What is Cerner Corp.?
Cerner Corp., now known as Oracle Health following its 2022 acquisition by Oracle, is a prominent health IT company based in North Kansas City, Missouri.
It provides a wide range of products, including electronic health records (EHRs), population health management tools, medical devices and IT infrastructure for healthcare organizations. While Cerner was best known for its EHR offerings, its strategic focus expanded under Oracle's leadership to integrate cloud-based analytics and AI capabilities for improved healthcare outcomes.
Cerner Corp.'s market share and global footprint
As of 2021, Cerner held a significant share of the EHR market in the U.S., rivaled closely by Epic Systems. According to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, Cerner and Epic dominated the certified Health IT Module market, together comprising nearly half of the U.S. acute care hospital market.
Before the Oracle acquisition, Cerner products were used by more than 27,000 healthcare providers in over 35 countries. The company employed over 26,000 associates globally.
Cerner Corp.'s top products
Cerner offers a range of health IT solutions tailored for hospitals, outpatient clinics and long-term care facilities, including the following:
- Cerner Millennium. Now called Oracle Health EHR, a comprehensive EHR platform that provides real-time access to patient health records and supports clinical workflows.
- Cerner PowerChart. An EHR system designed to enhance clinical efficiency, including features like patient portals and e-prescribing.
- PowerChart Touch. A mobile application that enables physicians to review patient charts and input data using iOS devices.
- CareTracker. A point-of-care documentation tool optimized for long-term care settings.
Oracle continues to invest in modernizing these platforms using AI, machine learning and analytical decision-making to reduce the administrative burden.
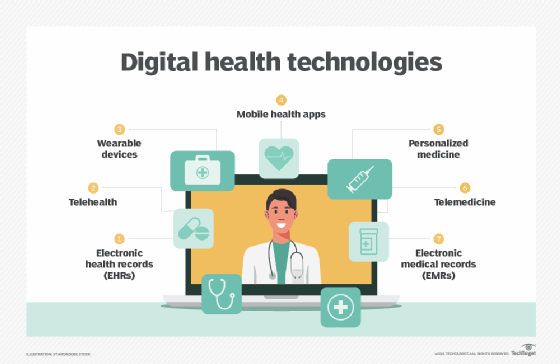
Cerner Corp.'s interoperability efforts
Cerner has long been an advocate for health data interoperability. In 2013, it became a founding member of the CommonWell Health Alliance, a nonprofit consortium that promotes seamless health information exchange across competing EHR platforms. This collaboration reflects Cerner's commitment to breaking down data silos and supporting more connected patient care.
Cerner Corp.'s government contracts and federal impact
In 2015, Cerner won the $4.3 billion U.S Department of Defense (DOD) contract for the federal agency's Healthcare Management System Modernization project. As part of the contract, Cerner's EHR replaced DOD's legacy health IT system in its 55 hospitals and more than 350 clinics worldwide, including on ships, submarines and other locations where the U.S. military has operations.
Cerner's EHR also serves the DOD's 9.6 million beneficiaries. Cerner rolled out its Military Health System Genesis system at four pilot sites in Washington, D.C., in October 2017. In 2018, the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs signed a $10 billion contract to replace its decades-old VistA system with Cerner Millennium, aiming to align VA systems with those used by DOD for improved continuity of care.
While implementation challenges and delays have been reported, these projects remain pivotal in modernizing government-run healthcare systems.
Cerner Corp.'s strategic partnerships
In 2013, Cerner partnered with Children's National Health System to form The Bear Institute, the first pediatric health informatics institute in the country. Located at the Children's National main hospital in Washington, D.C., the Bear Institute's goal is to advance the development of EHRs that are fully integrated and accessible to Children's National-affiliated healthcare providers, facilities, educators and researchers, as well as patients and their families.
Cerner Corp.'s history and legacy
Neal Patterson, Paul Gorup and Cliff Illig founded Cerner in 1979. The company was originally known as PGI & Associates after the founders' last initials. The company changed its name to Cerner in 1984. That same year, it launched its laboratory information system PathNet, which laboratory clinicians used for process automation. Two years later, after PathNet established itself as a leader in the market, Illig and Patterson took the company public.
Cerner began developing its Health Network Architecture (HNA) around this time, which the company envisioned as a way to automate different aspects of the healthcare process, from patient registration to pharmacy pickup and beyond. Cerner introduced Millennium as an upgrade to its HNA system in 1997, bringing the company's entire range of software services into one platform.
Since Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner in 2022 for $28.3 billion, it has integrated Cerner into its broader cloud infrastructure and data analytics portfolio under the Oracle Health brand.
Oracle has prioritized creating a unified national health records system and using its cloud infrastructure to streamline Cerner's operations. This includes integrating Oracle's AI and analytics capabilities into Cerner's EHR to reduce clinician burnout and improve healthcare delivery.
These efforts aim to enhance data sharing, patient access and system efficiency across the U.S. healthcare system.
See how digital health tools cuts hospital length of stay for surgery patients and a digital engagement approach lowers healthcare worker anxiety and depression. Explore the top challenges impacting patient access to healthcare and why -- with healthcare consumerism front and center -- organizations should look to personalized care strategies.





