
maxkabakov - Fotolia
Arista launches zero-trust security with a Forescout option
Arista's zero-trust security framework segments devices into groups and sets policies for network access. Forescout integration is available for dynamic device identification.
Arista has launched a zero-trust network security framework that's most effective through a combination of homegrown and partner technologies.
The Arista Multi-Domain Macro-Segmentation Service, introduced this week, builds a zero-trust architecture around data and services on the network. The system comprises technology within Arista's CloudVision management console and EOS network operating system.
Arista provides open APIs to third-party tools for more advanced zero-trust features, including those from Arista partner Forescout Technologies. Forescout provides software for discovering, classifying and assessing various IP-connected laptops, mobile devices, virtual computers, storage and network devices, operational technology systems and IoT devices.
Zero trust is a cybersecurity approach that defines a protective perimeter around data and services in public clouds or private data centers. The system authenticates people and devices before allowing them to access only the resources network managers have authorized them to use.
Arista zero trust
Arista built into its Extensible Operating System (EOS) technology called Macro-Segmentation Service-Group to provide zero-trust security. The MSS-Group architecture has three levels: policy, orchestration and enforcement.
CloudVision with MSS-Group lets network administrators use the former to categorize device groups and use a device's IP address to map it to a particular group. Managers also use CloudVision to create the policy that defines the resources a device can access.
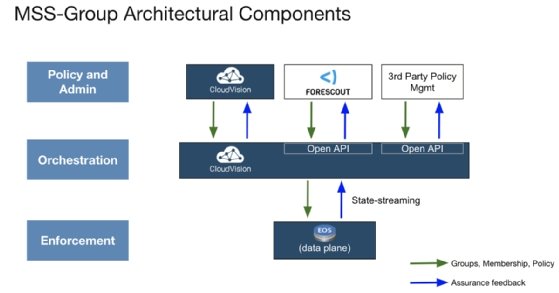
A third-party vendor like Forescout makes the security system more robust by swapping IP addresses for grouping with dynamic device identity. Forescout's software supports more than 600 versions of operating systems, 10,000 device types, and 5,700 vendors and models.
"The best insights are built with more context, and no single provider can have enough," said Eric Hanselman, an analyst at 451 Research. "That's leading to many partnerships to feed security analytics."
CloudVision would use Forescout to associate each connected device with a specific group and policy. It would also orchestrate all changes to groups and policies through communication with MSS-Group and enforcement through EOS. The latter would reconfigure underlying hardware switches to execute changes.
Arista's zero-trust system includes a firewall called MSS Firewall. There is also MSS Host, which extends security policies from a VMware NSX virtualized network to the physical network. Both ship as part of CloudVision.
Arista plans to make test versions of MSS-Group available by the end of March.
Besides group segmentation within a zero-trust architecture, Arista also supports broader network segmentation models, such as access control lists, VXLAN with EVPN, and VLANs.
Antone Gonsalves is the news director for the Networking Media Group. He has deep and wide experience in tech journalism. Since the mid-1990s, he has worked for UBM's InformationWeek, TechWeb and Computer Reseller News. He has also written for Ziff Davis' PC Week, IDG's CSO Online and IBT Media's CruxialCIO, and rounded all of that out by covering startups for Bloomberg News. He started his journalism career at United Press International, working as a reporter and editor in California, Texas, Kansas and Florida.





