KOHb - Getty Images
How to detect a deepfake with visual clues and AI tools
Forewarned is forearmed, but too many employees don't realize how sophisticated deepfakes have become. Integrate these deepfake detection tips into security awareness training.
Deepfakes -- once the stuff of science fiction -- are now so convincing that the best ones can fool even savvy end users.
While some AI-generated content can be useful and completely benign, deepfakes -- realistic, AI-generated images, video and audio recordings -- often aim to mislead and misinform. Cybercriminals increasingly use them to perpetrate identity theft, data theft and fraud.
In enterprises, deepfakes can lead to serious security incidents and substantial financial losses. One documented attack, for example, saw threat actors use deepfake technology to impersonate an organization's CFO on a video call and convince a finance employee to send them $25 million.
Many corporate end users remain unaware that such attacks are even possible, making deepfake education a critical addition to security awareness training. This article presents tips and tools to help employees identify deepfakes and protect their organizations from cyberattacks and fraud.
7 tips to spot a deepfake
Users should be alert for the following imperfections, inconsistencies and oddities, which often appear in deepfake images, videos and audio recordings and streams.
1. Facial and body movements
Although deepfake technology is rapidly improving, it often fails to produce facial expressions and body movements that appear human-like and natural under scrutiny.
When viewing images of people with inhuman qualities, the brain generates a negative emotional response -- dubbed the uncanny valley. Urge employees to heed that instinct, as it might serve as the only indicator that they are viewing deepfake content.
2. Lip-sync detection
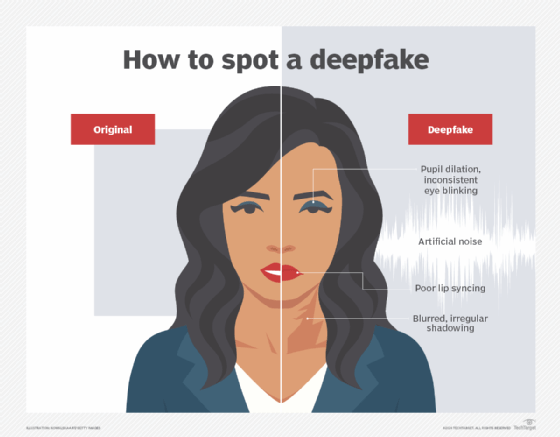
Lip movements that don't match the corresponding voice might suggest deepfake activity, due to altered audio and synchronization issues.
3. Inconsistent -- or lack of -- eye blinking
Currently, AI struggles to simulate natural eye blinking. As a result, deepfake algorithms often produce inconsistent blinking patterns or eliminate eye blinking altogether.
4. Irregular reflections or shadowing
Deepfake algorithms often fail to realistically depict shadows and reflections that make sense in the context of the image. Look closely at reflections and shadows on surrounding surfaces, in backgrounds and even within participants' eyes to see if they appear natural or set off alarm bells.
5. Pupil dilation
AI typically does not alter the diameter of subjects' pupils, which can sometimes lead to eyes that appear off. This is especially evident if the subject's eyes are focusing on objects that are either close or far away, or should be adjusting to multiple light sources. If you are watching subjects whose pupils aren't dilating naturally, that's a sign that the video is a deepfake.
6. Incongruent skin and facial features
Subjects of deepfakes often exhibit strangely uniform skin, lacking natural variation in texture and coloration that comes from wrinkles, freckles, sunspots, moles, scars and shadows. Additionally, facial features might not seem cohesive -- perhaps the person's eyes look much younger than their skin and hair, or vice versa.
7. Audio oddities
Voices that sound unnaturally flat, repetitive or glitchy should raise suspicion. Similarly, those that fail to respond to changes in tone, in the case of a real-time conversation, could be deepfake-generated. Some deepfakes also have obviously artificial background noise.
How to detect fake content with AI
As deepfake creation technologies continue to improve, it will become more difficult to determine if content has been altered. But AI can also be used to detect AI-generated deepfakes. And the good news here is, even as deepfake creation evolves, so too will AI-powered deepfake detection technologies.
Several deepfake detection tools are available today that ingest large sets of deepfake images, video and audio. Through machine learning and deep learning, the data is analyzed to identify unnatural patterns that signify the content has been artificially created.
The following are two additional ways that AI can be used to automatically spot deepfakes:
- Source analysis. Identifying the source of a multimedia file can be a giveaway that it has been altered. The challenge is that file source analysis is a daunting task when using manual methods. Deepfake detection algorithms can respond much more thoroughly and rapidly as they analyze file metadata to ensure a video is completely unaltered and authentic.
- Background video consistency checks. It used to be easy to identify a deepfake by its background. But, today, AI tools have progressed to a point where they are increasingly capable of altering backgrounds so they look complexly authentic. Deepfake detectors can pinpoint altered backgrounds by performing highly granular checks at multiple points to identify changes that might not be picked up by the human eye.
Alissa Irei is senior site editor of Informa TechTarget Security.
Andrew Froehlich is founder of InfraMomentum, an enterprise IT research and analyst firm, and president of West Gate Networks, an IT consulting company. He has been involved in enterprise IT for more than 20 years.