What is orchestration in IT?
In IT, orchestration is a commonly used term for the automated coordination and management of different processes, systems and tasks. In particular, IT orchestration focuses on automating multiple tasks into a larger workflow.
Orchestration is applied to IT components, like computer systems, applications and services. IT teams typically use many different tools to deploy, configure and manage these components. Orchestration tools are also used to coordinate the interactions between these components. These tools often use scripts or policies to define workflows and automate the provisioning, configuration and monitoring across systems.
The goal is to streamline the execution of frequent and repeatable IT processes. IT teams typically manage various components like servers, systems and applications across data centers, cloud services and distributed environments. Automating processes involved with these components into a larger automated workflow helps improve IT efficiency and reduce errors across complex IT ecosystems.
How does orchestration work?
Orchestration usually involves several different tools and will look different per organization. For example, an organization might use one tool to automate the deployment of containers and containerized applications while another tool automatically publishes code into a repository. In this instance, a broader orchestration tool can integrate these separate automated tools into one definable workflow. It does this through rules, scripts or policies that execute tasks in a predefined sequence.
Orchestration tools can integrate with IT infrastructure components like servers, networks and applications for provisioning, deployment, scaling or management.
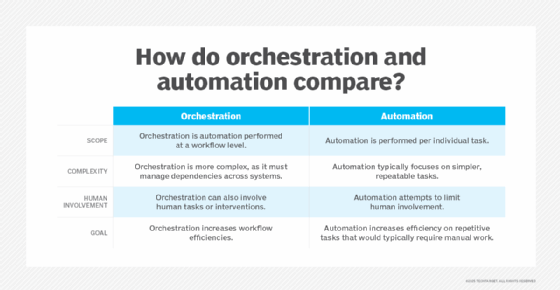
IT orchestration vs. IT automation
Orchestration and automation are two similar concepts with differing scopes. IT automation focuses on performing tasks without human intervention. IT automation is also usually limited to individual tasks so that each task will have its own automation process. For example, IT automation might be able to apply software patches and perform audit checks automatically, but they are performed as separate automation processes.
IT orchestration, however, is broader in scope. Orchestration tools can manage multiple automated tasks as part of a larger workflow. The process ensures each task is automated and executed in the correct order. Some orchestration tasks can also include human tasks.
Benefits of orchestration
Orchestration processes provide organizations with the following benefits:
- Collaboration. IT orchestration can improve collaboration between different IT teams, such as networking and security. The process also aligns with DevOps practices.
- Consistency. Automating repetitive tasks can reduce mistakes and misconfigurations that humans could make doing those same tasks.
- Efficiency. Orchestration focuses on automating workflows, particularly for repetitive tasks. This also frees up employees to work on other, more intensive tasks.
- Security. IT orchestration can be used to automate policy enforcement and incident response.
- Workflow. IT teams can choose what tasks to automate and orchestrate to define their workflow.
Types of orchestration
IT orchestration is defined into the following types depending on specific environments and use cases:
- Application orchestration. Application orchestration coordinates the deployment and configuration of two or more applications across different environments.
- Cloud orchestration. Cloud orchestration automates the management of different public and private cloud infrastructures and services.
- Container orchestration. These tools automate the management and coordination of containerized applications.
- Security orchestration. Security orchestration integrates security tools and workflows, enabling different automated security tools to operate together.
- Service orchestration. These tools connect and manage interactions between services, such as microservices, networks and application programming interfaces.
- Data orchestration. Data orchestration coordinates the data flow in an organization, enabling it to manage large volumes of data efficiently.
- Robotic process automation orchestration. RPA orchestration manages and coordinates software robots that perform repetitive tasks.
- Process orchestration. Process orchestration coordinates IT processes and individual tasks across different systems.
Orchestration tools
Numerous vendors provide orchestration tools for IT environments. The following is a sampling of such tools:
- AWS CloudFormation. This configuration orchestration tool sets up Amazon Web Services resource deployment and management.
- HashiCorp Terraform. Terraform orchestration includes tools to automate and streamline infrastructure deployment.
- Kubernetes. This open source tool is designed to orchestrate container management.
- Microsoft Azure Data Factory. This fully managed service and serverless data integration platform can orchestrate, schedule and manage data pipelines.
- Red Hat Ansible. This open source suite of configuration management and orchestration tools is used to automate IT tasks.
- ServiceNow Orchestration. ServiceNow Orchestration automates IT and business processes to improve operations management.
- VMware vRealize Orchestrator. This workflow orchestration tool automates tasks across VMware and third-party virtualized environments.
When choosing an orchestration tool, organizations should consider what they need to orchestrate. If it is containers, Kubernetes might be the right answer, for example. Other considerations include compatibility with existing hardware and software infrastructure, scalability needs, integration with other tools, and the ability of the tool to capture analytics.
IT teams can implement and reuse automation sequences to implement orchestration. Learn more about how to implement IT automation and orchestration effectively.







