What is a SIM card and how does it work?
A SIM card, also known as a subscriber identity module, is a smart card that stores the information necessary for a smartphone to connect to a mobile network.
SIM cards contain data including user identity, location, phone number, network authorization, personal security keys, contact lists and stored text messages. They enable a device to be identified and authenticated on the network.
Without a SIM card, some phones could not make calls, connect to internet services such as 4G Long-Term Evolution (LTE) and 5G, or send Short Message Service (SMS) messages. SIM cards are removable and can store from 32 to 128 kilobytes of data.
The foundation for cellular communications
Two distinct technologies formed the foundation for 2G and 3G networks, but have been phased out in the U.S. in recent years in favor of newer technologies such as 4G LTE and 5G: Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA). GSM, which was used by network carriers such as AT&T and T-Mobile, enabled users to remove their SIM cards from their devices and move them to other mobile devices, preserving their data and contacts.
CDMA-enabled phones did not need a SIM card because they used an electronic serial number (ESN). However, users who had a phone with an ESN could not switch between devices. Network carriers such as Sprint and Verizon used CDMA for their 2G and 3G networks, but phased out these technologies in 2022 in favor of 4G LTE and 5G.
While carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon no longer require SIM cards, these cards are still present in devices operating on their networks. The transition to 4G LTE and 5G requires SIM cards for accessing and authenticating on these networks. Although these newer technologies are now dominant, GSM and CDMA laid the foundation for modern cellular communication.
Both technologies established digital standards and made key contributions to global interoperability. Although providers such as Vodafone have also phased out the use of 3G in European markets, they still use 2G for voice calls and messaging. Shutdowns of legacy 2G networks are planned to be completed by 2033.
How does a SIM card work?
Every SIM card has its own unique ID number -- an IMSI, or International Mobile Subscriber Identity, which associates the device with its user. SIM cards also include an ICCID, or Integrated Circuit Card Identifier, which serves as a kind of serial number.
Information about a user's network plan, such as the plan type, data limits and voice minutes limit, is stored on the SIM card. The IMSI is also associated with the user's account to facilitate charges, fees, and other billing and usage.
When a person makes a call or sends a text, the device sends an access request to the network; using the ICCID, the SIM card verifies that the device is authorized to make the call or send the text on that network. The network will deny an unauthorized SIM card request.
SIM cards also store a user's personal data, including contacts and text message history. This is one of the primary ways of migrating that information from one device to another.
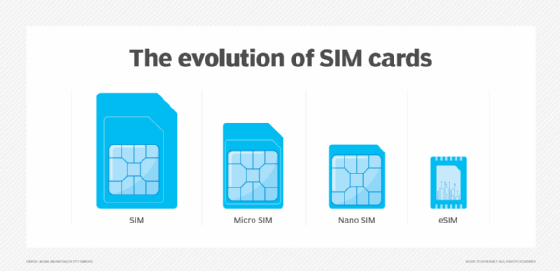
Types of SIM cards
SIM card sizes and forms have evolved over time in the following ways:
- Standard or full-size SIM cards measure 25 by 15 millimeters (mm) and are used in older and basic phones.
- Mini SIM cards measure 15 by 25 mm and are found in phones from the late 1990s and early 2000s.
- Micro SIM cards measure 15 by 12 mm and are more likely to be found in phones from the 2010s and later.
- Nano SIM cards measure 12.3 by 8.8 mm and are used in newer smartphones.
- Embedded SIMs (eSIMs) measure 6 by 5 mm and have the SIM card already installed in the phone. The network carrier activates eSIMs remotely.
- Dual SIM cards can be used with another SIM card in the same device, enabling two phone numbers on one phone, with two sets of incoming and outgoing calls and text messages on that one device. These are typically associated with nano SIMs and eSIMs.
The iPhone 16 series supports dual SIM. U.S. models are eSIM only, whereas international models -- excluding China -- retain a physical SIM card slot; one SIM card is removable, and the other is an eSIM.
Benefits of SIM cards
Users can easily switch a SIM card from one phone to another, and this data portability offers several benefits. For example, a user who buys a new phone can install their current SIM card to associate the new phone with the same number and user preferences as the old one. This includes contacts or text messages stored on the SIM card. However, users must manually transfer data stored on the phone's internal memory, including photos, videos, apps and other files.
In another common situation, if a phone's battery runs out of power, a user can easily install their SIM card in another subscriber's phone. Some vendors offer prepaid SIM cards that include unlimited talk and text to provide travelers with a local number if their cellphone is not locked to a specific carrier.
Challenges of SIM cards
SIM cards can also have their downsides, including the following common challenges:
- Vulnerability to hacking. SIM cards can be a prime target for hackers because of the sensitive personal information they contain.
- Billing issues. When a user travels to another country, the limitations of their existing SIM card can result in excessive international roaming and data charges. Therefore, it is advisable to obtain an international service plan that will be reflected on the SIM or purchase a local SIM card in the destination country.
- Easy misplacement. As seen above, SIM cards are getting smaller, making them far easier to lose if they are not installed in their host device.
SIM card security issues
An individual's SIM card can be a target for hackers because it is a key to their digital identity. A person's phone number is often linked to their email, banking and social media accounts. If a hacker gains access to a user's personal information, they could transfer the user's phone number to another SIM card using a SIM swapping attack.
In this kind of attack, the attacker tricks the mobile service provider into thinking they are the actual customer, after which the attacker can transfer the target user's account to a new SIM card that the attacker controls. This gives the hacker access to any of the user's accounts linked to that phone number through multifactor authentication.
SIM cards have a security code to prevent them from being used in a separate device, so users can go into their phone's settings and change the SIM card's personal identification code to something more complicated. Other SIM security features include authentication and encryption to protect data and prevent eavesdropping.
Future of SIM cards
Although several industry observers have suggested that SIM cards are an outdated technology, there is not yet a clear successor to replace them. The dual SIM paradigm noted above -- two phone numbers for one device -- is likely to grow in popularity. It is also likely that eSIMs will become more prevalent than physical SIMs.
Smartphones are being used to address global health concerns such as sleep apnea and hearing loss. Learn how groundbreaking technology is creating smartphone-based diagnostic tools.





