What is a hard disk drive (HDD)?
A computer hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile data storage device. Non-volatile refers to storage devices that maintain stored data when turned off. All computers need a storage device, and HDDs are just one type.
HDDs are usually installed in desktop computers, mobile devices, consumer electronics and enterprise storage arrays in data centers. They store operating systems (OSes), software programs and other files using magnetic disks.
More specifically, hard disk drives control the reading and writing of the hard disk that provides data storage. HDDs are used either as the primary or secondary storage device in a computer. They are commonly found in the drive bay and are connected to the motherboard via an Advanced Technology Attachment, Serial ATA, parallel ATA or Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) cable, among other formats. The HDD is also connected to a power supply unit and can retain stored data while powered down.
A hard disk drive -- often shortened to hard drive -- and hard disk are not the same things, but they are packaged as a unit and either term can refer to the whole unit.
Why do computers need hard disks?
Storage devices such as hard disks are needed to install OSes, programs and additional storage devices, and to save documents. Without devices like HDDs that retain data after they've been turned off, computer users wouldn't be able to store programs, files or documents on their computers. This is why every computer needs at least one storage device to permanently hold data as long as it's needed.
HDDs are for long-term storage. Random access memory, on the other hand, only stores data for immediate use until a computer is either shut down or restarted. RAM is also referred to as volatile memory. Specific file types, such as music, pictures or videos, are meant for long-term storage, making storage devices necessary.
How do hard disk drives work?
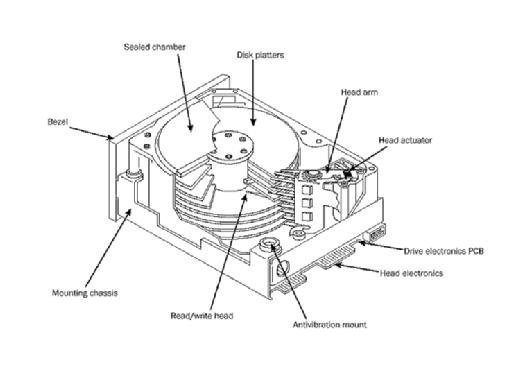
Most basic hard drives consist of several disk platters, which are circular disks made of either aluminum, glass or ceramic with a thin magnetic coating. The platters are positioned around a spindle inside a sealed chamber.
A motor connected to the spindle spins the platters at up to 15,000 rotations per minute. As the platters spin, a second motor controls the position of the read and write heads that record and read information to and from tracks on the platters using a magnetic head
Hard disk drive storage capacity
Some of the most common storage drive capacities include the following:
- 16 GB, 32 GB and 64 GB. This range is among the lowest for HDD storage space and is typically found in older and smaller devices.
- 120 GB and 256 GB. This range is considered an entry point for HDD devices such as laptops or computers.
- 500 GB. Most computer users have 500 GB or more disk drive storage. With this much space, users can most likely store all their music, photos, videos and other files.
- 1 TB and 2 TB. Individuals with games that take up a lot of space need 1 TB to 2 TB of HDD space.
- More than 2 TB. Users who work with high-resolution files need more than 2 TB of disk space. This is also a requirement for people who need to store or house a large amount of data, or who want to use that space for backup and redundancy.
The highest capacity HDD available is 36 TB. However, an HDD has less usable space than advertised because the OS, file system structures and some data redundancy procedures use a portion of the HDD. Enterprise use of disk drives, such as for large-scale file collections, can require anywhere from a few terabytes to the maximum number of terabytes on an HDD. Home office users often require less than a terabyte.
Hard drive components and form factors
Hard disk drive components include the spindle, disk platter, actuator, actuator arm and read/write head. Even though the term hard disk drive is used to refer to the unit as a whole, the term hard disk is the set of stacked disks. This is the part of the HDD that stores and provides access to data on an electromagnetically charged surface.
The HDD form factor refers to the physical size or geometry of the data storage device. HDD form factors follow a set of industry standards that govern their length, width and height, as well as the position and orientation of the host interface connector. Having an industry-standard form factor helps determine a common compatibility with different computing devices.
The most common form factors for HDDs in enterprise systems are 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch -- also known as small form factor and large form factor. The 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch measurements represent the approximate diameter of the platter within the drive enclosures.
While there are other form factors, by 2009, manufacturers discontinued the development of products with 1.3-inch, 1-inch and 0.85-inch form factors. The falling price of flash memory and flash drives made these other form factors almost obsolete. It's also important to note that while nominal sizes are in inches, actual dimensions are specified in millimeters.
Many solid-state drives are also designed for the HDD form factor. SSDs that fit into the same slots as HDDs generally use the SATA interface or serial attached SCSI, also known as a SAS interface, to transfer data to and from the host computing system.
What are external HDDs?
Most HDDs are internal hard drives inside a computer and work as described above. However, external hard drives are also available to expand a computer's storage capacity or act as a portable device to back up data. External drives connect to a computer or device through interfaces such as USB 2.0, USB-C or with external SATA. External hard drives might also have slower data transfer rates compared to internal HDDs.
The main advantage of an external hard drive, in addition to expanding a device's storage space, includes being portable. Users can store data from multiple devices and physically bring that data with them wherever they go.
Common hard disk errors
Hard disks can fail for all sorts of reasons. However, failures generally fall into the following six categories:
- Electrical failure occurs when, for example, a power surge damages a hard disk's electronic circuitry, causing the read/write head or circuit board to fail. If a hard disk powers on but can't read and write data or boot, it's likely that one or more of its components has suffered an electrical failure.
- Mechanical failure can be caused by wear and tear, as well as by a hard impact, like a hard drop. This might cause the read/write drive head to hit a rotating platter, causing irreversible physical damage.
- Logical failure results when the hard disk's software is compromised or ceases to run properly. All sorts of data corruption can lead to logical failure. These include corrupt files, malware and viruses, improperly closing an application or shutting down a computer, human error or accidentally deleting files that are critical to hard disk functionality.
- Bad sector failure can occur when the magnetic media on a hard disk's rotating platter is misaligned, resulting in a specific area on the platter becoming inaccessible. Bad sectors are common and often limited when they occur. Over time, the number of bad sectors can increase, eventually leading to a system crash, inaccessible files or the hanging or lagging of the operation of a hard disk.
- Firmware failure happens when the software that performs maintenance tasks on a drive and enables the hard disk to communicate with a computer becomes corrupted or stops working properly. Firmware failure can lead to the disk freezing during bootup or the computer a hard disk is connected to not recognizing or misidentifying it.
- Multiple unknown failures that accumulate over time can also occur. For example, an electrical problem could lead to a mechanical failure, such as a read/write head crash. It might also lead to a logical failure, resulting in several bad sectors developing on the hard disk platters.
History and technical evolution of HDDs
Some significant milestones in the development of hard disk drives include the following:
- 1953. IBM engineers created the first hard disk as a way to provide random access to high capacities of data at a low cost. The first disk drives were the size of refrigerators, could store 3.75 MB of data and began shipping in 1956. Memorex, Seagate Technology and Western Digital were other early vendors of hard disk drive technology.
- 1980s. Hard disk drive form-factor size decreased as the technology evolved. By the mid-1980s, 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch form factors were introduced and became standard in personal computers. Hard disk drive density has increased since the technology was first developed. The first hard disk drives could store megabytes of data, while today their storage capacity is in the terabyte range.
- 2007. Hitachi Global Storage Technologies (HGST) -- now a Western Digital brand -- released the first 1 TB hard drives in 2007.
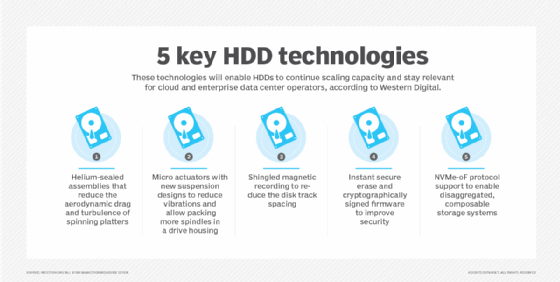
- 2012. HGST announced the first helium-filled hard disk drive in 2012. Helium is less dense, cooler and lighter than air, consumes less power, increases drive density and improves performance compared to traditional hard disk drives.
- 2013. Seagate Technology announced hard disk drives that use shingled magnetic recording technology. SMR increases storage density in HDDs by layering the magnetic tracks on each disk, rather than placing them parallel to each other. It's referred to as shingled because the tracks overlap similar to shingles on a roof.
- 2015. HGST announced the first 10 TB hard drive.
- 2018. Western Digital released the Purple 12TB with AllFrame AI-powered technology for surveillance and security systems.
- 2021. Western Digital unveiled two 20 TB HDDs -- the Ultrastar DC HC560 and WD Gold HDD Enterprise Class SATA HDD. The Ultrastar DC HC560 was designed for cloud storage providers and business servers, security systems and network-attached storage devices. The WD Gold HDD was designed for enterprise businesses that run heavy application workloads.
- 2025. Seagate releases its Exos series HDDs which can store 36 TB of data.
HDDs vs. SSDs
Solid-state drives are the main alternative to hard disk drives. Unlike hard disks, SSDs contain no moving parts and have lower latency than HDDs. SSDs are often favored to store critical data that must be accessed quickly and for applications with a high input/output demand.
SSDs are configured to deliver high read/write speeds for sequential and random data requests. They don't store data magnetically, so the read performance remains steady, regardless of where the data is stored on the drive. SSDs also have faster boot times. Because of these benefits and higher likelihood of breakdowns with hard disk drives, SSDs are replacing HDDs in many applications.
Non-volatile memory express, or NVMe SSD technology has also changed the storage landscape, including how HDDs are used. It provides faster data access and transfer speeds compared to traditional HDDs, leading to improved performance and user experience.
However, even though most PC users have started to favor SSDs, HDDs and magnetic tape are still used frequently to store large quantities of data. This is partly because SSDs are more expensive than HDDs from a price-per-gigabyte standpoint. Many enterprise storage arrays ship with a mix of HDDs and SSDs to reduce costs while providing better performance. SSDs also have a set life expectancy, with a finite number of write cycles before performance slows. Compared to an HDD, SSDs fail faster.
What is a hybrid hard drive?
A hybrid hard drive is an approach that combines the strengths of both HDDs and SSDs, aiming to address the drawbacks of each. Specifically, a hybrid hard drive combines the speed of SSD read/write operations with HDD storage capacity. Hybrid hard drives feature an intelligent algorithm that stores data based on user habits. Data used often is stored in the SSD, while data accessed less often is stored in the HDD component.
This combination is beneficial for performance improvements. It is also cheaper to purchase a single hybrid hard drive than to separately purchase an SSD and an HDD. While a hybrid hard drive might seem like a silver bullet due to its high performance and durability, it is nonetheless prone to mechanical failures, especially during outages. These drives also usually come with limited storage space.
How to improve hard disk drive performance
Multiple best practices must be followed to improve the performance of an HDD:
- Frequent cleanups. Deleting temporary files, junk data and apps that are unnecessary or obsolete will consume less memory. This is a common practice to create more drive space and improve performance. It's usually performed by either built-in cleanup tools, as is the case with Windows, or third-party software.
- Write caching. Enabling the write caching feature means data is quickly written to and kept in a cache instead of the HDD. This is appropriate for short-term data use, especially considering the cache is susceptible to data loss during technical failures. Write caching also reduces the operations an HDD is required to perform to prolong its lifespan.
- Defragmentation. This technique, performed with either built-in features or defragmentation software and tools, rearranges saved data to have it stored in sequential blocks. This makes it faster and easier for HDDs to access data.
- Performance monitoring. Scanning for defects that could corrupt or delete data and monitoring performance of an HDD is a proactive approach to improve drive performance.
- Routine upgrades. Multiple actions can address lagging HDD performance, including performing routine software updates, referring to HDD manufacturer websites for firmware updates or simply replacing old drives with new ones.
AI is having a profound effect on storage technology. Find out what the future might hold for enterprise storage.







