access points using a wireless connection such as Wi-Fi.
This type of ISP offers broadband service and allows subscriber computers and other devices, called stations, to access the internet and the web from anywhere within the service's coverage area. This is usually a region with a radius of several kilometers.
How do wireless ISPs work?
The simplest wireless ISP is a basic service set (BSS) consisting of one server and numerous stations all wirelessly linked to that server. More sophisticated WISP networks use the extended service set (ESS) topology, consisting of two or more BSSes linked together at access points. Both BSS and ESS are supported by the IEEE 802.11b specification.
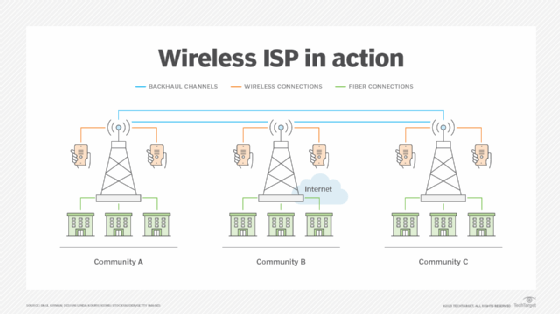
Figure 1 depicts a typical wireless ISP. It provides wireless and wireline cable internet connections from its cell towers to deliver internet access to its customers. Each service area connects to others using backhaul channels.
WISPs offer a variety of download speeds in megabits per second and even gigabits per second when providing high-speed internet service. ISPs offer a variety of internet service plans, such as fixed wireless internet, digital subscriber line or DSL, business and home internet.
WISPs must be diligent about maintaining their network infrastructures and regularly assess capacity to ensure that all customers have adequate bandwidth. Supporting WISPs are terrestrial fiber network rings that ensure sufficient bandwidth, fastest internet, network recoverability and overall reliability.
Benefits and drawbacks of wireless ISPs
Wireless ISPs, their infrastructure and services have changed the literal landscape as well as the communications capabilities of businesses. They also come with some challenges.
Advantages of WISPS
- More access. Wireless ISPs increase the reach of the internet to rural areas and regions that are distant from larger communities that are served by the major telecommunication operators, such as AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon.
- Variety of services. WISPs typically offer a variety of voice and data services, including internet access, to the communities they serve. Internet access can be delivered by fiber optic cable or wireless technology to buildings and residences.
- Flexibility. Customers can relocate within a wireless ISP's service area with minimal disruption. Remote customers can be added without the need to build an aerial or underground network.
Challenges of WISPS
- Weather issues. Severe weather can impact wireless transmission quality.
- Other interference. Power lines, trees and even buildings can interfere with wireless access and service.
- Bandwidth and performance issues. If the service provider builds out the wireless network without factoring in its effect on bandwidth and performance, it may result in slower data speeds and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Find out how 5G is affecting telecom infrastructure and ISPs and their wireless services.








