What is RHIA (Registered Health Information Administrator)?
A registered health information administrator (RHIA) is a certified professional who oversees the creation and use of electronic health records (EHRs). RHIAs work in healthcare and related settings, such as health IT vendors and insurance carriers. The acronym is pronounced by its letters: "R-H-I-A."
Holding an RHIA certification can potentially advance one's career in health information management through greater responsibilities and higher salaries. RHIA is among 10 credentials issued by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), a nonprofit organization that represents health information management professionals.
RHIA responsibilities and job description
AHIMA describes RHIAs as important links between providers, patients and payers in terms of managing and analyzing EHRs and administering some of the technology involved.
As such, RHIAs commonly talk and collaborate with a variety of colleagues who interact with health data, such as clinicians, finance reps, administrative workers and IT professionals. Managing certain people and budgets may also fall to RHIAs.
Professionals who hold an RHIA certification "focus on data governance, HIPAA privacy and security, and data analytics," according to an explanation of the certification's responsibilities by the University of Wisconsin, which offers a health information management and technology degree program.
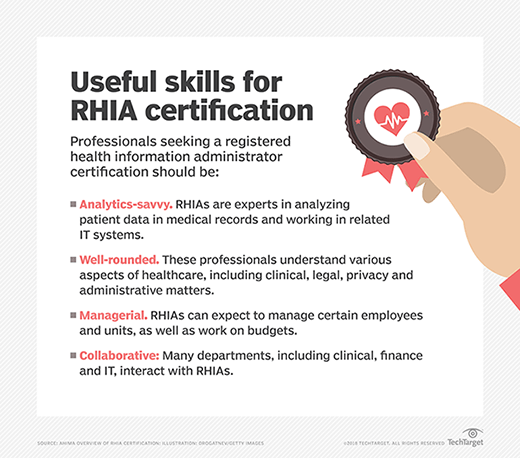
Necessary skills and qualifications
Based on information published by AHIMA, RHIA candidates should have the following skills and qualifications:
- Expertise in handling patient records and analyzing the data within those documents;
- Knowledge about medical, administrative, legal and ethical standards related to the delivery of healthcare and safeguarding protected health information (PHI), which includes HIPAA requirements;
- Ability to manage departments and people, prepare budgets and collaborate with administrative teams within healthcare systems; and
- Prowess in working with decision-makers in patient data activities.
RHIT vs. RHIA
The registered health information technician (RHIT) is another certification issued by AHIMA. The RHIT credential aims at ensuring the proper accuracy and entry of medical records in health IT systems.
Although patient information and EHRs can be updated by RHITs, it is an RHIA's job to manage the health information system's database. A RHIT is generally responsible for the individual records they manage, while a RHIA can be thought of as responsible for an entire system and all the records therein.
In short, RHIAs generally make more money and have more responsibilities than those who hold the RHIT credential. However, according to the University of Wisconsin, which compared the two credentials in 2017, RHIAs also require more education.
Obtaining RHIA certification
Candidates for RHIA certification must meet criteria set by AHIMA and the Commission on Accreditation of Health Informatics and Information Management Education (CAHIIM). In some cases, candidates may be able to graduate from a program approved by a foreign association that cooperates with AHIMA.
AHIMA and CAHIIM require candidates to complete certain academic requirements, such as a bachelor's or master's degree in health information management or a related post-degree program. Under certain conditions, people who hold an RHIT certification may also qualify for RHIA.
The RHIA exam is four hours long, with candidates answering 180 multiple-choice questions based on competencies needed to meet the certification. The exams are held at various locations and dates throughout the U.S. in cooperation with Pearson Education, which operates professional testing centers.
Recertification is based on a two-year cycle, with RHIAs required to obtain 30 continuing education units (CEUs) during that period.
Exam application fees are modest, ranging from about $217 to $299, depending on whether someone is an AHIMA member.
RHIA Exam domains
The RHIA exam is divided into five domains of knowledge. To pass, the applicant should be proficient in each domain.
Domain 1: Information Governance. This area involves how healthcare data is managed, controlled and the structure of records. It includes industry standards and how to interpret organizational policies.
Domain 2: Compliance with Uses and Disclosures of PHI. This area includes how to protect, monitor and process PHI. It also includes how to appropriately release or destroy it according to regulations. Appropriate reporting of breaches is also covered.
Domain 3: Data Analytics and Informatics. This area includes the ability to gather information from databases, optimize the databases and audit data integrity. Creating visualizations and statistics for stakeholders is also covered.
Domain 4: Revenue Management. This includes assigning appropriate cost codes, clinical documentation and reimbursement. The applicant should fully understand the entire revenue cycle.
Domain 5. Management and Leadership. This covers the administrative areas such as working with management, human resources, training, budgets and licensing.
RHIA salary
It is not easy to quantify the value of an RHIA certification in a paycheck. According to the latest available numbers from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, health information managers generally earn a median salary of $96,540 annually. An AHIMA survey places the average salary for RHIT professionals at about $91,450. Some job search sites, such as Indeed.com, indicate lower salaries for these careers.
Although a RHIA certification is not the sole determinant of salary levels, a job candidate who is an RHIA may be able to command higher pay and more responsibility.
For example, in the past, AHIMA indicated through survey results that a healthcare coder with an RHIA credential could earn 15% more in pay than a coder without the certification.
Common RHIA job titles
According to the University of Wisconsin, someone with an RHIT certification may hold one of the following job titles:
- Health Information Management (HIM) director or manager
- Coding supervisor or manager
- Privacy or security officer
- Compliance analyst
- Patient information coordinator
- Data quality manager
- Data integrity analyst
- EHR implementation specialist
Career growth and future outlook
A combination of heavy technology use in healthcare and an aging population has increased the demand for health information management professionals, including RHIAs.
Medical and health services jobs -- including those for health information management professionals -- were anticipated to grow by 29% from 2023 to 2033, reported the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
While continuing to hold jobs in traditional healthcare settings, such as hospitals and long-term care facilities, RHIAs are also finding job opportunities in nonpatient settings that have ties to the medical field, according to AHIMA.
For example, interest in RHIAs has risen at insurance companies, technology vendors and pharmaceutical firms. This interest is likely sparked by the growing importance throughout healthcare of analyzing patient data for efforts such as population health management and value-based care.
The popularity of telehealth has increased the need for RHIA-certified professionals to manage the electronic records involved. This information needs to be transmitted and stored securely, from the practitioner to the patient.
AI is expected to greatly affect the medical field, especially medical coding and other simple record management tasks. RHIA-certified professionals are positioned to take advantage of these changes as their role is less focused on individual record management and more focused on the integrity of the database and system. These management aspects are less likely to be easily automated and will usually require a human for security.
AI tools are changing healthcare by making it more efficient and improving care quality. Check out some of the top AI tools available in healthcare today.







