What is NFV MANO (network functions virtualization management and orchestration)?
NFV MANO (network functions virtualization management and orchestration), or just MANO, is an architectural framework used to manage and orchestrate virtual network functions (VNFs) and other software components.
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) Industry Specification Group defined the MANO architecture to facilitate the deployment and connection of services as they are decoupled from dedicated physical devices and moved to virtual machines (VMs).
In virtual environments, it's possible to deploy network components in hours rather than months. MANO reduces confusion by managing and orchestrating resources, including the following:
- Compute.
- Storage.
- Networking.
- VNFs, such as routing, firewalls and load balancing.
NFV MANO architecture
NFV MANO has three main functional blocks. Together, these blocks deploy and connect functions and services when needed throughout the network:
- NFV orchestrators. NFV orchestrators consist of two layers -- service orchestration and resource orchestration -- which control new network services and VNF integration into a virtual framework. They also validate and authorize NFV infrastructure (NFVi) resource requests.
- VNF managers. VNF managers oversee the VNF instances' lifecycle.
- Virtualized infrastructure managers. VIMs control and manage NFVi, which encompasses compute, storage and network resources.
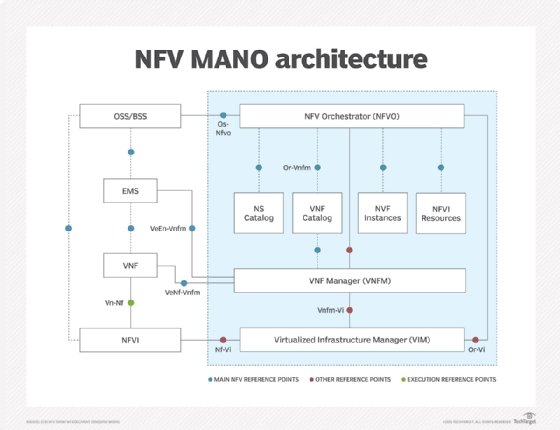
MANO works with templates for standard VNFs, so users can pick from existing NFVi resources to deploy their NFV platform. Effective NFV MANO must integrate with application programming interfaces in existing systems to work with multivendor technologies across multiple network domains. Telecommunications providers' operations and billing systems also must interoperate with MANO.







