WebLogic
What is Oracle WebLogic Server?
Oracle WebLogic Server is a leading e-commerce online transaction processing (OLTP) platform, developed to connect users in distributed computing production environments and to facilitate the integration of mainframe applications with distributed corporate data and applications.
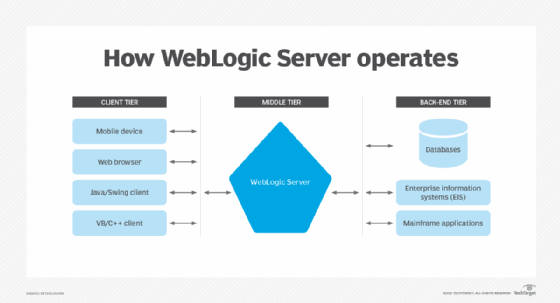
WebLogic is an Application Server that runs on a middle tier, between back-end databases and related applications and browser-based thin clients. WebLogic Server mediates the exchange of requests from the client tier with responses from the back-end tier.
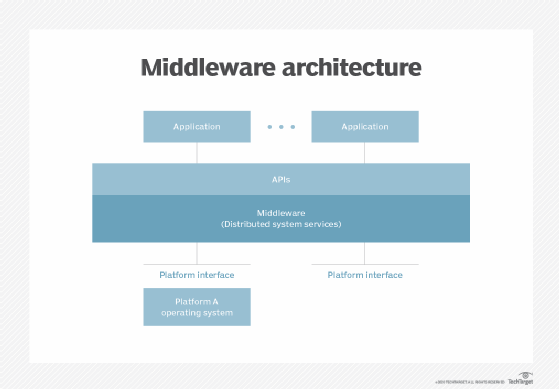
WebLogic Server is based on Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) (formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition or J2EE), the standard platform used to create Java-based multi-tier enterprise applications. Java EE platform technologies were developed through the efforts of BEA Systems and other vendors in collaboration with the main developer, Sun Microsystems.
Because Java EE applications are standardized modules, WebLogic can automate many system-level tasks that would otherwise have demanded programming time.
What is WebLogic used for?
Enterprises use WebLogic Server to develop distributed applications, enabling users to access applications from a client -- web browser, mobile device or any other type of client program or device using a program written in Java or any other language -- and systems on the back end -- databases, enterprise information systems or mainframe applications.
WebLogic features and capabilities
As one component of Oracle's Fusion middleware platform, WebLogic capabilities include the following:
- support for databases including Oracle Database, Oracle MySQL Enterprise, Microsoft SQL Server and IBM DB2;
- .NET interoperability;
- native integration with other middleware and APIs; and
- support for a security model that separates security code from business logic.
The main features of WebLogic server include the following:
- connectors that make it possible for any legacy application on any client to interoperate with server applications;
- Enterprise JavaBean (EJB) components;
- resource pooling;
- connection sharing enables improved application scalability; and
- an administration console with a user interface makes management tasks more efficient and includes features such as:
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) support for the encryption of data transmissions; and
- authentication and Authorization mechanisms to make applications and transactions secure.
WebLogic server architecture
A WebLogic server installation includes at least one WebLogic server instance but may include multiple server instances on one or more separate computer servers.
Multiple WebLogic servers are administered together as a unit called a domain. Each WebLogic domain includes a single administration server and may contain additional server instances managed by the administration server. When these managed servers are configured to be part of a WebLogic Server cluster, they enable scaling for high-availability applications.
WebLogic Server domains can also be deployed on a public cloud, using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes.
How popular is WebLogic?
WebLogic Server is intended for high-traffic applications, so it is not surprising that it is not used by many sites. According to W3Techs -- Word Wide Web Technology Surveys, usage statistics for WebLogic Server indicate it is used by less than 0.1% of all websites running a known web server.
However, WebLogic Server market share increases for the top-ranking busiest sites. As an integral part of Oracle's application server stack, WebLogic Server does not need to be popular outside of its target market: large enterprises that require highly scalable server environments for OLTP applications.
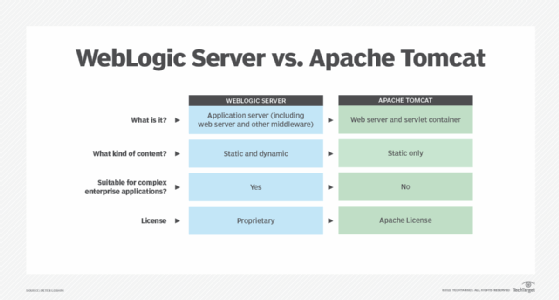
Oracle WebLogic Server vs. Apache Tomcat
The Apache Tomcat web server is often compared with WebLogic Server. The Tomcat web server serves static content and dynamic content in web applications delivered in Java servlets and JavaServer Pages.
The fundamental difference between WebLogic Server and Apache Tomcat is that WebLogic is an application server. That means WebLogic includes components that provide web services as well as a server environment for accessing enterprise data resources like databases and transaction processing.
History of WebLogic
WebLogic server was the first J2EE application server.
- 1995: WebLogic, Inc. founded.
- 1997: First release of WebLogic Tengah.
- 1998: WebLogic, Inc., acquired by BEA Systems.
- 2008: BEA Systems acquired by Oracle.
- 2020: WebLogic Server version 14 released.
WebLogic Server can solve some thorny problems for enterprises that need to tightly integrate their information systems with a scalable OLTP platform. It may be too much for simpler applications; find out if Apache Tomcat server works better for your applications.






